What Is The Valley Of A River
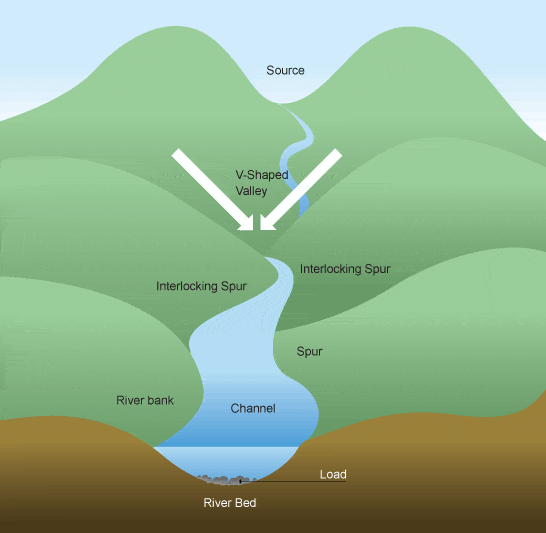
Valleys are defined as the low lying areas of land between hills or mountains normally with a river or some sort of water course running through them. River valleys are commonly V-shaped narrow and steeper near to the rivers source but become U-shaped wide and flatter as the river works its way down to sea level.
How To Draw Contour Lines Manually
You can easily generate contour lines with the click of a button in CAD or GIS software. But what if you want to draw it by hand?
First, you have to choose a contour interval. For example, were going to use a contour interval of 10 meters. So this means that there will be a contour every 10 meters.
Between transition points of ten , add markers where to draw lines. Basically, draw or interpolate between the lines.
Now that we have points to connect, lets draw smooth contour lines for each interval. Essentially, we are connecting the points with lines.
And there we have it.
What About Ridges And Gullies
Over time, gullies form through erosion of running water on hillsides. A consequence of two eroded gullies is a spur at the center on the face of a hillside that sticks out. Both gullies and spurs run from ridgelines to valley bottoms.
Gullies are characterized by U or V shaped contour lines with their closed-end pointing towards higher elevation. On the other hand, spur contour lines point toward lower elevation.
In 2D, these valley landscape features are a bit more difficult to see. But its key to remember how ridges point downslope and gullies point upslope.
Recommended Reading: What Is Theoretical Orientation In Psychology
What Do We Use Contour Lines For
In our example, contour lines represented constant elevation and showed the topography of the landscape.
But meteorology , magnetism and even drive-time also use contours for different purposes.
The closeness of contours indicates slope. Irregular contours mean rugged terrain. Its rare in nature for contours to cross. But they can for overhangs and cliffs.
What are some other types of contours youve seen in nature?
Spur In Geography Topic

Don’t Miss: Can I Do Masters In Psychology After Engineering
Tips Tricks And Common Mistakessome Tips Tricks And Common Mistakes To Avoid When Reading Topographic Maps
The real art of map reading comes with interpreting how individual landscape features fit together in the terrain: saddles connect ridges to knolls to cliffs gullies form into rivers and valleys. Interpreting how contour lines fit together helps understand the lay of the land and be able to navigate through it.
The big picture
1 hill, 2 valley, 3 ridge, 4 saddle, 5 depression, 6 gully, 7 spur, 8 cliff, 9 cut, 10 fill
This image describes a landscape by contours. In words:Running east to west across the complex landmass is a ridgeline. A ridgeline is a line of high ground, usually with changes in elevation along its top and low ground on all sides. The changes in elevation are the three hilltops and two saddles along the ridgeline. From the top of each hill, there is lower ground in all directions. The saddles have lower ground in two directions and high ground in the opposite two directions. The contour lines of each saddle form half an hourglass shape. Because of the difference in size of the higher ground on the two opposite sides of a saddle, a full hourglass shape of a saddle may not be apparent.
There are four prominent ridges. A ridge is on each end of the ridgeline, and two ridges extend south from the ridgeline. All of the ridges have lower ground in three directions and higher ground in one direction. The closed ends of the Us formed by the contour lines point away from higher ground.
Spur
Gully
Knoll
Depression
What Is A Spur In Geography
In geography, a spur is a piece of land jutting into a river or stream or a ridge descending from mountains into a valley. Spurs are formed from erosion over time and frequently divide tributaries or valleys.
Types of spurs include interlocking spurs and truncated spurs. Interlocking spurs are alternating spurs often formed near the upper part of a river or stream where vertical erosion impacts the flow of water. In this situation, water flows in one direction until vertical erosion pushes it toward the opposite direction. As the flow switches back and forth, spurs form on alternating sides of the river or stream. Truncated spurs are interlocking spurs affected by glaciation. In a river valley subject to glaciation, the direct movement of the glacier removes the tips of the spurs, reducing the amount of land protruding into the river.
Read Also: Kuta Software Infinite Geometry Naming Angles Answers
What Is A Spur Map Reading
a : a projecting root or branch of a tree, shrub, or vine. b : a stiff sharp spine especially : one on a cock’s leg. : a gaff for a gamecock. c : a hollow projecting appendage of a corolla or calyx d : bone spur.
Whats the difference between ridge and spur?A ridge is a landform feature characterized by a continuous elevational crest with sloping sides. Arête is a narrow ridge formed by glacial erosion. A spur is a lateral ridge projecting from the mountain or the main ridge crest.
What does a spur look like on a map?
Spur: A spur is a short, continuous sloping line of higher ground, normally jutting out from the side of a ridge. A spur is often formed by two roughly parallel streams cutting draws down the side of a ridge. The ground will slope down in three directions and up in one.
