Study Notes: Early Schools Of Thought: Structuralism And Functionalism
- Psychology is the study of human mind and behavior.
- Psychology sprung out of philosophy and biology.
- Wilhelm Wundt founded the first experimental psychology lab. This lead to psychology becoming its very own discipline.
- Wilhelm Wundt focused on the structures that make up the human mind through what he called Introspection. He would evaluate people based on thoughts and feelings and from what I understand he felt if one were properly trained they could diagnose mental illness via analyzing the subjects feelings and emotions. This was a very subjective approach.
Early Schools of Thought
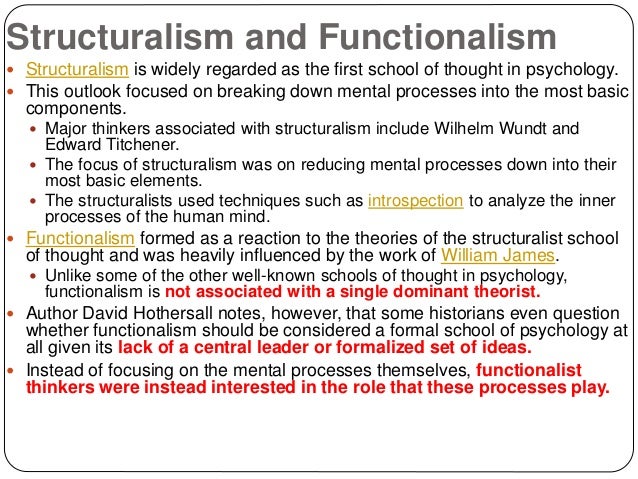
Structuralism was the first school of thought in psychology. The idea was to break down the human mind into its most basic elements. Through the use of Introspection researchers tried to understand the basic components of consciousnesses. As mentioned above, Wilhelm Wundt founded the first psychology lab and is credited with being the founder of Structuralism.
PROS:
CONS: This method was not around very long due to its basis in subjective introspection. There were not observable variables.
Why Are There So Many Schools Of Psychology
When psychology first emerged as a science separate from biology and philosophy, the debate over how to describe and explain the human mind and behavior began. The different schools of psychology represent the major theories within psychology.
With that said, let the drama unfold. Structuralism. Wundts ideas formed the basis of the first school of thought in psychology, known as structuralism. In reality, though, it was one of Wundts students, Edward B. Tichener, who formally established this psychological school of thought.
The early pioneers of psychology established it as a new and independent science. Wundt, Freud, Titchener, Wertheimer, Skinner, James and Watson proposed four seminal schools of thought, encompassing both experiments in laboratory and field, and also the development of clinical therapies. Updated: 05/30/2020
The Behaviorist School Of Thought In Psychology
Behaviorism became a dominant school of thought during the 1950s. It was based upon the work of thinkers such as:
Behaviorism suggests that all behavior can be explained by environmental causes rather than by internal forces. Behaviorism is focused on observable behavior. Theories of learning including classical conditioning and operant conditioning were the focus of a great deal of research.
The behavioral school of psychology had a significant influence on the course of psychology, and many of the ideas and techniques that emerged from this school of thought are still widely used today. Behavioral training, token economies, aversion therapy, and other techniques are frequently used in psychotherapy and behavior modification programs.
Don’t Miss: Ap Psychology Exam Tips
What Do You Need To Know About Becoming A Psychology Major
Psychology is a competency-based specialty that can prepare students for graduate programs in psychology, education, law, medicine, and business. It is a highly adaptable specialty and applicable to many professions. Students learn basic methods of psychological research, reasoning, and problem solving.
Criticism For The Theory

This theory was criticized with regards to several key factors for one, the subject that it chose to studythe consciousness. It was said that consciousness cannot be studied under controlled experimentation because it is a subjective matter, which cannot be observed and thereby measured. And secondly, the tool that was used to measure the consciousness, i.e. introspection, is not a scientific method, and therefore, even after taking into account how strict the guidelines are used, it is still not a reliable method as it can yield different results based on the subject.
