Why H2s Having Less Boiling Point Than H2o
H2S boiling point: -600C
H2O boiling point: 1000C
- At room temperature, hydrogen disulfide is a gas. But water is a liquid. That says us H2S has the less boiling point.
- H2S and H2O are bent shape molecules.
- O and S are group VIA elements.
- Molecular mass of H2S = 34 and molecular mass of H2O = 18. Molecular mass of H2S is greater than H2O.
- But, There are strong hydrogen bonds between H2O molecules. H2S molecules have only weak dipole dipole interactions.
Hydrogen bonds in H2O
- Due to existence of strong hydrogen bonds in H2O molecules, H2O has high boiling point than H2S , though H2S has greater molecular mass.
Is P Block Metals Melting Points Are Higher Than S Block
First we will look, what are the p block metals and what are the s block metals. You know when we discuss about melting points of metals, their metallic lattice is so important. So now you know what should we find out to compare melting points of p block metals and s block metals.
When metallic lattice of a metal is strong, that metal has a great chance to has a higher melting point.
As examples, two metals, sodium and aluminium are taken to compare. Sodium is s block metal and aluminium is a p block metal. But both are located in 3rd period of the periodic table.
Due to release of three electrons and less radius, metallic lattice of aluminium is much stronger than sodium. So melting point of aluminium is greater than sodium.
Please Enter Your Email Address So We May Send You A Link To Reset Your Password
We use/store this info to ensure you have proper access and that your account is secure. We may use this info to send you notifications about your account, your institutional access, and/or other related products. To learn more about our GDPR policies click here.
If you want more info regarding data storage, please contact .
You May Like: What Is On The Ap Biology Exam
Which S Block Metal Has The Highest Melting Point
Beryllium has the highest melting point from s block metals. It is about 1,287 0C
boiling and melting points of 1a group order
Li > Na > K > Rb > Cs > Fr > H
Lithium has the highest melting and boiling point while hydrogen has the lowest in IA group. Hydrogen exists as a gas at room temperature and francium is a liquid at room temperature. All other group IA materials are solids at room temperature.
Melting And Boiling Points Of Alkaline Earth Metals

Alkaline earth metals have low melting and boiling points when compared with d block metals. But their melting and boiling points are higher than corresponding alkali metals in the same period due to comparatively smaller size. But melting and boiling points do not show regular trends in alkali earth metal group.
Don’t Miss: Mitty High School Summer Geometry
Symmetry And Melting Point
Aside from the intermolecular interactions, however, the melting point depends also on how the molecules are packed or arranged in the solid form. The more symmetrical they are, the better they pack and form a perfect crystal lattice which results in a higher melting point. So, as the molecules fit tighter, more energy is required to break the lattice and melt them apart.
Lets go back to the examples we discussed for the boiling point. Remember, for the boiling point, it increased with less branching because of the increased surface. So, pentane had a higher point than 2,2-dimethylpropane 36.1 oC vs 9.5 oC.
Interestingly, the pattern is not observed for the melting points. 2,2-dimethylpropane has a higher melting point since it is more symmetrical than pentane and when in solid phase its molecules are better packed.
