Contrasting Properties Of Acids And Alkalis
Here is a list which contrasts their properties:
- Acids turn blue litmus paper red. Bases turn red litmus paper blue.
- Acids give off H+ ions in water bases give off OH- ions in water.
- Acids generally taste sour due to the sour H+ ion bases taste bitter due to the OH- ion but they may have other tastes depending on the other part of the molecule.
- Bases are usually soapy in nature.
- Acids corrode active metals Bases denature protein.
- Acids have a pH less than 7 Bases have a pH greater than 7
Have You Ever Had Acid Indigestion
Perhaps you have eaten too much pizza and felt very uncomfortable hours later. This feeling is due to excess stomach acid being produced. The discomfort can be dealt with by taking an antacid. The base in the antacid will react with the HCl in the stomach and neutralize it, taking care of that unpleasant feeling.
Limitations Of The Arrhenius Definition
The Arrhenius definitions of acidity and alkalinity are restricted to aqueous solutions and refer to the concentration of the solvated ions. Under this definition, pure H2SO4 or HCl dissolved in toluene are not acidic, despite the fact that both of these acids will donate a proton to toluene. In addition, under the Arrhenius definition, a solution of sodium amide in liquid ammonia is not alkaline, despite the fact that the amide ion will readily deprotonate ammonia. Thus, the Arrhenius definition can only describe acids and bases in an aqueous environment.
Recommended Reading: How Did Geography Influence The Greek Way Of Life
Strong And Weak Acids / Bases
Strong acids / strong bases: acids / bases completely dissociated in aqueous solutions strong acids are able to donate protons to water strong bases are able to accept protons from water
HBr is a strong acid:HBr + H2O Br- + H3O+
There are only a few strong acids / bases in waterMost acids / bases are weak in water weak acids are partially dissociated in water into H3O+ and its conjugate base weak bases are partially dissociated in water into HO- and its conjugate acid
NH3 is a weak base:NH3 + H2O
% dissociation of a weak acid = H
Acid dissociation reaction of an acid HA: HA + H2O Acid dissociation constant Ka: equilibrium constant of the acid dissociation reaction Acids with large values of Ka are stronger than acids with smaller values of Ka
Base dissociation reaction of a base A-: A- + H2O Base dissociation constant Kb: equilibrium constant of the base dissociation reaction
Examples Of Acids And Bases
Ready for a few acid and base examples? Youll be surprised to hear some of these are things you have in your house.
When you think of acids, you might think of solutions that can burn your flesh. However, there are all kinds of acids.
- Citric acid
- Acetic acid
- Carbonic acids
- Nitric acid
Looking for a common household base? Think baking soda. You might find these other bases as well.
- Ammonia hydroxide
- Magnesium hydroxide
- Sodium borate
Also Check: Edgenuity Unit 1 Test Answers
Difference Between Acids And Bases: Key Properties
Acids and bases are everywhere. However, you are most likely to hear those terms used in chemistry. The difference between acids and bases has to do with how they ionize in water. Keep things crystal clear by breaking down the properties of acids vs. bases. See each different substance through real-world examples.
Limitations Of Arrhenius Theory Of Acids And Bases
1. It recognises the dissociation of acids and bases in an aqueous medium only.2. It restricts acids to merely hydrogen-containing compounds and bases to merely hydroxide-containing compounds.
According to Arrhenius concept, carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, etc., are not regarded as acids and \ etc. are not regarded as bases.
Don’t Miss: Is Paris Jackson Biologically Related To Michael Jackson
Difference Between Acid And Base Ppt
Name a few examples of the base.
Sodium hydroxide, calcium carbonate, and potassium oxide are some of the examples of Base.
What are indicators?
Indicators are substances that change the solution or their colour due to changes in the pH level.
What is the taste of base?
Bases have a strong taste and are found in fewer foods than acids. Many bases are slippery to the touch, such as soaps. Bases also modify the colour of indicators.
Hopefully, through this blog that states the difference between acid and base, you are all clear about the topic. Reach out to our Leverage Edu experts and they will guide you in crucial decision making such as stream selection after class 10th.
-
Tags:
Physical Properties Of Acids
- Acids are sour in taste. . The sour taste of most citric fruits is due to the presence of citric acid.
- Acids have the ability to conduct electricity. Aqueous acidic solutions are used as strong electrolytes.
- Acids are corrosive in nature. Should be handled with care otherwise, they can corrode our skin
- Acids are mostly present in liquid or gaseous forms. But we do have solid acids like zeolitic materials.
- Acidic fumes will burn your nose
- Acids would turn litmus paper red
- Acids are colorless with the addition of phenolphthalein
- Acids turn red with the addition of methyl orange
- Acids are identified by shades of red and yellow color with universal indicator solution.
- Most acids can be diluted with water to reduce the intensity of their acidity.
