How Is Methemoglobinemia Diagnosed
Patients who apply to a health institution with symptoms of methemoglobinemia are asked some questions. Questions such as which substances he was exposed to and how long this situation has been observed are asked.
Then some tests are done. These tests are:
- complete blood count
- The level of nitrites in the blood
- The level of drugs in the blood
- Pulse oximetry, which shows the oxygen level of the blood
- Some tests to check for enzymes
Detailed examination is performed as a result of bruising on the lips, fingers or body . Methemoglobinemia is diagnosed with various blood tests and treatment is started in a short time.
How Do Healthcare Providers Treat This Condition
Treatment varies based on the kind of methemoglobinemia that you have. For example, a newborn with the Type 2 form of the condition will need very different treatment from someone who developed the condition because they were exposed to toxic substances or used certain recreational drugs.
People with Type 1 methemoglobinemia or Hemoglobin M disease may not need treatment. If they do, healthcare providers may use the following medications to reduce methemoglobin levels:
- Methylene blue: The medication is a well-known antidote for methemoglobinemia.
- Vitamins C and B2.
Treatment for acquired methemoglobinemia
Depending on circumstances, acquired methemoglobinemia may be a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment such as intravenous hydration and oxygen. Most people with acquired MetHb receive methylene blue.
What are treatment complications?
People with G6PD deficiency may develop hemolysis if they have repeated methylene blue treatments. Hemolysis happens when your red blood cells fall apart earlier than usual or inappropriately.
Congenital Methemoglobinemia With Multiple Limb Anomalies In An 11
Sheetal Agarwal, MD1, Dhirendra Singh, MD2, Ankur Agarwal, MS3*, Ridhima Sharma, MD4 and Savitri Singh, MD5
1Associate Professor, Department of Pediatrics, ABVIMS & RML Hospital, New Delhi, India
2Senior Resident, Department of Pediatrics, ABVIMS & RML Hospital, New Delhi, India
3Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Superspecialty Pediatric Hospital and Postgraduate Teaching Institute, Noida, India
4Assistant Professor, Department of Pediatric Anaesthesiology, Superspecialty Pediatric Hospital and Postgraduate Teaching Institute, Noida, India
5Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Superspecialty Pediatric Hospital and Postgraduate Teaching Institute, Noida, India
Don’t Miss: What Is Behaviour In Psychology
Acquired Methemoglobinemiatreatment Market Segment Analysis
The Acquired Methemoglobinemia Treatment Marketbased on Geography can be further segmented into North America, Europe,Asia-Pacific, South America, and the Rest of the World. North America held thelargest share with 40% of the overall market in 2021. The growth in thissegment is owing to the factors such as top-quality healthcare infrastructurewhich might include hospitals, clinics, ASCs, and research facilities. Inaddition, high health consciousness is due to better literacy rates andliving standards of people. Also, the widescale occurrence of top-of-the-linepharmaceutical companies such as Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, and othershave been a blessing to the American drug discovery portfolio. However,Asia-Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing segment over the forecastperiod 2022-2027. This growth is owing to ascending pharmaceutical industry ofcountries like China and India. On another hand, the overall healthcareinfrastructure is ameliorating as governments are allocating more funds toimprove healthcare capabilities. On another hand, growing economic affluencehas raised the living standards of people which in turn has made people quitecognizant regarding their health.
What Is Methemoglobinemia Causes Symptoms And Treatment
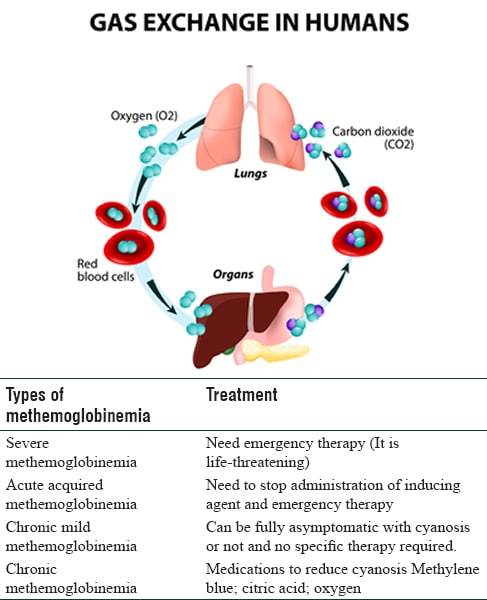
Methemoglobinemia is the name given to the disease that occurs when the amount of methemoglobin in the body increases and the hemoglobin level decreases. Methemoglobin does not have the ability to carry oxygen, and due to increased metHB levels, enough oxygen cannot be delivered to the body.