We can also see the effect of symmetry by comparing the melting point temperatures of the butanol isomers. All of these are constitutional isomers capable of hydrogen bonding. However, compared to the other isomeric alcohols, the tert-Butyl alcohol has a much higher melting point because of its symmetrical structure and therefore, compact packing in the solid phase:
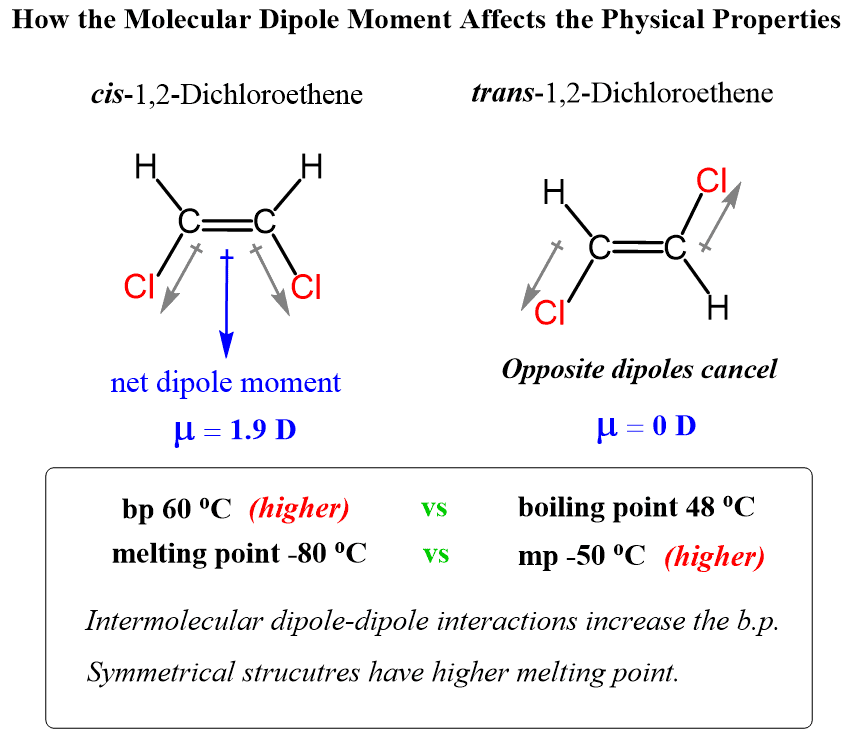
And another great example to illustrate the importance of packing and molecular symmetry is the comparison of melting and boiling points of cis and trans alkenes. In general, trans alkenes have a higher melting point.
D Thermodynamic / Pharmacopeia Mode
There are two modes for melting point evaluation: Pharmacopeia melting point and thermodynamic melting point. The pharmacopeia mode neglects that the furnace temperature is different during the heating process than the sample temperature, meaning that the furnace temperature is measured rather than the sample temperature. As a consequence, the pharmacopeia melting point depends strongly on the heating rate. Therefore, measurements are only comparable if the same heating rate is applied. The thermodynamic melting point on the other hand, is obtained by subtracting the mathematical product of a thermodynamic factor f and the square root of the heating rate from the pharmacopeia melting point. The thermodynamic factor is an empirically determined instrument-specific factor. The thermodynamic melting point is the physically correct melting point. This value does not depend on heating rate or other parameters. This is a very useful value as it allows melting points of different substances to be compared independently of experimental setup.
You May Like: Common Core Algebra 1 Unit 6 Lesson 2 Answer Key
Factors Affecting Melting Point Of Organic Compounds
The factors that affect the melting point of organic compounds are as follows:
-
The Size of the Molecule- Melting point determination of organic compounds helps to identify the organic compound properties, both physical and chemical. The structure of the molecule has a big role to play. The tighter the molecules are packed, the higher the melting point. If the structure of the molecules is loose, then the melting point would be lower.
For instance, in Isopentane, the molecules are loosely packed, so the melting point is lower. Whereas, in the case of symmetrical neopentane molecules, the melting point is higher. Another point is if all the other factors are equal, smaller molecules’ melting point will be lower. For instance, ethanol melts at -114.1 degrees, while the bigger ethyl cellulose molecule’s melting point is 151 degrees Celsius.
Why Boiling Point Of Calcium Is Greater Than Potassium
Lattice strength of calcium is greater than potassium due to two reasons.
Due to these two reasons, metallic lattice of calcium is much greater than potassium.
You May Like: What Is Elastic Force In Physics
Temperature Behavior Of The Sample And The Furnace
Melting point determination starts at a predefined temperature close to the expected melting point. The red solid line represents the temperature of the sample . At the beginning of the melting process, both sample and furnace temperatures are identical the furnace and sample temperatures are thermally equilibrated beforehand. The sample temperature rises proportionally to the furnace temperature. We have to bear in mind that the sample temperature increases with a short delay which is caused by the time needed for heat transmission from the furnace to the sample. While heating up, the furnace temperature is always higher than the sample temperature. At a certain point the furnace heat melts the sample inside the capillary. The sample temperature remains constant until the whole sample is molten. We identify different furnace temperature values TA and TC which are defined by the respective melting process stages: collapse point and clear point. The sample temperature inside the capillary rises significantly once the sample is completely molten. It increases parallel to the furnace temperature showing a similar delay as in the beginning.