You May Like: Ccl4 Electron Pair Geometry
Behaviorism And Psychoanalytic Ideas Of Psychology
Psychology evolved in the 1800s from philosophy and physiology because Wilhem Wundt argued for it to be in its own discipline. He established the first psychology lab in America and after that schools sprang up all around the country. As more schools were established new ways of thinking were introduced to psychology. The first two introduced were functionalism and structuralism. These two focused on consciousness in different way, they somewhat battled for attention. After these ideas died out
What Are Some Of The Major Schools Of Thought In Psychology
Six great schools of functionalist psychology. Functionalism is the most influential of all theories in modern psychology. Gestaltism. According to Gestalt psychologists, the human mind works by interpreting data using various laws, rules or organizing principles and creating a coherent whole from partial information. Psychoanalysis. Behaviorism. Humanistic psychology.
Don’t Miss: Mcdougal Littel Geometry Answers
What Branch Does Psychology Belong To
Psychology as a separate field is a true branch of evidence-based medicine and peer-reviewed research. Like all other branches of medicine, use the scientific method to learn about the various ailments of its kind and how they can be relieved or cured. It is also an area that has strong links to the more complex areas of medicine.
What Was The First Theory Of Modern Psychology
Theory Contributions for Modern Psychology Development. The first scientific and systematic school of thought, emerged from Wundts work, was structuralism. It focused on the structure or the basic elements mind, consciousness, sensations and ideas. The procedure used in structuralism was introspection.
Also Check: What Does Span Mean Linear Algebra
Critically Compare How The Nature
Critically compare how the nature-nurture debate has been addressed by three different researchers or schools or thought in Psychology and/or Philosophy. At least one of the researchers/schools must have been active before the 20th century.Theories whose fundamental understanding of human behaviour focuses on characteristics in which, we are born with like our genetic make-up, stable personality traits, and physical predispositions are Naturists. In contrast theorists who are on the nurture side
Psychology In Everyday Life: How To Effectively Learn And Remember
One way that the findings of psychological research may be particularly helpful to you is in terms of improving your learning and study skills. Psychological research has provided a substantial amount of knowledge about the principles of learning and memory. This information can help you do better in this and other courses, and can also help you better learn new concepts and techniques in other areas of your life. The most important thing you can learn in college is how to better study, learn, and remember. These skills will help you throughout your life, as you learn new jobs and take on other responsibilities. There are substantial individual differences in learning and memory, such that some people learn faster than others. But even if it takes you longer to learn than you think it should, the extra time you put into studying is well worth the effort. And you can learn to learnlearning to study effectively and to remember information is just like learning any other skill, such as playing a sport or a video game.
Don’t Miss: Beth Thomas Therapy
What Psychologist Coined The Term Structuralism
The term structuralism was first coined by psychologist Edward B. Tyhener. Structuralism by definition refers to the different building blocks that make up culture, society and linguistics. Great Anthropologists: Claude Levi Strauss emphasized structuralism and mainly studied linguistics as the fundamental building blocks of culture.
Behaviourism And The Question Of Free Will
The most famous behaviourist was Burrhus Frederick Skinner , who expanded the principles of behaviourism and also brought them to the attention of the public at large. Skinner used the ideas of stimulus and response, along with the application of rewards or reinforcements, to train pigeons and other animals. And he used the general principles of behaviourism to develop theories about how best to teach children and how to create societies that were peaceful and productive. Skinner even developed a method for studying thoughts and feelings using the behaviourist approach .
Also Check: Im Kendall Hunt Answer Key
Structuralism: Introspection And The Awareness Of Subjective Experience
Perhaps the best known of the structuralists was Edward Bradford Titchener . Titchener was a student of Wundts who came to the United States in the late 1800s and founded a laboratory at Cornell University . . Perhaps he was ahead of his time Brenda Milner did not open the Montreal Neurological Institute until 1950.) In his research using introspection, Titchener and his students claimed to have identified more than 40,000 sensations, including those relating to vision, hearing, and taste. An important aspect of the structuralist approach was that it was rigorous and scientific. The research marked the beginning of psychology as a science, because it demonstrated that mental events could be quantified. But the structuralists also discovered the limitations of introspection. Even highly trained research participants were often unable to report on their subjective experiences. When the participants were asked to do simple math problems, they could easily do them, but they could not easily answer how they did them. Thus the structuralists were the first to realize the importance of unconscious processesthat many important aspects of human psychology occur outside our conscious awareness, and that psychologists cannot expect research participants to be able to accurately report on all of their experiences.
