Factors Affecting The Pcr:
1. Denaturing Temperature and Time:
The specific complementary association due to hydrogen bonding of single-stranded nucleic acids is referred to as annealing: two complementary sequences will form hydrogen bonds between their complementary bases and form a stable double-stranded, anti- parallel hybrid molecule.
One may make nucleic acid single-stranded for the purpose of annealing, if it is not single-stranded already, like most RNA viruses, by heating it to a point above the melting temperature of the double- or partially-double-stranded form, and then flash-cooling it this ensures the denatured or separated strands do not re-anneal. Additionally, if the NA is heated in buffers of ionic strength lower than 150 mM NaCl, the melting temperature is generally less than 100°C which is why PCR works with denaturing temperatures of 91-97°C.
Taq polymerase is given as having a half-life of 30 min at 95°C, which is partly why one should not do more than about 30 amplification cycles. However, it is possible to reduce the denaturation temperature after about 10 rounds of amplification, as the mean length of target DNA is decreased. For templates of 300 bp or less, denaturation temperature may be reduced to as low as 88°C for 50% templates, which means one may do as many as 40 cycles without much decrease in enzyme efficiency.
2. Annealing Temperature and Primer Design:
Tm = 4 + 2°C.
3. Primer Length:
4. Degenerate Primers:
The reverse primer sequence was as follows:
Construction Of Cdna Libraries
This section goes over the typical experimental setup for cDNA library construction and basic principles. The cDNA library uses mRNA as the source of information, so it onlyincludes the organisms expressed genes from a particular source. This mRNA can be extracted from the organisms cells, a specific tissue, or even an entire organism. mRNA needs to be converted into cDNA by reverse transcriptase,in order to allow the host organism to perform the correct replication and transcription processes for mRNA. This means that it represents the genes that were being actively transcribed in that particular source under the exactconditions that existed at the time the mRNA was extracted and purified. cDNA libraries are useful in reverse genetics, although they only represent less than 1% of the overallgenome in a given organism
The main advantage behind the choice of mRNA as the source for the DNA library preparation is to avoid junk DNA from genomic DNA and introns from eukaryotic genes. This ensures thatonly expressed genes from a specific cell or tissue are being stored. Although bacterial cells do not process introns, the use of mature mRNA allows the successful expression of the cDNA genes inbacterial host cells for further physiological tests.
What Is Pcr The Beginners Guide
Listen to one of our scientific editorial team members read this article.Click here to access more audio articles or subscribe.
PCR is THE technique of modern molecular biology labs.
If you need to copy, sequence, or quantify DNA, you need to know PCR. But how do you get started with PCR?
In short, PCR is a biochemical technique that uses thermocycling and enzymes to quickly and reliably copy DNA.
It was invented in a flash of inspiration when scientist Kary Mullis was driving on Highway 128 from San Francisco to Mendocino.
This article gives a brief overview of the PCR process, with a few tips to help you avoid the most common pitfalls.
If youre new, or relatively new, to PCR then this is for you.
Recommended Reading: What Is Human Geography Class
What Is Pcr Used For
Once amplified, the DNA produced by PCR can be used in many different laboratory procedures. For example, most mapping techniques in the Human Genome Project relied on PCR.PCR is also valuable in a number of laboratory and clinical techniques, including DNA fingerprinting, detection of bacteria or viruses , and diagnosis of genetic disorders.
- What is PCR used for?
Once amplified, the DNA produced by PCR can be used in many different laboratory procedures. For example, most mapping techniques in the Human Genome Project relied on PCR.PCR is also valuable in a number of laboratory and clinical techniques, including DNA fingerprinting, detection of bacteria or viruses , and diagnosis of genetic disorders.
