Cathode Ray Oscilloscope Construction And Working
Electron Gun
Deflection System
Fluorescent Screen
Application Of Cathode Ray Oscilloscope
There are uncountable applications of Cathode Ray Oscilloscopes. It is next to impossible to provide a complete list of such applications here.
Displaying A Ripple Signal Using The Ac Switch
1. Switch in normal DC position.
The ripple is difficult to see clearly but if VOLTS/CM is reduced to try enlarge the ripple,the trace will disappear off the screen.
2. Switch moved to AC position.
The constant part of the signal has been removed, leaving just the ripple part.
3. VOLTS/CM reduced to enlarge the ripple.
The ripple can now be examined more closely.
Next Page:Power Supplies | Study
Rapid Electronicshave kindly allowed me to use their images on this website and I am very grateful for their support.They stock a wide range of components, tools and materials for electronics and I am happy torecommend them as a supplier.
Privacy Policy & Cookies
This website does not collect personal information.If you send an email your email address and any personal information will beused only to respond to your message, it will not be given to anyone else.This website displays advertisements, if you click onthese the advertiser may know that you came from this site and I may be rewarded.No personal information is passed to advertisers.This website uses some cookies classed as ‘strictly necessary’, they are essential for operation of the website and cannot be refused but they do not contain any personal information.This website uses the Google AdSense service which uses cookies to serve advertisements based on your use of websites as explained by .To learn how to delete and control cookies from your browser pleasevisit AboutCookies.org.
You May Like: Who Are Paris Jackson’s Biological Parents
Block Diagram Of Cro :
The figure below shows the block diagram of a general purpose CRO .
As we can see from the above figure above, a CRO employs a cathode ray tube ,which acts as the heart of the oscilloscope.
In an oscilloscope, the CRT generates the electron beam which are accelerated to a high velocity and brought to focus on a fluorescent screen. This screen produces a visible spot where the electron beam strikes it. By deflecting the beam over the screen in response to the electrical signal, the electrons can be made to act as an electrical pencil of light which produces a spot of light wherever it strikes.
For accomplishing these tasks various electrical signals and voltages are needed, which are provided by the power supply circuit of the oscilloscope.
Low voltage supply is required for the heater of the electron gun to generate the electron beam and high voltage is required for the cathode ray tube to accelerate the beam. Normal voltage supply is required for other control units of the oscilloscope.
Horizontal and vertical deflection plates are fitted between the electron gun and the screen so that these can deflect the beam according to the input signal.
To deflect the electron beam on the screen in horizontal direction i.e. X-axis with constant time-dependent rate, a time base generator is provided in the oscilloscope.
Since CRT is the heart of the oscilloscope, we are going to discuss its various components in detail.
Physics Notes For High School
DEDICATED TO HELP STUDENTS EXCEL IN PHYSICS BY GIVING NOTES, MOTIVATION AND RESOURCES ESPECIALLY FOR , High School, Secondary School Students.Grade 9 | Grade 10 | Year 9 | Year 10 | Form 4 | Form 5|| This site is best seen using Web version. If this site helps, please consider sharing this in your social media. Thanks heaps! |
You May Like: Span Linear Algebra Example
Measurement Of The Phase Difference
We know that the Lissajous figure is constructed and displayed on the screen of a cathode ray oscilloscope when sinusoidal signals are employed to both horizontal and vertical deflection probes of the CRO. Therefore, supply the sinusoidal signals with the identical amplitude and frequency to both horizontal and vertical deflection channels of the CRO.
For a few Lissajous figures based on their shape, we can directly recognise the phase difference between the two sinusoidal signals used.
-
If the Lissajous figure resulted in a straight line that is inclined at an angle of 450with the positive x-axis of the CRO display, then the phase difference between the two sinusoidal signals used will be 00. This implies that there is no phase difference between those two sinusoidal signals used.
-
If the Lissajous figure resulted in a straight line that is inclined at an angle of 1350 with the positive x-axis of the CRO display, then the phase difference between the two sinusoidal signals used will be around 1800. This implies that the sinusoidal signals used are out of phase.
-
If the Lissajous figure resulted in a circular shape, then the phase difference between the two sinusoidal signals used will be either 900 or 2700.