Don’t Miss: Kuta Software Infinite Algebra 2 Solving Inequalities Answers
The Observable Properties Of Acids And Bases
The words acid and alkaline are derived from direct sensory experience.
Acid Property #1: The word acid comes from the Latin word acere, which means “sour.” All acids taste sour. Well known from ancient times were vinegar, sour milk and lemon juice. Aspirin tastes sour if you don’t swallow it fast enough. Other languages derive their word for acid from the meaning of sour. So, in France, we have acide. In Germany, we have säure from saure and in Russia, kislota from kisly.
Base Property #1: The word “base” has a more complex history and its name is not related to taste. All bases taste bitter. For example, mustard is a base. It tastes bitter. Many medicines, because they are bases, taste bitter. This is the reason cough syrups are advertised as having a “great grape taste.” The taste is added in order to cover the bitterness of the active ingredient in cough syrup.
Acid Property #2: Acids make a blue vegetable dye called litmus turn red.
Base Property #2: Bases are substances which will restore the original blue color of litmus after having been reddened by an acid.
Acid Property #3: Acids destroy the chemical properties of bases.
Base Property #3: Bases destroy the chemical properties of acids.
Neutralization is the name for this type of reaction.
Acid Property #4: Acids conduct an electric current.
Base Property #4: Bases conduct an electric current.
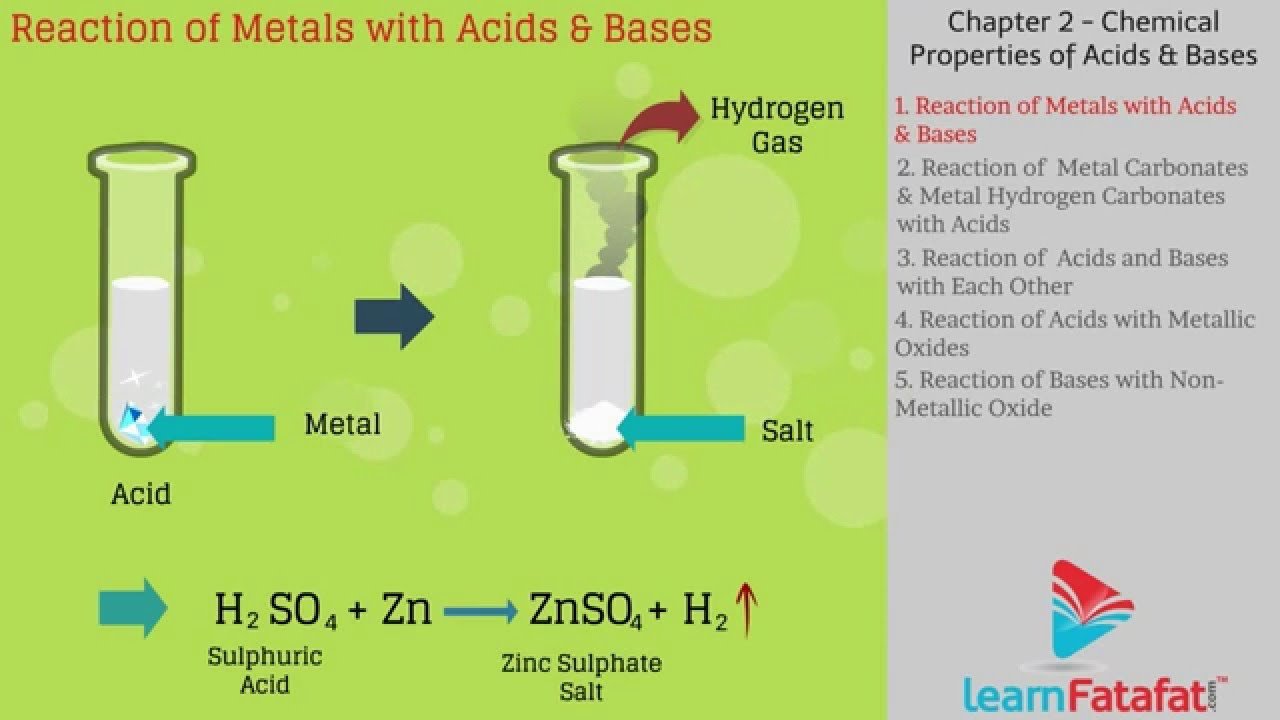
Zn + 2HCl —> ZnCl2 + H2
2HCl + Na2CO3 —> CO2 + H2O + 2NaCl
Some Historical Comments
Ions In Acid / Base Solutions
Aqueous solutions generally consist of some combination of water, acids, bases and salts. These compounds may be partially or fully ionized which means the compound separates into its ions.
For example, in pure water, a small percentage of the water molecules ionize into H3O+ and OH ions.