In Vitro Method Synthesizes And Amplifies Specific Sequences Of Target Dna
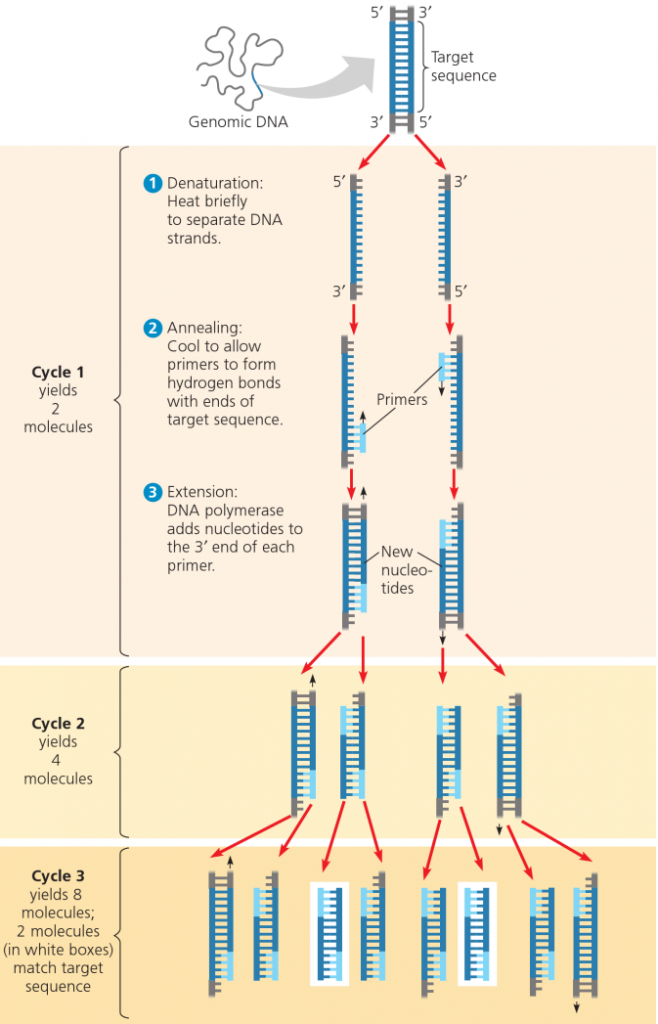
The Polymerase Chain Reaction is a very prominent molecular biology technique, originally conceived by Dr. Kary Mullis during a moonlit mountain drive in California in 1983. It dawned on him that the property of DNA to separate into single strands at warm temperatures and the ability of the polymerase enzyme to exactly replicate single strands could be used together to multiply sequences of DNA. Dr. Mullis received the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 1993 for his development.
PCR is a technique that is used to amplify the number of copies of a specific region of DNA, in order to produce enough DNA to be adequately tested. It is, essentially, an in vitro method that synthesizes and amplifies specific sequences of target DNA through a repeating enzymatic thermocycling process. In each cycle the amount of target DNA is doubled until there is enough to be detected by gel electrophoresis, another common molecular biology technique.
Now, lets say that the above sequences flank the gene, which includes a long stretch of letters designated as: .. These are known, absolutely identified, to be the sequence of letters, which only flank a particular region of a particular organisms DNA, and no other organisms DNA. This region would be a target sequence for PCR.
The following steps are generally used for PCR:
Don’t Miss: Is Grade 12 Physics Hard
How Does Pcr Work
To amplify a segment of DNA using PCR, the sample is first heated so the DNA denatures, or separates into two pieces of single-stranded DNA. Next, an enzyme called “Taq polymerase” synthesizes – builds – two new strands of DNA, using the original strands as templates. This process results in the duplication of the original DNA, with each of the new molecules containing one old and one new strand of DNA. Then each of these strands can be used to create two new copies, and so on, and so on. The cycle of denaturing and synthesizing new DNA is repeated as many as 30 or 40 times, leading to more than one billion exact copies of the original DNA segment.The entire cycling process of PCR is automated and can be completed in just a few hours. It is directed by a machine called a thermocycler, which is programmed to alter the temperature of the reaction every few minutes to allow DNA denaturing and synthesis.
The Standard Technique For Detecting Sars
PCR was an acronym that dominated the news in 2020. What is the technique, how useful is it, and what does it tell us?
Polymerase Chain Reaction refers to a technique that makes a large volume of DNA or RNA from a small sample. This is a standard technique in molecular biology that has been used for forensics and DNA fingerprinting, sequencing the human genome, identifying and developing good crops, building evolutionary family trees, prenatal screening, and, more recently, for detecting SARS-CoV-2.
Just as a thermometer is the standard measuring tool for temperature, PCR is the standard technique for identifying and amplifying DNA and RNA.
