Complete Octet Of The Molecule
To complete the of the molecule, the carbon atom will donate its electrons to both oxygen atoms to form a double bond. The carbon atom will donate its electrons to oxygen atoms as they are more electronegative. Now that you know how the carbon dioxide Lewis structure is drawn, let us quickly look at the CO2 molecular geometry.
What Is The Hybridization Of Carbon Dioxide
In determining the hybridization of carbon dioxide, we will take the carbon atom first. The carbon atom has two effective pairs or two double bonds exist in it. However, this is not enough to form bonds with oxygen. What happens next is that one electron from 2s orbital moves from the 2s level to 2p level which results in the formation of two hybrid orbitals. Now, these sp hybridized orbitals of the carbon atom overlap with two p orbitals of the oxygen atoms to form 2 sigma bonds. As for the two remaining p electrons they will be used to form a pi bond.
In carbon dioxide molecule, oxygen also hybridizes its orbitals to form three sp2 hybrid orbitals. The p orbital in oxygen remains unchanged and is mainly used to form a pi bond. However, out of the three sp hybrid orbitals, only one will be used to form a bond with the carbon atom.
Co2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry And Hybridization
Carbon Dioxide is one of the best compounds to start with learning the concepts of Lewis structure and Molecular Geometry. This molecule can be a good start for beginners who want to learn the fundamentals of such concepts and want to know how to draw Lewis dot structures for other molecules as well.
CO2 or Carbon Dioxide is made up of two types of atoms: Carbon and Oxygen. Although this gaseous molecule is known for its contribution to the greenhouse effect and global warming, one cannot deny that there are quite a lot of uses for this gas in several industries.
To understand the physical properties, reactivity, and other chemical properties of a given compound, it is essential to know its molecular geometry. And to help you understand it, I have discussed the CO2 Lewis structure and its hybridization below.
| Name of molecule | |
| No of Valence Electrons in the molecule | 16 |
| Linear |
Read Also: Common Core Algebra 1 Unit 10 Statistics Lesson 6
Type Of Hybridization Exists In Co2
Carbon has 6 electrons, whereas Oxygen has 8 electrons.
Before hybridization, the Carbon atom has 2 unpaired electrons to form bonding, which is not enough to form bonds with an oxygen atom. So, one electron from 2s orbital jumps from the 2s level to 2p level, and the orbitals hybridize to form the hybrid orbitals. The type of hybridization in CO2 is sp hybridization, and each carbon atom forms two sp hybrid orbitals. Out of two hybrid orbitals, one will be used to produce a bond with one oxygen atom, and the other will be used to produce a bond with another oxygen atom. The remaining two p electrons will be used to form a pi bond.
Also, oxygen hybridizes its orbitals to form three sp2 hybrid orbitals. The unhybridized p orbital is used to form a pi bond, and out of three sp hybrid orbitals, only one will be used to form a bond with Carbon.
Lewis Structure Of Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a colourless, odourless, incombustible gas produced by the combustion of carbon. The carbon-oxygen ratio in a CO2 molecule is 1:2. Two double bonds connect the carbon and oxygen atoms in the Lewis structure. Two oxygen atoms are present at the terminals, where they share electrons and form bonds with the central carbon atom.
Lewis structure diagrams show how many valence electrons are available within an atom for bond formation. It also allows for the visualisation of the behaviour of the valence electrons within the molecule as well as the determination of whether or not a lone pair of electrons exist.
Also Check: How Are Biology And Technology Related
What Is A Carbon Footprint
A carbon footprint, according to the World Health Organization, is a measurement of the influence of our activities on the earths natural greenhouse. Carbon emissions are mostly caused by human activities such as the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and land-use changes, which result in an increase in greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere. To find out more, check out the article How to Reduce Carbon footprint.
Co2 Lewis Structure Setup
Lets think in terms of dots to make the CO2 Lewis structure.
Carbon has four valence electrons that form a total of four bonds. So carbon is shown with four dots around it. Oxygen needs just two bonds, represented as the lone dots to the left and right of the O atoms. The pairs of dots above and below the Os wont bond.
The first thing about the CO2 Lewis structure is to put carbon in the center. Make both O atoms connect to C. There wont be any bonds between the Os directly. As a rule, carbon is always going to be in the center, and the other atoms connect to it.