Pharmacopeia Mp Vs Thermodynamic Mp
There are two modes for melting point evaluation: Pharmacopeia melting point and thermodynamic melting point. The pharmacopeia mode neglects that the furnace temperature is different during the heating process than the sample temperature, meaning that the furnace temperature is measured rather than the sample temperature. As a consequence, the pharmacopeia melting point depends strongly on the heating rate. Therefore, measurements are only comparable if the same heating rate is applied.
The thermodynamic melting point on the other hand, is obtained by subtracting the mathematical product of a thermodynamic factor f and the square root of the heating rate from the pharmacopeia melting point. The thermodynamic factor is an empirically determined instrument-specific factor. The thermodynamic melting point is the physically correct melting point . This value does not depend on heating rate or other parameters. This is a very useful value as it allows melting points of different substances to be compared independently of experimental setup.
You May Like: What Is The Highest Level Of Analysis In Psychology
Why Alkali Metals Have Low Melting Points Than Alkaline Earth Metals
Both alkali and alkali earth metals are in s block. We know alkali metals have only one valence electron per metal atom.
But alkaline earth metals have two valence electrons per metal atom.
Also alkali earth metals are small in size than alkali metals.
When number of valence electrons in the lattice increases, the metallic bond is strong. Also when atomic radius decreases, metallic bond become strong. Also Therefore metallic bonds of alkali earth metals are much stronger than alkali metals.
Therefore melting and boiling points of alkali metals are less than melting and boiling points of alkali earth metals
Why beryllium have high melting point and boiling point than other member of group two?
Beryllium is the smallest size atom of the group 2 elements. So its ionic lattice is more stronger than other alkaline earth metals.
Procedure To Determine The Melting Point Of Naphthalene:
Figure
Figure
Read Also: What Is An Equation In Chemistry
Regulatory Implications Of Melting Point
Knowing the melting point of a chemical is very important for its storage & transport. You probably do not want to store or transport a solid at a temperature close to or above its melting point in which case melting may cause leaking and severe consequences.
In addition to that, melting point is often used to predict the partition behavior of a chemical between solid and gas phases. A higher melting point indicates greater intermolecular forces and therefore less vapour pressure.
Melting point test is not required for every chemical. Usually it is conducted for solid materials under normal conditions. Under REACH, a vapor pressure test does not need to be conducted if the melting point of a substance is above 300 °C.
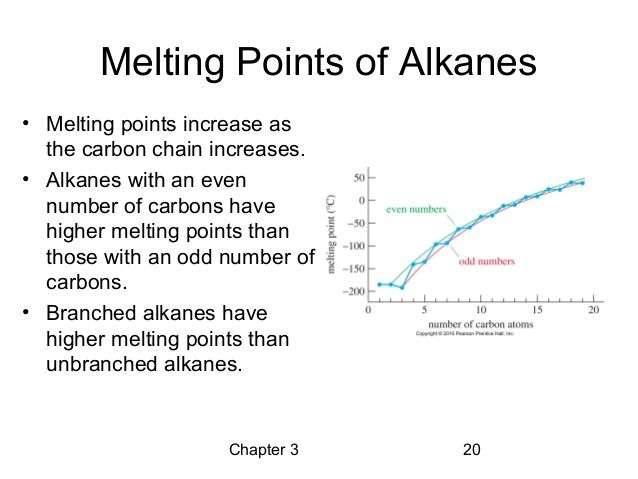
Melting And Boiling Points Of Alkanes Alkenes Alkynes
- Alkanes are non polar molecules. There are only Van der Waals forces between alkane molecules. When relative molecular mass increases in alkane compounds, melting and boiling points values are also increased.
- Melting and boiling points increases alkane, alkene, alkyne respectively.
Consider ethane, ethene, ethyne
ethyne has the highest melting and boiling point.
Also Check: What Is 1 Mole In Chemistry
Melting Point Determination Lab Report
A small experiment can be conducted to determine the melting point determination of organic compounds. One such is given below.