In this article, you can find the most comprehensive answer to the questions of what is methemoglobinemia , what are the causes of metHB, what symptoms it manifests, how to diagnose and treat it, what are its complications and how to prevent it.
Also Check: What Is Pcr In Biology
Proliferating Usage Of Topical Anesthetics And Antibiotics Isexpected To Boost Product Demand
Spikingsurgical procedures as the magnitude at which cardiovascular hitches such ascancer, heart attack, heart valve complications, and strokes are prevailing ismind-boggling. Millions of people all over the globe suffer from atrialfibrillation every year. Administering patient with sprays of tropicalanesthetics lead to an adverse reaction and increases the risk of developingacquired methemoglobinemia. Therefore, enlarging the prevalence ofcardiovascular hitches is a blessing in disguise for the acquiredmethemoglobinemia market. For instance, arrhythmia prevalence is anticipated toreach 12 million by 2050 in the U.S., whereas, more than 17 million cases in theEuropean Union are projected by 2058. Similarly, mounting cancer incidenceshave heightened the demand for local anesthetics like benzocaine, pramoxine,dibucaine, and proxymetacaine as these drugs plays a significant role innumbing certain area of the body which is indeed a driver driving therespective market.
Acquired Methemoglobinemia Treatment Market Segment Analysis
The Acquired Methemoglobinemia Treatment Marketbased on the disease type can be further segmented into inherited and acquired.The acquired segment held the largest share in 2021. The growth is owing tohigh prevalence as compared to congenital form. Generally, the inherited form of thisdisease occurs due to inherited genetic blemishes in which patient bloodexperiences unadorned scarcity of cytochrome 5 which is accountableto alter methemoglobin into oxygen-carrying protein hemoglobin, and such casesare very sporadic. Whereas, acquired form has more occurrence rate as peopleslives in the modern-day world are surrounded by a number of factors such asexposure to oxidizing substances, consumption of polluted well water, andothers that might lead to this disease. Moreover, the acquired form isestimated to be the fastest-growing segment with a CAGR of 5.6% over theforecast period 2022-2027. This growth is owing to enlarging consumption ofnitrate-rich vegetables such as squash, beans, spinach, carrot, and others. Onanother hand, products with benzocaine presence, excess usages of anesthetics,and antibiotics like prilocaine and chloroquine have their fair share in theprevalence of this disease.
Read Also: Do You Need Physics For Med School
Why Does Methemoglobinemia Cause Blue Skin
In methemoglobinemia, the hemoglobin is unable to carry oxygen and it also makes it difficult for unaffected hemoglobin to release oxygen effectively to body tissues. Patients’ lips are purple, the skin looks blue and the blood is “chocolate colored” because it is not oxygenated, according to Tefferi.
A Rare Culprit Of Methemoglobinemia
- Encyclopedia of Cancer and Society2007
- Kimberly R. Dong and more…Encyclopedia of Lifestyle Medicine & Health2012
- The SAGE Encyclopedia of Stem Cell Research2015
- Alkiviadis G. Nacopoulos and more…Encyclopedia of Lifestyle Medicine & Health2012
- M. Waqas Khan and more…Encyclopedia of Sports Medicine
You May Like: What Is The Geography Of Libya
What Are Methemoglobinemia Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the condition type. Most people with MetHb develop the condition because they use certain pain medications or recreational drugs or they were exposed to certain toxic substances. This is acquired methemoglobinemia and symptoms may include:
Sometimes, people with acquired methemoglobinemia may have symptoms that require immediate medical attention. Those may include:
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Extreme drowsiness, slurred speech and slow reflexes: These are signs of central nervous system depression.
- Loss of consciousness or uncontrollable jerking motions: These are signs of seizures.