Second, connect the lone dots on each O to the C in the center. Each O needs to bond twice. And carbon needs four bonds. So it works out that C bonds with each O twice.
Don’t Miss: What Is Population Geography Definition
The Lewis Structure Of Co
Quick steps to draw the CO lewis structure are listed below:
Co2 Molecular Orbital Diagram
The molecular orbital diagram of CO2 is as below.
A molecular orbital diagram of any compound gives us an idea about the bonding of the orbitals. It also helps us to find the bond order, bond length, bond strength of the molecule.
In the diagram, the left-hand side consists of the atomic orbitals of carbon. Likewise, the left side has AOs of oxygen. And in the middle is the MO.
We can see that the 2s orbital of oxygen is not involved in mixing and remains a nonbonding orbital. The reason for this is the high energy difference between the orbitals of carbon and the 2s orbital of oxygen.
All the 16 electrons are filled precisely as per rules. The antibonding orbitals are vacant in the case of CO2 as observed from the MO diagram.
Apart from these concepts, let us also study the methods of formation of CO2 gas.
Recommended Reading: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Algebra 2 Answer Key
Carbon Dioxide In Air
Carbon dioxide is a trace gas in air. While the concentration varies geographically, it averages around 0.04% or 412 parts per million. CO2 levels are on the rise. In pre-industrial times, the level of carbon dioxide in air was about 280 ppm. Much of the increase in carbon dioxide is attributed to deforestation and the burning of fossil fuels. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, so the increase in its concentration produces global warming and ocean acidification.
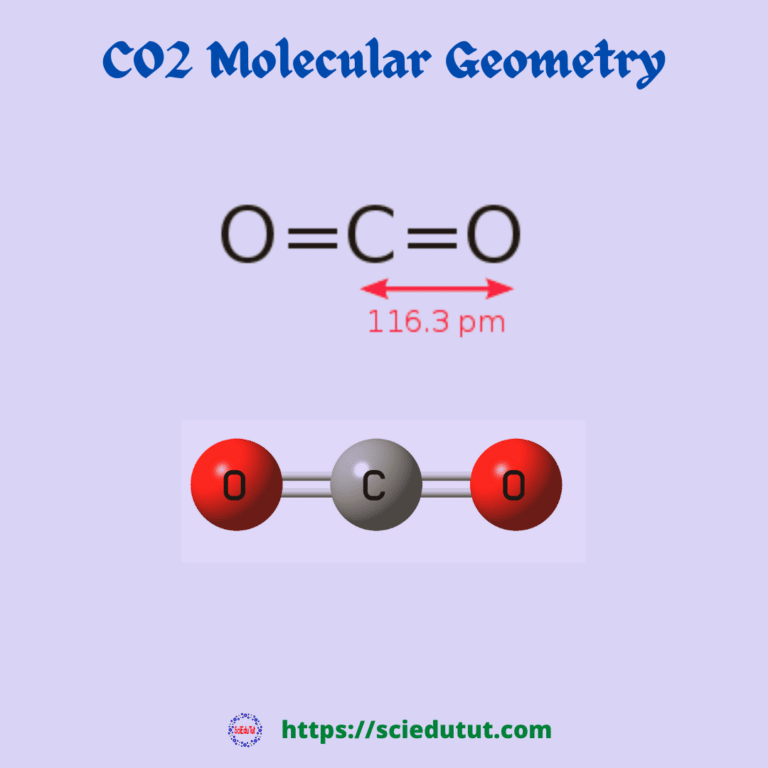
What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Carbon Dioxide
CO2 has a linear geometric shape due to the two sigma bonds between the carbon and oxygen valence electrons. Both oxygen molecules are sp2 hybridized meaning they both have one sigma bond and two pairs of un bonded electrons.
CO2 has a linear geometric shape due to the two sigma bonds between the carbon and oxygen valence electrons. Both oxygen molecules are sp2 hybridized meaning they both have one sigma bond and two pairs of un bonded electrons.
CO2 has a linear geometric shape due to the two sigma bonds between the carbon and oxygen valence electrons. Both oxygen molecules are sp2 hybridized meaning they both have one sigma bond and two pairs of un bonded electrons.