We can estimate the phase difference between the two sinusoidal signals by applying formulae when the constructed Lissajous figures are of elliptical shape i.e., lissajous ellipse.
Where,
Where,
Introduction To Cathode Ray Oscilloscope: The Stethoscope Of Electronics
In a similar manner when are studying electronics then we require similar probes or devices to see the entities that are not visible otherwise.Electronics is the study of the controlled flow of electronsWe are neither able to see the electrons or their controlled flow. What we observe by various instruments is the effect of such controlled flows of electrons.
You May Like: How To Avoid Parallax Error In Physics
What Are The Functions Of An Oscilloscope
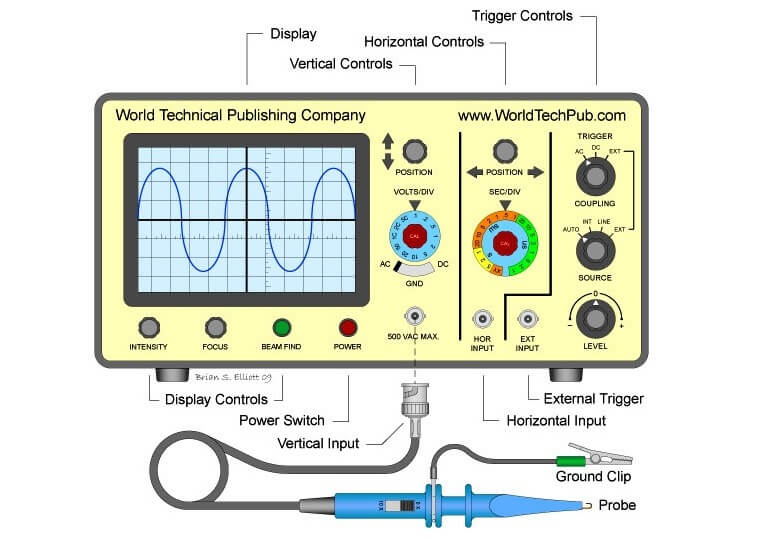
Figure shows the front panel of a typical C.R.O.The functions and explanations for the control knobs are listed in Table.
| Control knob |
Measuring Short Time Intervals:
Displaying Wave Forms:
Obtaining A Clear And Stable Trace
If you are using an oscilloscope for the first time it is best to start with an easy signal such as the outputfrom an AC power pack set to about 4V. The picture shows the trace you should see after setting the controls correctly.
After connecting the oscilloscope to the circuit you wish to test you will need to set the controlsto obtain a clear and stable trace on the screen:
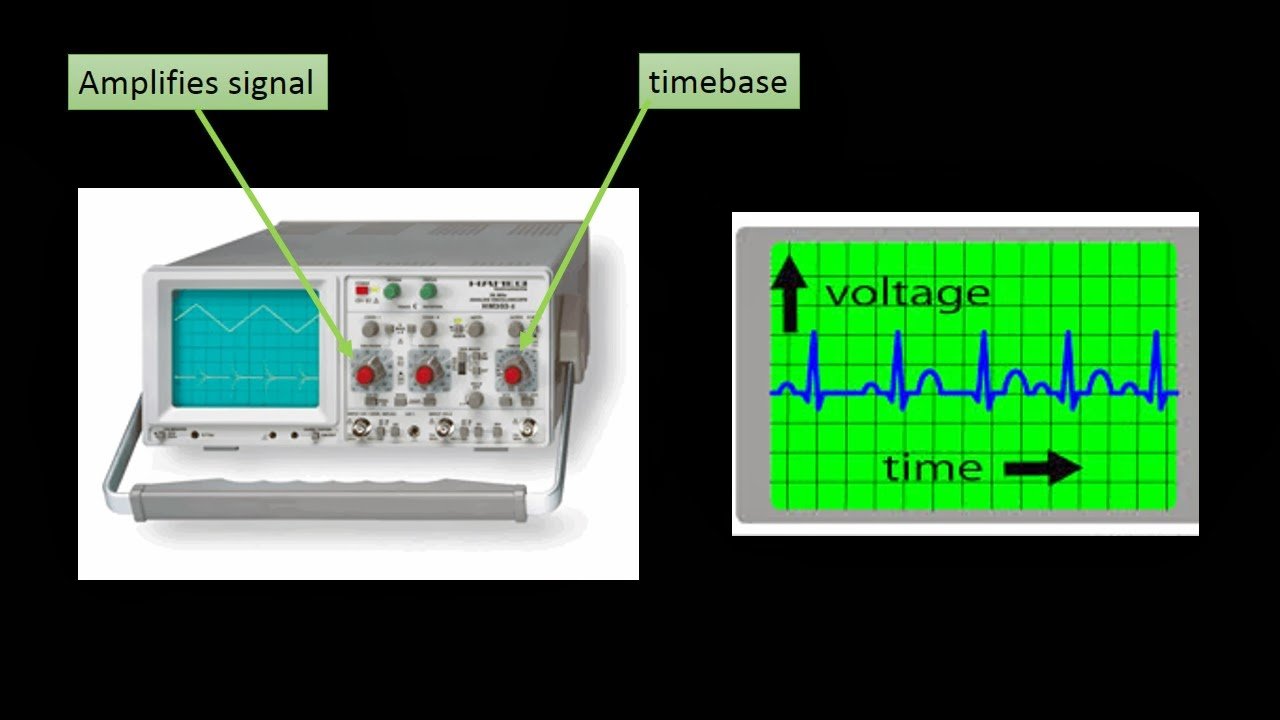
- The Y AMPLIFIER control determines the height of the trace.Choose a setting so the trace occupies at least half the screen height, but does not disappear off the screen.
- The TIMEBASE control determines the rate at which the dot sweepsacross the screen. Choose a setting so the trace shows at least one cycle of the signal across the screen.Note that a steady DC input signal gives a horizontal line trace for which the timebase setting is not critical.
- The TRIGGER control is usually best left set to AUTO.
Further information on the controls: Timebase |Y amplifier | AC/GND/DC
You May Like: Eoc Fsa Warm Ups Algebra 1 Answers
Timebase And Trigger Controls