Introspection: Structuralism’s Main Technique
Introspection is the process by which a person looks inward at their own mental processes to gain insight into how they work. It is the self-observation of one’s consciousness.
Wundtâs introspection was not a casual affair, but a highly practiced form of self-examination. He trained psychology students to make observations that were biased by personal interpretation or previous experience, and used the results to develop a theory of conscious thought.
Highly trained assistants would be given a stimulus such as a ticking metronome and would reflect on the experience. They would report what the stimulus made them think and feel. The same stimulus, physical surroundings and instructions were given to each person.
Titchener trained his students to become skilled at trained introspection, and to report only the sensations as they were experienced without reliance on âmeaning wordsâ, which he called a stimulus error.
Using this approach, Titchenerâs students reported various visual, auditory, tactile, etc experiences: In An Outline of Psychology , he reported over 44,000 elements of sensation, including 32,820 Visual, 11,600 Auditory, and 4 Taste.
Recommended Reading: Cpm Algebra 2 Answers
What Similarities Do Structuralism And Functionalism Share
Structuralism and functionalism are the first two schools of thought to emerge in psychology during the 19th century. In 1906, Mary Whiton Calkins, the first female president of the American Psychological Association, published an article in the Psychological Review arguing that structuralism and functionalism were not very different ways as both schools of thought were primarily concerned with consciousness of thought.
Structuralism was the first school of thought to develop in the field of psychology. The theoretical term was coined by Edward Titchener, a student of Wilhelm Wundt. Wundt is credited with opening the first structuralist psychology lab. The school of thought behind structuralism primarily deals with breaking down mental processes into the most basic components. About.com notes that structuralist theory did not last very far beyond Titcheners death, as it was widely criticized for its subjectivity. Structuralism is credited with helping to develop many of the ideas used in experimental psychology. Functionalism emerged soon after structuralism, and it is widely associated with William James and Charles Darwin. Functionalism sought to understand the elements of behavior and was more focused on the process of breaking down consciousness into its basic parts, rather than the parts themselves like structuralism. Functionalism is credited with influencing later schools of thought of behaviorism and applied psychology.
What Should I Major In To Become A School Psychologist
In general, prospective school psychologists must first earn a bachelor’s degree in school psychology, counseling psychology, educational psychology, or general psychology. Regardless of their specialization, future school psychologists must take courses in each of these areas, as well as courses such as developmental psychology.
Recommended Reading: Cool Math For Kids Happy Wheels
What Do You Look For In A College
Traits that universities look for in students. While you may be looking for the qualities that certain colleges look for, for example: B. Ivy League colleges, there are a few characteristics that you will come across time and again on college websites: Leadership. Engagement. Work ethic. Public service. Opening.
Six Major Schools Of Thought In Psychology
DAVID KOENIG
Every academic discipline, from literature and history to sociology and theology, has competing theories or schools of thought: perspectives from which to study the subject. Psychology, the study of the mind, has hundreds of theories and sub-theories, but the six main schools of thought are often the foundation for those new to the world of psychology.
Explore this article
Also Check: Exponential Growth And Decay Common Core Algebra 1 Homework Answers
What Was Structuralism
Structuralism emerged as the first school of thought in psychology. Wilhelm Wundt, the founder of the first experimental psychology lab, advocated some of the ideas associated with the structuralist school.
Structuralism was the first school of psychology and focused on breaking down mental processes into the most basic components. Researchers tried to understand the basic elements of consciousness using a method known as introspection.
One of Wundt’s students, Edward B. Titchener, would later go on to formally establish and name structuralism, although he broke away from many of Wundt’s ideas and at times even misrepresented the teachings of his mentor. Wundt’s theories tended to be much more holistic than the ideas that Titchener later introduced in the United States.
