Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison
Deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid are perhaps the most important molecules in cell biology, responsible for the storage and reading of genetic information that underpins all life. They are both linear polymers, consisting of sugars, phosphates and bases, but there are some key differences which separate the two1. These distinctions enable the two molecules to work together and fulfil their essential roles. Here, we look at 5 key differences between DNA and RNA. Before we delve into the differences, we take a look at these two nucleic acids side-by-side.
A comparison of the helix and base structure of RNA and DNA
What Does S Stand For And What Occurs In This Stage
Synthesis
. Keeping this in view, what occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle?
The S phase of a cell cycle occurs during interphase, before mitosis or meiosis, and is responsible for the synthesis or replication of DNA. In this way, the genetic material of a cell is doubled before it enters mitosis or meiosis, allowing there to be enough DNA to be split into daughter cells.
One may also ask, what does the S phase mean? S phase. S–phase is the part of the cell cycle in which DNA is replicated, occurring between G1 phase and G2 phase. Precise and accurate DNA replication is necessary to prevent genetic abnormalities which often lead to cell death or disease.
Moreover, what is s in biology?
noun Cell Biology.the period of the cell cycle prior to mitosis, during which the chromosomes are replicated.
What happens at the S checkpoint?
A checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted until conditions are favorable. The G2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes have been replicated and that the replicated DNA is not damaged before cell enters mitosis.
How Is The Dna Described And What Does This Mean
Deoxyribonucleic acid, more commonly known as DNA, is a complex molecule that contains all of the information necessary to build and maintain an organism. All living things have DNA within their cells. In fact, nearly every cell in a multicellular organism possesses the full set of DNA required for that organism.
Don’t Miss: Geography Movement Definition
How To Play Sirf Ek Minutequiz
Page Content
1.. You can download App From Google Play Store OR Apple Store.
2. Open & Sign in to the Flipkart App.
3. Open Games Section in the app & Find Sirf Ek Minute Contest
4. There are always 6 questions in this quiz
5. Answer all Flipkart Sirf Ek Minute Quiz questions correctly to enter the lucky draw.
Double Helix And Antiparallel Strands
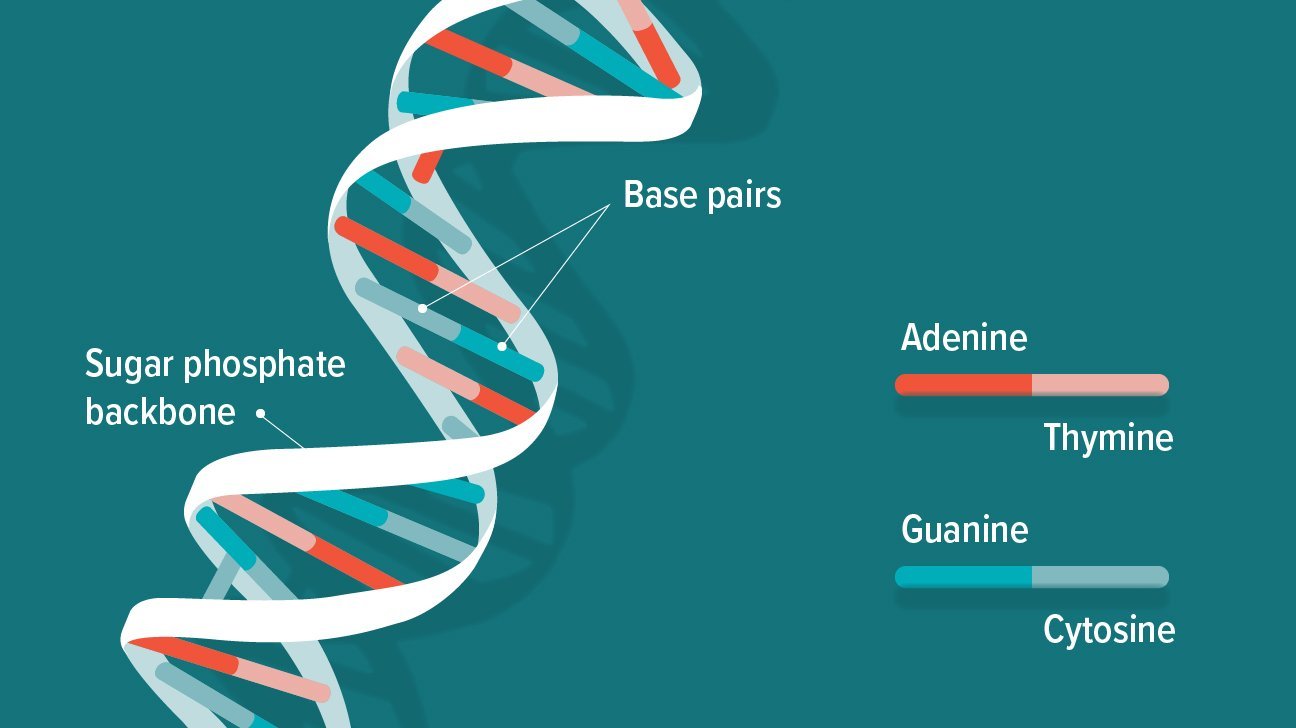
The image is a simplified representation of a short DNA molecule, with deoxyribose sugar molecules in orange, linked to phosphate molecules through a special type of covalent linkage called the phosphodiester bond. Each nitrogenous base is represented by a different color thymine in purple, adenine in green, cytosine in red and guanine in blue. The bases from each strand form hydrogen bonds with one another, stabilizing the double-stranded structure.