Thiele tube method for this experiment, a tube known as Thiele tube is used, which is designed to contain oil and experiment with heat. A capillary, a thermometer, and a bunsen burner are required to complete the experiment well. The substance whose melting point will be observed is placed in the capillary tube, and a rubber band is tied around it. Ensure that the rubber band is not getting dipped into the oil as with the rise of temperature the rubber will tend to melt.
The Thiele tube is designed so that the heat that is being emitted from the bunsen burner is evenly distributed. During the experiment, the rate of the temperature is carefully controlled. In and around the melting point of the substance, the heating will be slow so that the rate of temperature increase is not faster than the ability of the heat to be transferred to the sample being observed. The thermometer bulb and the capillary tube sample must be at thermal equilibrium at the melting point.
Your Jove Unlimited Free Trial
Fill the form to request your free trial.
We use/store this info to ensure you have proper access and that your account is secure. We may use this info to send you notifications about your account, your institutional access, and/or other related products. To learn more about our GDPR policies click here.
If you want more info regarding data storage, please contact .
Also Check: How To Do Math Problems
Force Of Attraction Between The Molecules
The force of attraction between the molecules affects the melting point of a compound. Stronger intermolecular interactions result in higher melting points. Ionic compounds usually have high melting points because the electrostatic forces holding the ions are much stronger. In organic compounds the presence of polarity, or especially hydrogen bonding, generally leads to higher melting point.
Consider the following examples.
The only force of attraction between butane molecules is weak Van der Waals force of attraction, so it has very low melting point. But in the case of methyl propionate, because of the presence of polar C O group, the molecules are held together by dipole-dipole interaction. Therefore, its melting point is greater than that of butane. In the case of butyric acid, the molecules are held together by hydrogen bonding, so it has a higher melting point. The melting point of sodium butanoate is higher than that of butyric acid because the attractive force in sodium butanoate is strong ionic interation.
What Does Melting Point Depend On
The melting point of a material is the point at which the liquid water present in it no longer freezes. The melting point of metals is often quoted as the boiling point of water, but this is not always true. The boiling point is the point at which a liquid water droplet is capable of forming a boil. However, the melting point of a metal is not always the boiling point. For example, copper has a melting point of 1,202 degrees Fahrenheit, but its boiling point is 1,700 degrees Fahrenheit.
Also Check: What Does The Slash Mean In Math
What Is Boiling Point
The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the liquid becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure of the liquids environment. At this temperature, the liquid is converted into a vapour.
The boiling point of the liquid depends upon the pressure of the surrounding. When the liquid is at high pressure, it has a higher boiling point than the boiling point at normal atmospheric pressure. The boiling point of different liquids is different for a given pressure. In 1982, IUPAC defined the standard boiling point of a liquid as the temperature at which the liquid boils under a pressure of 1 bar.
Performance Verification With Mp Vpac
- 8.1 Ready-to-use Kit of Traceable Reference Substances
Performance verification by temperature calibration is the recommended workflow to ensure faultless routine operation of a melting point instrument and to secure result reliability. The MP VPac provides 3 different certified reference substances in prefilled, sealed capillaries for a simple method of verifying instrument accuracy over the temperature range 40 to 230 °C.
No sample grinding and time-consuming manual upfront filling of melting point capillaries is required. Just take the pre-filled capillaries and insert them into the MP instrument furnace, as in a normal method. The preprogrammed calibration method can be started directly without any modification.
Each of the three reference substances included in the MP VPac comes with a certificate that states the certified temperature value including measurement uncertainty. The purity is routinely checked by DSC measurements. The subsequently measured melting point is therefore a reliable way of checking the temperature accuracy of the instrument and whether an adjustment is required.
- 8.2 Do-it-yourself Service
Read Also: How To Find Force In Physics
What Affects Boiling Point Of Water
The surrounding pressures are the greatest determinant of the boiling point of a liquid. The air pressure in an open system is most definitely the atmosphere on earth. For instance, water reaches the standard atmospheric pressure at 100 degrees centigrade. Water can boil at a lower temperature as elevation increases.
To learn more about melting point and boiling point, download BYJUS The Learning App.
Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click Start Quiz to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the Finish buttonCheck your score and answers at the end of the quiz