Other Types Of Studies

Surveys are used in psychology for the purpose of measuring attitudes and traits, monitoring changes in mood, and checking the validity of experimental manipulations . Psychologists have commonly used paper-and-pencil surveys. However, surveys are also conducted over the phone or through e-mail. Web-based surveys are increasingly used to conveniently reach many subjects.
Exploratory data analysis refers to a variety of practices that researchers use to reduce a great many variables to a small number overarching factors. In Peirce’s three modes of inference, exploratory data analysis corresponds to abduction.Meta-analysis is the technique research psychologists use to integrate results from many studies of the same variables and arriving at a grand average of the findings.
You May Like: Homework 2 Segment Addition Postulate
What Is A Niche College
A niche is where students choose their university. More than 50 percent of college high school students use the university’s research niche. Universities can apply to their school for free to manage their niche presence and upgrade to a premium profile to showcase their school and motivate next steps: apply, visit, etc.
What Is The Education Path Of A Psychologist
The path to becoming a psychologist generally begins with a bachelor’s degree in psychology, in which students learn the basics. Then you have to graduate. While some graduate programs accept applicants with bachelor’s degrees in other disciplines, most encourage students to earn a bachelor’s degree in psychology.
Don’t Miss: Child Of Rage Brother Jonathan Now
Why Is Psychology So Important
Essentially, psychology helps people in large part because it can explain why people act the way they do. With this kind of professional insight, a psychologist can help people improve their decision making, stress management and behavior based on understanding past behavior to better predict future behavior.
What Are The Main Branches Of Social Psychology
A social psychologist studies group behavior, social perception, non-verbal behavior, conformity, aggression, prejudice, and leadership. Social perception and interaction are considered important for understanding social behavior. Other industries include military, consumer, educational, intercultural, and environmental psychology.
Read Also: How Do You Find Displacement
An Overview Of Wundt And His Work
Wilhelm Wundtpsychologist,
Wilhelm Wundt was trained as a physiologist, with extensive knowledge on anatomy and physiology of both humans and animals. This formal training is important because it heavily influenced the attitude and process of his later psychological research, which mainly focused on an intensive study of consciousness by way of reaction time, sensory processes and perception.
However, his writings were as diverse as they were extensive. In the course of his researches he covered a broad array of physiology including that of both humans and animals. He also studied poisons, vision, spiritualism, hypnotism, history, and politics. Though while these subjects seem, and in some cases are independent, even here we can detect that they were all directly related to the human being and human experience, and thus related to psychology. Which I believe we can assume was his own belief as well, since he did not consider himself a multidisciplinary scholar and thinker.
As a teacher he personally trained 186 graduate students, 116 of whom were trained in psychology. So directly from him, his laboratory, and his revolutionary work he influenced and even spawned an entire generation of psychologists, and even psychology as an intellectual discipline.
What Is The School Of Thought
A school of thought or intellectual tradition is the point of view of a group of people who share a common feature of opinion or point of view of philosophy, discipline, faith, social movement, economics, cultural movement or artistic movement. Schools are often formed according to their currency and are therefore divided into new and old schools.
Read Also: Parallax Error Chemistry
Wilhelm Wundt & Structuralism
The school of psychology founded by Wundt eventually became known as structuralism, and is the first ever school of psychology. While it was Wilhelm Wundt himself who established the founding principles, theories, and experimental protocols that became structuralism, it was his student Edward Titchener who expanded upon Wundts foundation, developing the sophistication of his ideas and bringing them to a wider audience.
A core idea of structuralism is that the mind was a sum total of an individuals life experiences, and that if a psychologist was able to deconstruct the mind/consciousness into its constituent elements then each individuals unique processes of reasoning and decision making could be understood.
This theory seems to identify consciousness or inner experience almost as some sort of machine with specific parts with different functions that should respond to to stimuli in specific, predetermined ways. And that once one aspect of the human mind was understood, its relationship to various other areas of the psyche could be determined also. Then if the basic elements of mind were understood, along with the rules with how they interacted, then we could theoretically understand or deconstruct every thought, impulse, action or behavior than an individual could take by understanding the parts and their relationship to the whole.