The structure of the sugar phosphate backbone in a DNA molecule results in a chemical polarity. Each deoxyribose sugar has five carbon atoms. Of these, the third and the fifth carbon atoms can form covalent bonds with phosphate moieties through phosphodiester bonds. A phosphodiester linkage essentially has a phosphate molecule forming two covalent bonds and a series of these bonds creates the two spines of a double-stranded DNA molecule.
Alternating sugar and phosphate residues results in one end of every DNA strand having a free phosphate group attached to the fifth carbon of a deoxyribose sugar. This is called the 5 end. The other end has a reactive hydroxyl group attached to the third carbon atom of the sugar molecule and makes the 3 end.
Recommended Reading: How To Calculate Half Life Chemistry
Chemical Isolation Of Dna
DNA was first chemically isolated and purified by Johann Friedrich Miescher who was studying immunology. Specifically, he was trying to understand the biochemistry of white blood cells. After isolating the nuclei from the cytoplasm, he discovered that when acid was added to these extracts, stringy white clumps that looked like a tufts of wool, separated from the solution. Unlike proteins, these precipitates went back into solution upon the addition of an alkali. This led Miescher to conclude that the macromolecule was acidic in nature. When further experiments showed that the molecule was neither a lipid nor a protein, he realized that he had isolated a new class of molecules. Since it was derived from the nucleus, he named this substance nuclein.
The work of Albrecht Kossel shed more light on the chemical nature of this substance when he showed that nuclein was made of carbohydrates, phosphates, and nitrogenous bases. Kossel also made the important discovery connecting the biochemical study of nucleic acids with the microscopic analysis of dividing cells. He linked this acidic substance with chromosomes that could be observed visually and confirmed that this class of molecules was nearly completely present only in the nucleus. The other important discovery of Kossels was to link nucleic acids with an increase in protoplasm, and cell division, thereby strengthening its connection with heredity and reproduction.
What Does Dna Stand For Full Form Meaning And Definition
Do you want to know, What Does DNA Stand For?, In this post, we are going to learn about the full form of DNA in Biology, Not only this, But you will also come to know the Meaning of DNA in Different Categories? and also what are the Abbreviations of DNA ka Full Form? So You should read this post till the End?
Also Check: Glencoe Mcgraw Hill Geometry Concepts And Applications Answers
Dna Helps Your Body Grow
DNA contains the instructions that are necessary for an organism you, a bird, or a plant for example to grow, develop, and reproduce. These instructions are stored within the sequence of nucleotide base pairs.
Your cells read this code three bases at a time in order to generate proteins that are essential for growth and survival. The DNA sequence that houses the information to make a protein is called a gene.
Each group of three bases corresponds to specific amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. For example, the base pairs T-G-G specify the amino acid tryptophan while the base pairs G-G-C specify the amino acid glycine.
Some combinations, like T-A-A, T-A-G, and T-G-A, also indicate the end of a protein sequence. This tells the cell not to add any more amino acids to the protein.
Proteins are made up of different combinations of amino acids. When placed together in the correct order, each protein has a unique structure and function within your body.
What Does Dna Do
DNA contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop, survive and reproduce. To carry out these functions, DNA sequences must be converted into messages that can be used to produce proteins, which are the complex molecules that do most of the work in our bodies.Each DNA sequence that contains instructions to make a protein is known as a gene. The size of a gene may vary greatly, ranging from about 1,000 bases to 1 million bases in humans. Genes only make up about 1 percent of the DNA sequence. DNA sequences outside this 1 percent are involved in regulating when, how and how much of a protein is made.
- What does DNA do?
DNA contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop, survive and reproduce. To carry out these functions, DNA sequences must be converted into messages that can be used to produce proteins, which are the complex molecules that do most of the work in our bodies.Each DNA sequence that contains instructions to make a protein is known as a gene. The size of a gene may vary greatly, ranging from about 1,000 bases to 1 million bases in humans. Genes only make up about 1 percent of the DNA sequence. DNA sequences outside this 1 percent are involved in regulating when, how and how much of a protein is made.