The technique takes small pieces of DNA or RNA and makes millions of copies that can be detected, sequenced, cloned or diagnosed.
If you had thousands of grains of a substance, you would be able to tell if its sand, or sugar. But imagine trying to identify something if you only had one grain. Likewise, small amounts of DNA are hard to identify, but large quantities are easy.
Don’t Miss: What Does Quantum Physics Mean
Pcr Enhancers And Additives
Addition of PCR-enhancing agents can increase yield of the desired PCR product or decrease production of undesired products. There are many PCR enhancers, which can act through a number of different mechanisms. These reagents will not enhance all PCRs the beneficial effects are often template- and primer-specific and will need to be determined empirically. Some of the more common enhancing agents are discussed below.
Addition of betaine, DMSO and formamide can be helpful when amplifying GC-rich templates and templates that form strong secondary structures, which can cause DNA polymerases to stall. GC-rich templates can be problematic due to inefficient separation of the two DNA strands or the tendency for the complementary, GC-rich primers to form intermolecular secondary structures, which will compete with primer annealing to the template. Betaine reduces the amount of energy required to separate DNA strands . DMSO and formamide are thought to aid amplification in a similar manner by interfering with hydrogen bond formation between two DNA strands .
Some reactions that amplify poorly in the absence of enhancers will give a higher yield of PCR product when betaine , DMSO or formamide are added. Concentrations of DMSO greater than 10% and formamide greater than 5% can inhibit Taq DNA polymerase and presumably other DNA polymerases as well .
Common Applications For Dna Libraries
- Identification of new genes
- In vitro functional characterization of genes
- Transcriptomic analysis
- Identification of gene versions depending on alternative splicing
cDNA libraries are used to express eukaryotic genes in prokaryotes since it does not include introns, and therefore, can be expressed in prokaryotic cells. cDNA libraries remove the large numbers of non-coding regions from the library, and it is also useful for subsequently isolating the gene that codes for that mRNA.
Read Also: What Psychology Says About Love In Hindi
Polymerase Chain Reaction : Stages Types Factors And Other Details
Read this article to learn about the stages, primer design, types, sensitivity, factors affecting, applications and variations of polymerase chain reaction.
PCR has been one of the most important techniques developed in recent years. The reason behind is its simplicity of the reaction and relative case of the practical manipulation steps.
The PCR is used to amplify a precise fragment of DNA from a complex mixture of starting material usually termed as template DNA.
The reaction requires some information about sequence of flanking fragment of DNA to be amplified. From this information two oligonucleotide primers can be synthesized each complimentary to the stretch of DNA to the 3-side of the target DNA, one for each of the two DNA strands. This technique in many cases has replaced traditional DNA cloning methods, since it fulfills the same function of producing large amount of DNA from small amount of starting materials.
How Effective Is Pcr
PCR was first invented in 1985 and is a well-established, common, standard laboratory practice for molecular biology, genetics and medical diagnostics. PCR is highly accurate and sensitive and is considered the gold standard DNA/RNA identification and SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis.
The technique is so accurate at building the right DNA strand that it is used to build DNA for use in CRISPR and other cloning techniques.
Occasionally, false negatives or positives will arise. Regardless, the rates are extremely low and usually happen because of a low quality or old sample the problem is the sample collection, rather than the test itself. One study of PCR SARS-CoV-2 tests found that just 5 patients in 96,000 came back with a false negative result.
Thankfully, it is usually easy to flag which results might be a false negative because low quality samples are visible to experts, and they are able to retest the sample. This means that the actual number of false negatives upon COVID diagnosis is even lower.
The test is also very sensitive and only needs tiny volumes of sample, such as what is on a swab, where other techniques need a higher volume .
It is also a relatively quick test. It only takes a couple of hours to run, and multiple samples can be run together.
The speed, ease, sensitivity, and accuracy of PCR is very fine-tuned, and is therefore an unshakable standard in the world of molecular biology. It has been used for decades and will continue to be used for decades to come.
Recommended Reading: What Is Neuron In Biology
Standard Pcr Experiment Overview
The PCR is used to amplify a specific DNA fragment from a complex mixture of starting material called template DNA. The sample preparation and purification protocols depend on the starting material, including the sample matrix and accessibility of target DNA. Often, minimal DNA purification is needed and some techniques such as direct PCR or extraction-free PCR require no pre-purification of DNA or RNA. However, PCR does require knowledge of the DNA sequence information that flanks the DNA fragment to be amplified .