- Rapid breathing, increased heart rate and confusion: These are signs of metabolic acidosis.
What are congenital methemoglobinemia symptoms?
Congenital methemoglobinemia is very rare, with only a few cases documented worldwide. Based on what theyve learned, healthcare providers have established three classifications of congenital methemoglobinemia Type 1, Type 2 and hemoglobin M disease .
People with hemoglobin M disease often have cyanosis but are otherwise healthy. People with Type 1 MetHb have cyanosis but rarely have other medical issues. On the other hand, babies born with Type 2 MetHb often develop severe neurological issues by the time theyre 9 months old and rarely live beyond infancy.
What Questions Should I Ask Healthcare Providers
Methemoglobinemia is a very rare blood disorder that some people inherit but most people develop . Depending on your situation, you may want to ask your healthcare provider some of the following questions:
Acquired MetHb
- Why do I have this condition?
- Will treatment make my symptoms go away?
- Will my symptoms come back?
- What should I do to prevent another incident?
Type 1 congenital MetHb
- Is cyanosis a serious medical issue?
- Will I always need treatment for MetHb?
- Will I develop other symptoms?
- Can I pass this condition on to my biological children?
Type 2 congenital MetHb
- How will this condition affect my baby?
- Are there treatments to ease my babys symptoms?
- What can I do to help my baby?
- If I have more children, will they have this condition?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Methemoglobinemia is a rare blood disorder that affects how red blood cells deliver oxygen throughout your body. Some people inherit the disorder, but most people develop it after using certain medications, being exposed to certain toxic substances or using recreational drugs. Congenital methemoglobinemia rarely causes serious medical issues. People who develop the condition may develop life-threatening medical conditions. If you think you may be at risk of developing MetHb, talk to a healthcare provider about your situation. Theyll be glad to help.
Read Also: Exponential Growth And Decay Common Core Algebra 1 Homework Answers
Inherited Forms Of Methemoglobinemia
Inherited methemoglobinemia is caused by rare genetic problems present from birth. Different genetic problems lead to different levels of severity, which sometimes need slightly different treatments. There are two forms of inherited methemoglobinemia: types 1 and 2.
People with type 1 congenital methemoglobinemia often have an average lifespan and don’t experience complications.
The affected gene in type 2 inherited methemoglobinemia leads to a problem with a protein . This protein helps keep the iron in the right configuration for regular hemoglobin .
People with type 2 congenital methemoglobinemia have a severe problem with this protein. Because of this, symptoms are most severe for people with type 2 congenital methemoglobinemia. Most people with type 2 die in infancy. They also tend to have developmental delays and other neurological issues.
Other congenital disorders can also cause increased levels of methemoglobin. These include:
- Hemoglobin M disease
- Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
Warning On Teething Products
Because of the risks of methemoglobinemia, the Food and Drug Administration recommends against using over-the-counter teething products that include benzocaine in children younger than 2. Silicone teething rings are a good alternative.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Definition Of Conductor In Physics
What Is Methemoglobinemia
Methemoglobinemia is a very rare blood disorder, sometimes called blue baby syndrome, which affects how red blood cells deliver oxygen to cells and tissues. People can inherit this condition but MetHb usually happens when people use certain medications or recreational drugs or exposure to certain chemicals. MetHb can be life-threatening, especially for babies born with a severe type of the condition or people who use recreational drugs. Most of the time, healthcare providers treat methemoglobinemia with a medication that reduces methemoglobin levels and eliminates symptoms.
How does this affect my body?