CO2 is a little different than might be expected. It has more of a linear arrangement to it molecule. This is because the valence shell electron pairs will repel each other. When they do they are forced to the opposite side of the Carbon atom giving CO2 a line likemolecular shape. The CO2 bond angle will be 180 degrees since it has this linearmolecular geometry.
CO2 is a little different than might be expected. It has more of a linear arrangement to it molecule. This is because the valence shell electron pairs will repel each other. When they do they are forced to the opposite side of the Carbon atom giving CO2 a line likemolecular shape. The CO2 bond angle will be 180 degrees since it has this linearmolecular geometry.
But more specifically, in CO2 there are 16 valence electrons to work with.
Don’t Miss: What Is Debriefing In Psychology
Co2 Molecular Geometry And Bond Angles
CO2 molecular geometry and bond angles are important chemistry chapters. This article will discuss in detail CO2 molecular geometry and Bond angles.
Table of Content
Carbon dioxide, ie, CO2, is considered one of the best compounds for understanding the concepts of Lewis structure and Molecular Geometry in the beginning. The beginners who want to learn such concepts and their fundamentals or want to know the procedure of drawing the Lewis dot structures for other molecules can also consider this molecule. CO2 is composed of two different types of atoms oxygen as well as carbon. However, this gaseous molecule is popular for its presence in global warming and the greenhouse effect. Moreover, this gas is very useful in various industries. To know about a given compounds reactivity, physical and chemical properties, it is important to be aware of its molecular geometry.
Here is the CO2 Lewis Structure for a better understanding:
Other Names For Carbon Dioxide
While “carbon dioxide” is the usual name for CO2, the chemical goes by other names as well. The solid is called dry ice. The gas is called carbonic acid gas. More general names for the molecule are carbonic anhydride, carbonic dioxide, and carbon oxide. As a refrigerant, carbon dioxide is named R-744 or R744.
Don’t Miss: Navigating Through Geometry In Grades 6 8
Lewis Structure Of Co2
The formation of CO2 consists of two particles: Oxygen and Carbon. Carbon is in group 4, whereas oxygen is in group 6. Furthermore, there are 2 Oxygen atoms.
Therefore, CO2= 4 + 6 = 16. So, the total valence electrons are 16.
Carbon is the least electronegative, which means it stays at the centre. So, place the Carbon in the middle and then keep the oxygen either side of that!
Here we can observe some chemical bonds. Now, let us place an electron pair between each of these oxygen atoms. It will look like the following.
We have used 4 now. Then, we can complete the octets on the outer shell.
Now, lets check and see whether we have octets. The oxygen on the right has 8, and the left has 8. So, both of these have octets. But, the carbon has only 4 valence electrons it does not have octets.
Now, its time to share these nonbonding electrons between both atoms! It will look as shown below if we started from considering the Oxygen atom.
As we can see, Oxygen has 8 electrons, which is perfect. And the carbon has 6, which is a bit closer. Repeat the same process now to the other Oxygen electron. Lets pick some electrons and share them across the other side so that Oxygen can have 8 and carbon as 6.
Finally, we have completed the formation of an octet. In Total, we used 16 valence electrons. We can also write it as a structural formula, and that would look like the one given below.
Why Water Is Bent And Carbon Dioxide Is Linear
Both water and carbon dioxide consists of atoms connected by polar covalent bonds. Yet, water is a polar molecule while carbon dioxide is nonpolar. The polarity of the chemical bonds within a molecule is not sufficient to make the molecule polar. Each water molecule has a bent shape because of the lone electron pair on the oxygen atom. Each C=O bond in carbon dioxide is polar, with the oxygen atom pulling the electrons from carbon toward itself. The charges are equal in magnitude, yet opposite in direction, so the net effect is to produce a nonpolar molecule.
Recommended Reading: What Is Consolidation In Psychology
Co2 Lewis Structure Hybridization Molecular Geometry And Mo Diagram
Carbon dioxide is a colorless gas that is well known to many of us!
From the time we were in school, we knew that we inhale oxygen and exhale CO2. But is that all we need to know?
Probably no! As we indulge more in chemistry, we can see, there are many more things related to CO2. To learn all those things smoothly we need to know about this gas in more detail.
So without further adieu, lets quickly jump into the Carbon dioxide world!!