From a practical point of view, a PCR experiment is relatively straightforward and can be completed in a few hours. In general, a PCR reaction needs five key reagents:
Figure 1:
Each of these steps, termed cycles, is repeated 30-40 times, , doubling the amount of DNA at each cycle and obtaining amplification .
Figure 2:
Let’s take a closer look at each step.
Pcr With Biotechnology 101 Kit
For all experiments using PCR in the Biotechnology 101 Kit, you will be provided with a specific set of primers.
You also have PCR tubes already prepared with a freeze-dried PCR master mix bead . This bead contains:
Finally, you will prepare, as part of each experiment, specific template DNA . These need to be mixed in precise proportions, for which you will need the micropipette .
Also Check: What Does The Symbol K Mean In Chemistry
Pcr Applied To Diagnosis
PCR is a fabulous diagnostic tool. It is already widely used in the detection of genetic diseases. The amplification of all or part of a gene responsible for a genetic disease makes it possible to reveal the deleterious mutations , their positions, their sizes, and their natures. It is thus possible to detect deletions, inversions, insertions, and even point mutations, either by direct analysis of PCR products by electrophoresis or by combining PCR with other techniques . But PCR can still be used to detect infectious diseases , as is already the case for AIDS, hepatitis C, or chlamydia infections. Although other diagnostic tools are effective at detecting these diseases, PCR has the enormous advantage of producing very reliable and rapid results from minute biological samples in which the presence of the pathogen is not always detectable with other techniques .
Digital Pcr And Digital Droplet Pcr
Digital PCR is another adaptation of the original PCR protocol.4 Like qPCR, dPCR technology uses DNA polymerase to amplify target DNA from a complex sample using a primer set and probes. The main difference, though, lies in the partitioning of the PCR reactions and data acquisition at the end.
dPCR and ddPCR are based on the concept of limiting dilutions. The PCR reaction is split into large numbers of nanoliter-sized sub-reactions . The PCR amplification is carried out within each droplet. Following PCR, each droplet is analyzed with Poisson statistics to determine the percentage of PCR-positive droplets in the original sample. Some partitions may contain one or more copies of the target, while others may contain no target sequences. Therefore, partitions classify either as positive or negative , providing the basis for a digital output format.
ddPCR is a recent technology that became available in 2011.5 ddPCR utilizes a water-oil emulsion to form the partitions that separate the template DNA molecules. The droplets essentially serve as individual test tubes in which the PCR reaction takes place. This technology was put to use in creating sensitive SARS-CoV-2 tests.
Also Check: Algebra Lineal Ejercicios Resueltos Numeros Complejos
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism
Restriction fragment length polymorphisms are identified using restriction enzymes that cut DNA only at specific restriction sites . At present, the most common use of RFLPs is downstream PCR to detect alleles that differ in sequence at a given restriction site. A gene fragment is first amplified using PCR and then exposed to a specific restriction enzyme that cuts only one of the allelic forms. The digested amplicons are usually resolved by electrophoresis. Microsatellites or SSRs or STRs consist of a few nucleotides26 base pair DNA sequenceepeated several times in tandem . They are spread on a eukaryotic genome. Microsatellites are relatively small in size and, therefore, are easily amplified using DNA PCRs extracted from different sources, such as blood, hair, skin, or even feces. Polymorphisms can be visualized on a sequencing gel, and the availability of automated DNA sequencers allows high-throughput analysis of a large number of samples .
What Pcr Is Looking For
Lets first establish what DNA and RNA are.
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a long chain polymer make of small units called nucleotides. It is a double helix make of two strands that are joined together by complimentary nucleotides that are unique to each person.
RNA is also a polymer made of nucleotides, but it is only a single strand. Instead of DNA, some viruses have RNA that is unique to them. It is more fragile than DNA, and cant be used for all diagnostic purposes.
Thankfully, PCR is accurate, fast and sensitive, and can amply both DNA and RNA.