The oscilloscope sweeps the electron beam across the screen from left to right at a steadyspeed set by the TIMEBASE control. Each setting is labelled with the time the dot takes tomove 1cm, effectively it is setting the scale on the x-axis. The timebase control may be labelled TIME/CM.
At slow timebase settings you can see a dot moving across the screen, as in the upper picture.
At fast timebase settings the dot is moving so fast that it appears to be a line, as in the lower picture.
The VARIABLE timebase control can be turned to make a fine adjustment to the speed, but it must be left at the positionlabelled 1 or CAL if you wish to take time readings from the trace drawn on the screen.
The TRIGGER controls are used to maintain a steady trace on the screen. If they areset wrongly you may see a trace drifting sideways, a confusing ‘scribble’ on the screen,or no trace at all. The trigger maintains a steady trace by starting the dot sweeping acrossthe screen when the input signal reaches the same point in its cycle each time.
For straightforward use it is best to leave the trigger level set to AUTO, but if you havedifficulty obtaining a steady trace try adjusting this control to set the level manually.
Fluorescent Screen For Crt
The front of the CRT is called the face plate. It is flat for screen sized up to about 100mm×100mm. The screen of the CRT is slightly curved for larger displays. The face plate is formed by pressing the molten glass into a mould and then annealing it.
The inside surface of the faceplate is coated with phosphor crystal. The phosphor converts electrical energy into light energy. When an electronics beam strike phosphor crystal, it raises their energy level and hence light is emitted during phosphorous crystallisation. This phenomenon is called fluorescence.
Also Check: Algebra 1 Eoc Fsa Practice Test No Calculator Portion Answers
Setting Up An Oscilloscope
Oscilloscopes are complex instruments with many controls and they require some care to setup and use successfully. It is quite easy to ‘lose’ the trace off the screen if controls are set wrongly!
The picture shows what you should see after setting up, when there is no input signal connected.There is some variation in the arrangement and labelling of the many controls so theinstuctions may need to be adapted for your instrument.