We will use H+ as a shorthand for H3O+ ions, even though technically H+ ions do not exists by themselves.
Hydronium and hydroxide ions have a love-hate relationship with each other in aqueous solutions. The more H+ ions there are, the less OH ions there, and vice-versa.
You May Like: Who Is The Mother Of Paris Jackson
Chemical Properties Of Bases
Reactions of Bases with Metals
Alkalis react with the metal to produce salt and hydrogen gas. For example reaction of zinc with sodium hydroxide.
NaOH + Zn Na2ZnO2 + H2
The Reaction of Non-metal Oxide with Bases
Non-metal oxides react with bases to produce salt and water. For example the reaction of carbon dioxide and lime water .
CO2 + Ca2 CaCO3 + H2O
The Reaction between Acids and Bases
Acid + Base -> salt + water
This is the reaction of acids and bases with metals.
Reactions between bases and water
The following reaction represents the general reaction between a base and water to produce a conjugate acid and a conjugate base :
B + H2O BH+ + OH-
The equilibrium constant, Kb, for this reaction can be found using the following general equation:
Kb = /
Lewis Theory Of Acids And Bases
In \, G.N. Lewis proposed a more general theory of acids and bases. According to this theory,
A substance that can accept an electron pair to form a coordinate covalent bond with the donor is called acid.
Examples: \ etc.
A substance that can donate a lone pair of electrons to form a coordinate covalent bond with the acceptor is called a base.
Examples: \ etc.
Recommended Reading: Definition Of Similar In Geometry
Acid Strength And Strong Acids
The strength of an acid refers to how readily an acid will lose or donate a proton, oftentimes in solution. A stronger acid more readily ionizes, or dissociates, in a solution than a weaker acid. The six common strong acids are:
- hydrochloric acid
- sulfuric acid
- nitric acid
- perchloric acid
Each of these acids ionize essentially 100% in solution. By definition, a strong acid is one that completely dissociates in water in other words, one mole of the generic strong acid, HA, will yield one mole of H+, one mole of the conjugate base, A, with none of the unprotonated acid HA remaining in solution. By contrast, however, a weak acid, being less willing to donate its proton, will only partially dissociate in solution. At equilibrium, both the acid and the conjugate base will be present, along with a significant amount of the undissociated species, HA.
Litmus Test And Other Reactions
Litmus paper is made from dyes derived from lichens it is water-soluble, meaning it can be fully dissolved in water. Acids turn blue litmus paper red, and bases turn red litmus paper blue. The following video shows how red and blue litmus paper reacts to ammonia, hydrochloric acid, water, and baking soda.
Strong acids have a corrosive effect on metals. They react with most of them to form hydrogen gas. Strong bases have a caustic effect on organic matter.
You May Like: What Is Vo In Physics
Bronsted Lowry Theory Of Acids And Bases
- The Bronsted-Lowry theory defines an acid as a donor of protons.
- A base is defined as a proton acceptor by this theory.
- Bronsted acids undergo dissociation to yield protons and therefore increase the concentration of H+ ions in the solution.
- On the other hand, Bronsted bases accept protons from water to yield hydroxide ions.
- An advantage of the Bronsted-Lowry definition of acids and bases is its ability to explain the acidic or basic nature of ionic species.
- An important limitation of this theory is that it fails to explain how compounds lacking hydrogen exhibit acidic properties, such as BF3 and AlCl3.
What Are The Real
- A combination of acids is used to purify metal surfaces due to the corrosive property of acids.
- Acids are used to etch off metal surfaces like copper for designing propose or for purification
- The neutralization reaction of acid and base is used to generate different types of salt. You can read our article 7 types of salts for more details.
You May Like: Slader Holt Geometry
Definitions Of Acids And Bases
In the Arrhenius theory, acids are defined as substances that dissociate in aqueous solution to give H+ , while bases are defined as substances that dissociate in aqueous solution to give OH .
In 1923 physical chemists Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted in Denmark and Thomas Martin Lowry in England both independently proposed the theory that carries their names. In the BrønstedLowry theory acids and bases are defined by the way they react with each other, which allows for greater generality. The definition is expressed in terms of an equilibrium expression
With an acid, HA, the equation can be written symbolically as:
- HA + }}
The equilibrium sign, , is used because the reaction can occur in both forward and backward directions. The acid, HA, can lose a proton to become its conjugate base, A. The base, B, can accept a proton to become its conjugate acid, HB+. Most acidbase reactions are fast, so the components of the reaction are usually in dynamic equilibrium with each other.
Educators And Parents Sign Up For The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News for Students in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
In the ocean, acids and bases are even more critical. Mollusks in the ocean rely on certain chemicals to build their shells. Sharks rely on a specific pH in water for their hypersensitive noses. As humans produce more carbon dioxide from fossil fuels, some of it ends up in the ocean where it acidifies the water. A more acidic sea means animals have a harder time building their shells.