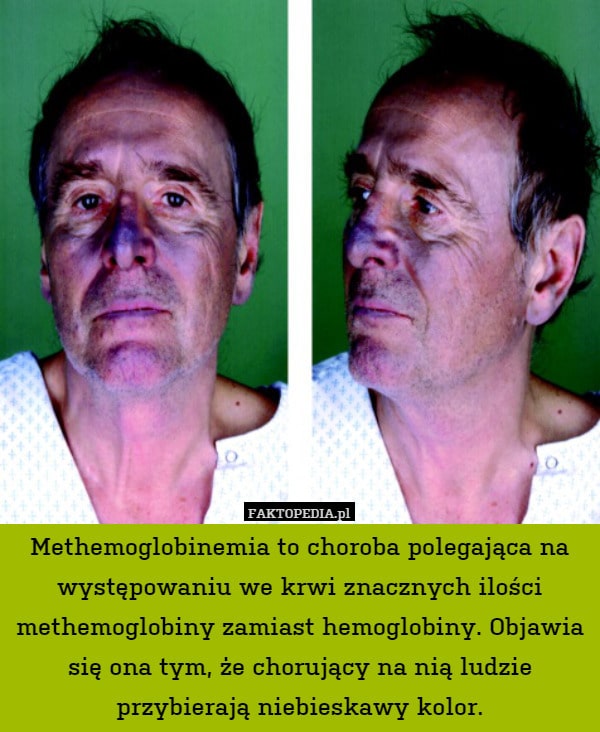
Most people with methemoglobinemia have some level of cyanosis a condition that turns your nail beds, tongue, lips and skin a distinctive shade of light blue or purple. Cyanosis happens when you dont have enough oxygen in your blood. Normally, red blood cells carry oxygen throughout your body. Red blood cells rely on the protein hemoglobin to carry oxygen. In MetHb, a genetic mutation turns hemoglobin into methemoglobin. Methemoglobin doesnt carry oxygen. Without adequate blood oxygenation the amount of oxygen in your blood you develop cyanosis.
What Is Methemoglobin
Methemoglobin is a metalloprotein form of hemoglobin. It is not able to bind to the oxygen. It does not have enough capacity to carry oxygen. The normal range of methemoglobin is 0-3%. Higher levels of methemoglobin can reach up to 15%. When your body is producing too much of methemoglobin, it will start replacing the normally present hemoglobin. This can cause oxygen to be removed from the cells. The level of methemoglobin can be determined by blood cell count and examination of the color.
Don’t Miss: What Is On The Ap Biology Exam
Is Blue Skin Real
Yes, it turns out, and a family living in Appalachia had the condition for generations. In their case, blue skin was caused by a rare genetic disease called methemoglobinemia. Methemoglobinemia is a blood disorder in which an abnormally high amount of methemoglobin a form of hemoglobin is produced.
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
If you inherited a type of methemoglobinemia, you should contact your healthcare provider if you notice changes in your body such as fatigue or weakness. These symptoms may be signs your red blood cells are carrying even less oxygen throughout your body. People who have cyanosis and more serious symptoms, like seizures or extreme drowsiness, should call 911 or go to the emergency room.
Read Also: Do I Need Chemistry For Psychology
Fugates Of Kentucky: Skin Bluer Than Lake Louise
Genetics and in-breeding cause six generations of family to turn blue.
As a transfusion was being readied, the baby’s grandmother suggested to doctors that he looked like the “blue Fugates of Troublesome Creek.” Relatives described the boy’s great-grandmother Luna Fugate as “blue all over,” and “the bluest woman I ever saw.”
In an unusual story that involves both genetics and geography, an entire family from isolated Appalachia was tinged blue. Their ancestral line began six generations earlier with a French orphan, Martin Fugate, who settled in Eastern Kentucky.
Doctors don’t see much of the rare blood disorder today, because mountain people have dispersed and the family gene pool is much more diverse.
But the Fugates’ story still offers a window into a medical mystery that was solved through modern genetics and the sleuth-like energy of Dr. Madison Cawein III, a hematologist at the University of Kentucky’s Lexington Medical Clinic.
Cawein died in 1985, but his family charts and blood samples led to a sharper understanding of the recessive diseases that only surface if both parents carry a defective gene.
The most detailed account, “Blue People of Troublesome Creek,” was published in 1982 by the University of Indiana’s Cathy Trost, who described Benjy’s skin as “almost purple.”
The Fugate progeny had a genetic condition called methemoglobinemia, which was passed down through a recessive gene and blossomed through intermarriage.
Such was the case with the Fugates.
Who Is At Risk
Methemoglobinemia can result from genetic problems , or something in the environment might change the configuration of some of a persons hemoglobin to methemoglobin .
People with certain health conditions, like lung disease, heart disease, or anemia also have an increased risk of developing methemoglobinemia.