Also Check: Calculating Half-life
Why Is Dna Important
DNA is important because it holds all of the genetic information that makes you, you. This information is needed for your development and survival and is able to be passed along to the next generation. It also influences your traits, ranging from what you look like to the food you like with lots of things in between.
Given how different you are from someone else, it might seem like everyones DNA should be very different from one another. Amazingly this is not the case. On average, you share around 99.5% of your DNA with someone you are not related to.
A big part of what makes you unique is found in that 0.5% of your DNA. And even though were overall more alike than different, everyones DNA tells a different story about who their relatives are and where they are from. What story does your DNA tell?
What Does Dna Stand For In Biology Quizlet
4.1/5DNA stands
Correspondingly, what does the letters DNA stand for in biology?
deoxyribonucleic acid
Additionally, what are the subunits of DNA called quizlet? Nucleotides are the subunits of DNA and RNA Flashcards | Quizlet.
Consequently, what does DNA stand for and what is its function?
abbreviation. DNA, which stands for deoxyribonucleic acid, is defined as a nucleic acid that contains the genetic code.
What is the main function of DNA quizlet?
A nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and function of all known living organisms. To store information. DNA is like a set of blueprints or a book of instructions. DNA has all the “recipes” for making chemicals or proteins.
You May Like: Age Word Problems Algebra
How Is Dna Sequenced
DNA sequencing involves technology that allows researchers to determine the order of bases in a DNA sequence. The technology can be used to determine the order of bases in genes, chromosomes or an entire genome. In 2000, researchers completed a “working draft” sequence of the human genome, according to the National Human Genome Research Institute, and finished the project in 2003.
Where Is Dna Found
In organisms called eukaryotes, DNA is found inside a special area of the cell called the nucleus. Because the cell is very small, and because organisms have many DNA molecules per cell, each DNA molecule must be tightly packaged. This packaged form of the DNA is called a chromosome.During DNA replication, DNA unwinds so it can be copied. At other times in the cell cycle, DNA also unwinds so that its instructions can be used to make proteins and for other biological processes. But during cell division, DNA is in its compact chromosome form to enable transfer to new cells.Researchers refer to DNA found in the cell’s nucleus as nuclear DNA. An organism’s complete set of nuclear DNA is called its genome.Besides the DNA located in the nucleus, humans and other complex organisms also have a small amount of DNA in cell structures known as mitochondria. Mitochondria generate the energy the cell needs to function properly.In sexual reproduction, organisms inherit half of their nuclear DNA from the male parent and half from the female parent. However, organisms inherit all of their mitochondrial DNA from the female parent. This occurs because only egg cells, and not sperm cells, keep their mitochondria during fertilization.
Also Check: Chapter 7 Quiz 3 Geometry Answers
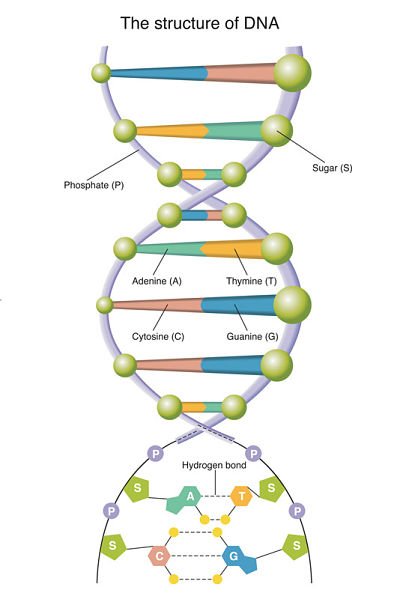
Each Dna Strand Is Composed Of Nucleotidesunits Made Up Of A Sugar A Phosphate Group And A Nitrogenous Base
Each strand of DNA is a polynucleotide composed of units called nucleotides. A nucleotide has three components: a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
The sugar in DNAs nucleotides is called deoxyriboseDNA is an abbreviation for deoxyribonucleic acid. RNA molecules use a different sugar, called ribose. Covalent bonds join the sugar of one nucleotide to the phosphate group of the next nucleotide, forming the DNA strands sugar-phosphate backbone.
A nitrogenous base is an organic molecule that contains nitrogen and has the chemical properties of a base. There are four nitrogenous bases that occur in DNA molecules: cytosine, guanine, adenine, and thymine . RNA molecules contain cytosine, guanine, and adenine, but they have a different nitrogenous base, uracil instead of thymine.
A Molecule Of Dna Consists Of Two Strands That Form A Double Helix Structure
DNA is a macromolecule consisting of two strands that twist around a common axis in a shape called a double helix. The double helix looks like a twisted ladderthe rungs of the ladder are composed of pairs of nitrogenous bases , and the sides of the ladder are made up of alternating sugar molecules and phosphate groups.