Don’t Miss: What Are The 5 Themes Of Geography Definitions
Principle And Working Mechanism
The main objective of using a PCR is to produce a huge number of DNA copies. Therefore, template DNA molecules are the first essential component of the whole process. Apart from that primers are also an important component that binds with the template DNA. The reaction mixture also contains all four deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates i.e., dATP, dCTP, dGTP,dTTP and DNA polymerase.
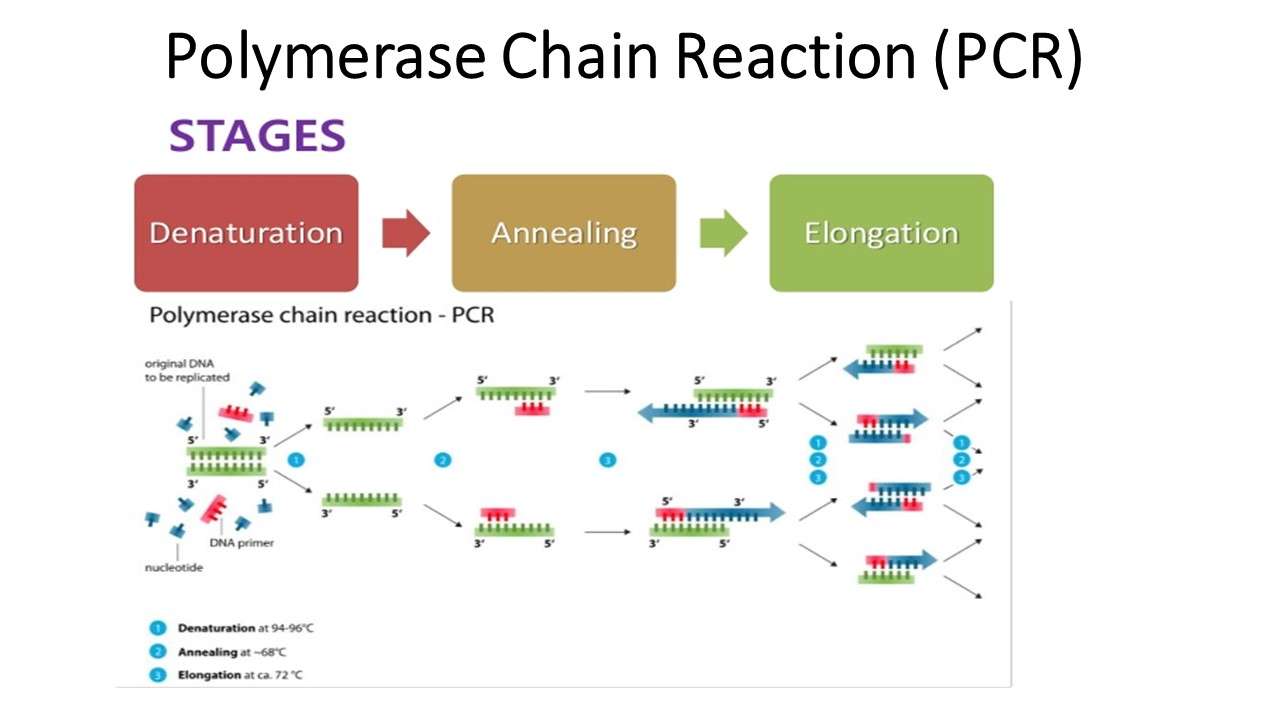
The major steps of PCR can be divided into three parts:
Denaturation at 940C
This is the first step of the process when the temperature is maintained at 940C. At this temperature, the DNA double helix is converted to a single strand and other enzymatic reactions such as the extension of DNA from a previous cycle is arrested.
Annealing at 540C
Then the temperature is reduced to 540C and the primers present at the reaction mixture started to get attached with the template DNA molecule. Due to the low temperature, the bonding between the primer and template occurs. The primer helps the polymerase to find out its attachment site.
Extension at 720C
It is the optimum temperature for the polymerase. At this temperature, the polymerase starts working. The synthesis starts from 5 end and moves towards 3 end. The polymerase helps to join the nucleotides at the complimentary position to the template DNA. As a result, another copy of DNA is produced. The whole process goes for 30-40 cycles which leads to amplification of the template DNA into billion copies. These copies are then further analyzed.