You May Like: What Is Specific Epithet In Biology
What Are The Symptoms Of Methemoglobinemia
The symptoms might change based on the variant of methemoglobinemia. When the level of methemoglobin rises, symptoms begin to get worse. The common symptoms are:
-
Cyanosis. It involves the bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membrane. This occurs due to the deoxygenation of the blood. There will be an elevation in deoxyhemoglobin levels. This will be most prominently evident in lips and fingers. Because of the cyanosis in methemoglobinemia, this condition is referred to as Blue baby syndrome. The connection between high nitrate levels and the blue baby syndrome is the water level crossing the standard limit of 10 mg/L
-
Blood becomes chocolate brown in color.
-
Rapid heart rate.
Based on the concentration, the signs and symptoms shown may vary.
0-3 % – No symptoms will be shown.
10-20 % – Mild symptoms.
20-50 % – Decreased exercise tolerance, tachycardia, fatigue, and dyspnea.
Higher than 50 % – Seizure, hypoxia, coma, and metabolic acidosis.
Higher than 70 % – Severe hypoxia and death.
What Are the Types of Methemoglobinemia?
-
Depending on the duration of the condition, it may be classified as acute or chronic.
-
Depending on the cause of the condition, methemoglobinemia is of different types. The congenital methemoglobinemia is divided into two types. It is hereditary or acquired. This genetic defect is accompanied by a deficiency of either an enzyme or a protein responsible for converting methemoglobin to hemoglobin.
What Tests Do Healthcare Providers Use To Diagnose This Condition
Healthcare providers typically do the following tests:
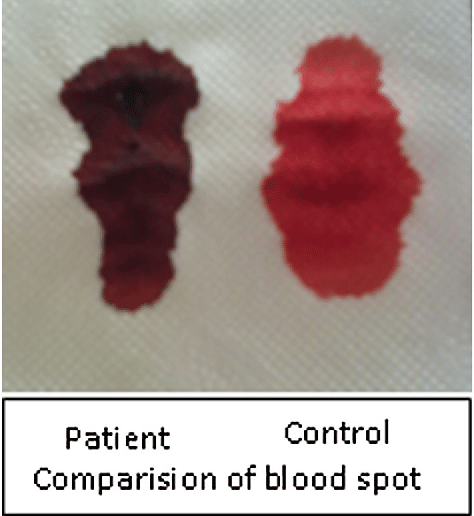
- Blood tests: People with this condition often have dark brown-colored arterial blood. The dark-brown color is a sign arterial blood isnt carrying oxygen.
- MetHb evaluation: Healthcare providers measure methemoglobin levels in your blood.
- CYB5R enzyme activity: Lower-than-normal enzyme activity is a sign of congenital methemoglobinemia.
- Genotyping: Healthcare providers may do genotyping, examining your DNA for signs of genetic differences to confirm suspected congenital methemoglobinemia. Genotyping also helps healthcare providers identify the condition type.
- Hemoglobin electrophoresis: This is a technique healthcare providers use to examine hemoglobin in your red blood cells. They may use this test when diagnosing HbM.
You May Like: Does Organic Chemistry Have Math
What Are The Causes
The acquired type occurs in some people due to the exposure of harmful chemicals and medicines. The commonly involved chemicals, food, and medications are:
-
Nitrates: Babies who are younger than six months may develop acquired methemoglobinemia from the excess of nitrites present in the contaminated water. The bacterial flora present in the babys digestive system adversely reacts with the nitrates and causes methemoglobinemia. Completely developed digestive systems can avoid this kind of nitrate poisoning.
-
Benzocaine: Benzocaine over-the-counter product. It is used to soothe sore gums of the baby. The U.S.Food and Drug Administration organization has advised the baby-sitters, parents, and caregivers not to use them.
-
Medications like Dapsone. This medication is used to treat dermatitis, acne, and blisters in the arms and buttock region. It is also known to be useful for fungal infections in the lungs of HIV patients.
-
Antimalarial drugs like Chloroquine.
-
Solid foods: Certain home foods, including fruits and vegetables like beetroot, carrots, spinach, and beans, are known to have high nitrates. So, these kinds of solid foods are not advised for children. Parental counseling therapy includes food that can be fed to babies. In this therapy, parents are advised not to give babies solid foods before they are four months old.