Molecules of DNA range in length from hundreds of thousands to millions of base pairs. The smallest chromosome in the human genome, Chromosome 21, has around 48 million base pairs.
Read Also: What Does The Suffix Clast Mean
How Many Genes Do Humans Have
In humans, genes vary in size from a few hundred DNA bases to more than 2 million bases. An international research effort called the Human Genome Project, which worked to determine the sequence of the human genome and identify the genes that it contains, estimated that humans have between 20,000 and 25,000 genes.
How Does Dna Create Proteins
For genes to create a protein, there are two main steps:
Transcription: The DNA code is copied to create messenger RNA . RNA is a copy of DNA, but it is normally single-stranded. Another difference is that RNA does not contain the base thymine , which is replaced by uracil .
Translation: The mRNA is translated into amino acids by transfer RNA .
mRNA is read in three-letter sections called codons. Each codon codes for a specific amino acid or building block of a protein. For instance, the codon GUG codes for the amino acid valine.
There are 20 possible amino acids.
Don’t Miss: Algebra Word Problems Age
What Does Dna Look Like
DNA is like a spiral ladder. Each piece of DNA has two long strands/ chains that twist around each other. This spiral and twisted shape is known as the double helix. The long chains are nucleotides which are of four types- adenine , thymine , cytosine and guanine . These four are also known as bases. These bases form special rungs. They are like a jigsaw puzzle and only fit with their partners. A and T always go together while C and G fit together.
Specific Sequences Of Nitrogenous Bases That Code For Particular Proteins Or Regulatory Rna Molecules Are Called Genes
Each strand of DNA is like a recipe book for synthesizing proteins. Certain sequences of nitrogenous bases along the strand encode particular RNA molecules. These sequences are called genes. mRNA molecules transcribed from genes are translated into proteins later.
Chromosomes can vary widely in their number of base pairs and genes. The longest chromosome in human cells, Chromosome 1, is around 249 million base pairs long and has between 2000 and 2100 distinct genes. Chromosome 21, the shortest human chromosome, consists of 48 million base pairs and contains between 200 and 300 genes. Overall, prokaryotic cells have shorter chromosomes with fewer genes. For example, the bacterium Carsonella rudii has only 159,662 base pairs and 182 genes in its entire genome.
Although genes get most of the credit for what DNA does, they make up only about 1% of DNA . Genes are separated from one another by sequences of nitrogenous bases that dont provide instructions for RNA synthesis. These are called intergenic regions. Even within genes, there are regions of noncoding DNA called introns.
Noncoding regions of DNA are important because they provide binding sites for proteins that help activate or deactivate the process of transcription. They can also provide protection for the coding regions. For instance, telomeres consist of repetitive sequences that protect the genetic information on each DNA molecule from being damaged during cell division.
Read Also: Segment And Angle Addition Worksheet
In Biology What Does A Stand For In Dna
Flipkart Sirf Ek Minute Quiz is the latest video online quiz program from the Flipkart Company. Flipkart regularly brings new quizzes and challenges for Indian audiences. After a short lag of no episodes for a few quizzes, Flipkart Sirf Ek Minute Quiz is back with a bang. The quiz program will help Flipkarts further endeavor at moving above commerce and increasing their social presence or social impressions.
The Sirf Ek Minute Quiz is another quiz besides ongoing quizzes like Flipkart Fake or Not Fake, Flipkart Daily Trivia, Flipkart Dating Aajkal, and Flipkart Daam Sahi Hai. In this quiz, you are being quizzed with 5 or 6 interesting questions asked by the Anchor of the quiz. You need to answer all questions correctly to win the coins and we provide you the fastest answers so stay with us.
Dna Damage And Mutations
The DNA code is prone to damage. In fact, its estimated that tens of thousands of DNA damage events occur every day in each of our cells. Damage can occur due to things like errors in DNA replication, free radicals, and exposure to UV radiation.
But never fear! Your cells have specialized proteins that are able to detect and repair many cases of DNA damage. In fact, there are at least five major DNA repair pathways.
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence. They can sometimes be bad. This is because a change in the DNA code can have a downstream impact on the way a protein is made.
If the protein doesnt work properly, disease can result. Some examples of diseases that occur due to mutations in a single gene include cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia.
Mutations can also lead to the development of cancer. For example, if genes coding for proteins involved in cellular growth are mutated, cells may grow and divide out of control. Some cancer-causing mutations can be inherited while others can be acquired through exposure to carcinogens like UV radiation, chemicals, or cigarette smoke.
But not all mutations are bad. Were acquiring them all of the time. Some are harmless while others contribute to our diversity as a species.
Changes that occur in more than 1 percent of the population are called polymorphisms. Examples of some polymorphisms are hair and eye color.
Also Check: Special Triangles Worksheet Answers