To know if somethings an acid or a base, scientists use a pH scale. This scale runs from zero to 14. A pH of seven is neutral this is the pH of pure water. Anything with a pH lower than seven is an acid from lemon juice to battery acid. Substances with a pH higher than seven are bases including oven cleaner, bleach and your own blood.
Want to know more? Weve got some stories to get you started:
Study acid-base chemistry with at-home volcanoes: Baking soda volcanoes are a fun demonstration, and with a few tweaks they can be an experiment, too. Readability: 6.4
Explainer: What are acids and bases?: These chemistry terms tell us if a molecule is more likely to give up a proton or pick up a new one. Readability: 7.5
Tongues taste water by sensing sour: Water doesnt taste like much, but our tongues need to detect it somehow. They may do it by sensing acid, a new study shows. Readability: 6.7
Explore more
Recommended Reading: Theory Of Everything 2 All Coins
Strong And Weak Acids
Let us consider the strengths of acids first. A small number of acids ionize completely in aqueous solution. For example, when HCl dissolves in water, every molecule of HCl separates into a hydronium ion and a chloride ion:
| Ca2 |
| HClO4 |
By analogy, a strong baseA base that is 100% ionized in aqueous solution. is a compound that is essentially 100% ionized in aqueous solution. As with acids, there are only a few strong bases, which are also listed in Table 10.2 “Strong Acids and Bases “.
If an acid is not listed in Table 10.2 “Strong Acids and Bases “, it is likely a weak acidAn acid that is less than 100% ionized in aqueous solution., which is a compound that is not 100% ionized in aqueous solution. Similarly, a weak baseA base that is less than 100% ionized in aqueous solution. is a compound that is not 100% ionized in aqueous solution. For example, acetic acid is a weak acid. The ionization reaction for acetic acid is as follows:
Depending on the concentration of HC2H3O2, the ionization reaction may occur only for 1%5% of the acetic acid molecules.
What Is An Acid

Acids and bases can be described via The Bronsted Lowry Theory which models acids as substances that donate protons , and bases as substances that accept protons. This shall be explored in greater depth in later posts.
Acids can donate single protons such as HCL, or multiple protons such as H2SO4 , H3PO4 .
This video will introduce you to the Bronsted Lowry Theory which will be the main mode of describing acids.
Also Check: Hawkes Learning College Algebra Answers
What Is The Real
- In real life, the foods that we consume like citrus fruits, milk, vinegar, etc. get their characteristic sour taste from the acids.
- Acidic juices in our stomach are used to break down complex food into simpler molecules.
- Acid rain is said to be harmful due to the corrosive nature of the acids which are mixed with water.
What Are Acids And Bases
Acids are chemical substances which are characterized by a sour taste in an aqueous medium. They have the tendency to turn blue litmus red. On the other hand, bases are chemical substances which are characterized by a bitter taste and are slippery to the touch. Some bases are soluble in water while others are not.
Water soluble bases are known as alkalis. They have the tendency to turn red litmus blue. Acids and bases react with a wide range of chemical compounds to form salts. Some chemical reactions of acids and bases are:
Recommended Reading: Bridge To Algebra Answers
Neutralization Of Acid And Base
The reaction between an acid and a base invariably gives salt and water and is called neutralization. In a neutralization reaction, one H+ ion of acid is neutralized by one OH ion is base. When all the H+ ions in the acidic solution are neutralized by the same number of OH ions of basic solution, it is called complete neutralization. The relative amounts of acid and base required for complete neutralization depends upon the total number of H+ and OH ions produced by the respective acid and base.
Differences In Uses Between Acid And Base
Uses of Acids
Acids are used for a plethora of things such as:
- It is used for cleaning households.
- It is used as a metal dissolver.
- Its used for industrial purposes, for example, sulfuric acid and nitric acid are both commonly used in paints, dyes, fertilizers, and explosives.
- They are used to make batteries for flashlights and cars.
- In the chemical industry, acids are used as neutralizers in the production of salts.
- They are used to ward off rust and corrosion from metals, by means of a technique termed pickling.
Uses of Bases
Bases are used for a plethora of things such as:
- Bases like Sodium hydroxide is used in manufacturing soap, synthetic fiber rayon and paper.
- Bases are also used in manufacturing some medicines and petroleum-refining, in cleaning sinks, ovens and drains.
- They are used in toothpaste, fire extinguisher, and baking soda.
- Bases like Calcium hydroxide is used in the manufacture of bleaching powder. It is mixed with water and sand to create mortar that is used in the construction of buildings.
- They are also used to clean grease stains from clothes.
Read about the greatest Unsolved Mysteries in Science
Don’t Miss: Span Meaning Linear Algebra