This gas has a different use in different fields. From being used as a refrigerant to carbonated beverages, CO2 is everywhere. We must not forget how important it is for the plants!!
It is used in different industries as well.
The molar mass of CO2 is 44.009 g/mol and density is 1562 Kg/m3. Now let us learn the basic concepts about CO2 molecules.
How Is Vsepr Theory Used In Molecular Geometry
According to the VSEPR theory the number of valence electrons on the central atom decide the molecular structure of the compound. The central atom can either form bond pairs or lone pairs with its valence electrons. The bond pairs are formed when the central atom shares the electrons with another atom. The lone pair are the electrons which belong to the central atom in a molecule and are not shared with any other atom. Lone pairs are also called as non-bonding pair of electrons. Here is how the number of bond pairs and lone pairs can be calculated for a given atom. Number of bonding electrons = – Number of non-bonding electrons = 2 x Using the formulas for finding the bonding and non-bonding electrons for some atoms:
| Atom | Total number of valence electrons possible. | Number of valence electrons |
| 8 – 2 = 8 |
According to the table mentioned above here is how the atoms will look like: Depending on the number of bonding pairs and the lone pairs the molecular geometry of atoms can be predicted. Here is the table mentioned by the VSEPR theory:
| Bonding Electron pairs |
| 900, 1800 |
You May Like: What Does Kw Mean In Chemistry
Why Is Co2 Nonpolar While Co Is Polar
CO is polar because of the electronegativity difference between C and O atoms. Both atoms have unequal charge distribution, and therefore the CO bond has a net dipole moment, making it a polar molecule. On the other hand, CO2 is nonpolar because it has a linear, symmetrical structure.The 2 oxygen atoms have equal electronegativity, pulling the electron density from carbon at an angle of 180 degrees from either direction. Since theres no unequal sharing of valence electrons in the case of carbon dioxide, it is nonpolar.
Faqs On Hybridization Of Co2
1. What is the molecular Geometry of CO2?
Molecular geometry is the bond lengths and angles, determined experimentally. Lewis structures give an approximate measure of molecular bonding. There is a simple method that enables us to predict the overall geometry, which is Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion . It means, the valence shell electron pairs are involved in bonding, and that these electron pairs will keep very far away from each other, because of the electron-electron repulsion.But in CO2, more specifically, there are 16 valence electrons to work with.Only, the central carbon has a share in 4 valence electrons, so it is possible to move a lone pair from each oxygen, to produce two double bonds between Carbon and Oxygen. Only the central carbon has a share in 4 valence electrons, so, possibly, we can pass a lone pair from each oxygen, to form two double bonds between the C and O atoms.
The double bond acts as a single bond for our purpose of predicting it as a molecular shape.
2. Does CO2 support Combustion? How?
On the basis of which orbitals are involved in hybridization, it is of the following types:
1) sp3
Don’t Miss: What Is The Branch Of Biology Called
Co2 Molecular Geometry & Shape
In a CO2 molecule, the carbonatom is in the center double bonded with two oxygen atoms by each side. Both oxygenatoms have two lone pairs of nonbonding electrons present and the central carbonatom has no lone pairs of nonbonding electrons present.
The presence of same atoms oneither side of the central carbon atom nullifies the charge distribution becauseof the symmetrical structure. Thus, CO2 has a linear molecular geometry.
I)Electron Domain Geometry
From the above Lewis dot structure, CO2 has only two regions ofelectron density around the central carbon atom because no lone pair ofelectrons presence of carbon atom.
Bothoxygen atoms have two lone pair of electrons presence but due to thesymmetrical structure, the effects of lone pairs are canceled which results in alinear geometry of CO2, not bent or angular.
II) VSEPR Shape
According to VSEPR theory, there is a total of 16 valence electrons in which C contributes4 electrons and two O contribute 12 electrons.
From the Lewis structure of Carbon, we know that there are not anylone pair of electrons presence on carbon.
Also, four pairs of electrons participate in the two C=Oformations that show there are a total of 4 pairs of electrons pairs present whichforms two sigma bond.
But the effects of lone pairs of oxygen atoms are nullified due to thesymmetrical structure, the CO2 molecule acquires linear molecular geometry andhas a linear shape.