Further information on the controls: Timebase | Y amplifier | AC/GND/DC
Ncert Resources And Supplements For Cbse Students
The Central Board of Secondary Education abbreviated as CBSE is one of the most prominent and prestigious educational boards of India. We, at BYJUS, provide various resources for CBSE students to help students with their exams. The study materials given here are prepared with respect to the latest syllabus. These resources include syllabus, books, sample papers, question papers, NCERT solutions, NCERT exemplar solutions, important questions and CBSE notes. Below, we have provided an exhaustive list of all the resources that a student would require for efficient preparation of exams.
|
Physics NCERT Solutions |
Also Check: Paris Jackson Biological Mother
Cathode Ray Oscilloscope Questions & Answers
1. Explain what is a cathode ray oscilloscope ?
A CRO is an electronic device with a CRT as its main component and other associated circuits consisting of a power supply unit, a sawtooth-wave generator, horizon and vertical amplifiers .
2. How is CRO superior to ordinary measuring instruments?
CRO is an electronic device that gives graphical representation of alternating quantities under examination. The CRO gives very accurate measurements and is free from the errorsintroduced by the moving parts. It is also from damping mechanisms and other inertia containing parts.
3. For Explain what vertical and horizontal plates are provide in a CRO?
Horizontal and vertical plates are provided between electron gun and screen to deflect the beam according to the input signal.
4. For what a triggering circuit is provided in a CRO?
In a CRO, a triggering circuit is provided for synchronising two types of deflections so that horizontal deflection starts at the same point of the input vertical signal each time it sweeps.
5. Explain what are the essential components of a CRT?
The essential components of a CRT are electron gun, focussing and accelerating anodes, horizontal and vertical deflection plates, and evacuated glass envelope with phosphorescent screen.
6. For Explain what electron gun assembly is provided in CRT?
The sole function of an electron gun assembly in a CRO is to provide a narrow and sharply focused electron beam with is accelerated towards the phosphor screen.
Working Principle Of Cro
The working principle of a cathode ray oscilloscope is simple enough. It depends on the movement of an electron beam due to the electrostatic force. When an electron beam strikes a phosphor surface, it creates a glowing spot on it. A CRO applies the electrostatic force on the electron beam from two perpendicular directions. That means we apply one force along the X-axis and another along the Y-axis. The spot on the phosphor screen moves due to the effect of these two mutually perpendicular electrostatic forces. It moves to create the required waveform of the input signal.
You May Like: Fsa Warm Ups Grade 5
How Does Cro Measure Voltage And Frequency
The simplest way to measure signal is to set the trigger button to auto that means oscilloscope start to measure the voltage signal by identifying the zero voltage point or peak voltage by itself. As any of these two points identified the oscilloscope triggers and measure the range of the voltage signal.
Measuring Voltage And Time Period
The trace on an oscilloscope screen is a graph of voltage against time.The shape of this graph is determined by the nature of the input signal.
In addition to the properties labelled on the graph, there is frequencywhich is the number of cycles per second.
The diagram shows a sine wave but the properties apply to any signalwith a constantly repeating shape.
- Amplitude is the maximum voltage reached by the signal.It is measured in volts, V.
- Peak voltage is another name for amplitude.
- Peak-peak voltage is twice the peak voltage .When reading an oscilloscope trace it is usual to measure peak-peak voltage.
- Time period is the time taken for the signal to complete one cycle.It is measured in seconds but time periods tend to be short so milliseconds and microseconds are often used.1ms = 0.001s and 1µs = 0.000001s.
- Frequency is the number of cycles per second.It is measured in hertz , but frequencies tend to be high so kilohertz and megahertz are often used.1kHz = 1000Hz and 1MHz = 1000000Hz.
Frequency and time period
Frequency and time period are the inverse of each other:
| frequency = |
| 1 |
| frequency |
The picture shows the trace of an AC signal on an oscilloscope with the controls on these settings:
- Y AMPLIFIER: 2V/cm
- TIMEBASE: 5ms/cm
- Each grid square represents 1cm
Some low cost oscilloscopes have small screens where the grid lines are less than 1cm apart.On these instruments the controls will be marked ‘/div’ instead of ‘/cm’.
Also Check: What Is Elastic Force In Physics