What is a spur ridge?
A small ridge which extends finger-like from a main ridge.
What is a spur of land?
A spur is a long, gently-sloping ‘tongue’ of ground that runs down from a hill to lower ground. Spurs often provide access to and from the high ground, for walkers, for roads, etc.
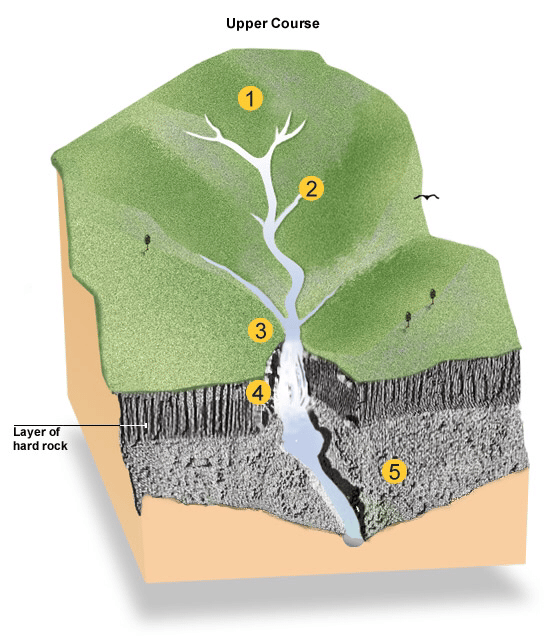
Why Are Waterfalls In The Upper Course
In the upper course of a river gradients are steep and river channels are narrow. Vertical erosion is greatest in the upper course of a river. As the river or stream wears away the weak rocks they travel across the surface of stronger rocks. These more resistant rocks become the capstones to waterfalls. See also how much water will 10 inches of snow melt down to
You May Like: How To Do Math Problems
Can A Bone Spur Go Away Without Surgery
Bone spurs will not go away with alternative treatments, but it is possible that certain treatments can help to manage any pain associated with bone spurs compressing on spinal nerves without involving surgery.
What is the origin of the word Spur?
Origin of the word. The word spur has a lengthy European history. In Old English , spura or spora was used to indicate the metal implement worn on the heel and used to goad a horse . This was related to the verb spurnan meaning to kick.
What Is The Starting Point Of A River Called
The place where a river begins is called its source. River sources are also called headwaters. Rivers often get their water from many tributaries or smaller streams that join together. The tributary that started the farthest distance from the rivers end would be considered the source or headwaters.
Don’t Miss: How The Mind Works Psychology
What Are The Height Lines On A Map Called
Contour lines are added to a map to show height and gradient. On OS maps they are shown as thin orange or brown lines some of which have the land height written on them. The lines join areas of equal height: Contour lines that are close together show land that increases or decreases in height quickly.
What Is A Spur In Mountains
What is a spur of land?A spur is a long, gently-sloping ‘tongue’ of ground that runs down from a hill to lower ground. Spurs often provide access to and from the high ground, for walkers, for roads, etc.
What is a spur in a mountain?
spur mountain wicklow geography A spur is a long, gently-sloping ‘tongue’ of ground that runs down from a hill to lower ground. Spurs often provide access to and from the high ground, for walkers, for roads, etc.
What is called spur?
a : a projecting root or branch of a tree, shrub, or vine. b : a stiff sharp spine especially : one on a cock’s leg. : a gaff for a gamecock. c : a hollow projecting appendage of a corolla or calyx d : bone spur.
What is a river valley and spur?
A spur is formed between two river valleys. In the case of a river valley, the greatest height is to the outer side and the land sinks down towards the inner side, where the riverbed is. In the case of a spur, the greatest height is to the inner side and the land sinks down towards the outer side of the spur.
Don’t Miss: Chapter 5 Test Algebra 1
Why Do Contour Lines Never Cross
Its unlikely that contours cross, but sometimes they do. When the terrain is an overhang or cliff, contour lines will cross or touch.
The cliffs in Látrabjarg, Iceland are up to 440 meters tall. When you generate 100-meter contours, they are very close to converging.
In 3D, you can see how steep these cliffs are. So if these contours did cross, its very likely an overhang. Or it could be an error in the program.
If you use your imagination, picture an overhang where the terrain hangs outward. This would be a rare exception when two contours that cross.
How Is A Spur Formed In Geography
Spurs and Interlocking Spurs. Spurs and interlocking spurs are features found in the upper reaches of river valleys. They are erosional features meaning that they are formed by water flowing over the land and eroding it as it moves. Imagine two gently sloping hillsides forming the sides of a small valley.
Read Also: Khan Academy High School Geometry
What Does Hanging Valley Mean In Geography
A hanging valley is a smaller side valley left hanging above the main U-shaped valley formed by a tributary glacier. A waterfall can often be seen. During glaciation the smaller side valley contains less ice than the main glacial valley, which is why it is not as deeply eroded.
What is the difference between a draw and a valley?
The area of low ground itself is the draw, and it is defined by the spurs surrounding it. Draws are similar to valleys on a smaller scale however, while valleys are by nature parallel to a ridgeline, a draw is perpendicular to the ridge, and rises with the surrounding ground, disappearing up-slope.
What does the name Spur mean?
Define spur. spur synonyms, spur pronunciation, spur translation, English dictionary definition of spur. n. 1. A short spike or spiked wheel that attaches to the heel of a riders boot and is used to urge a horse forward. 2. An incentive: a spur to action. 3.
Common Terrain Featuresunderstanding How Common Terrain Features Are Depicted On Topographic Maps
All terrain features are derived from a complex landmass known as a ridgeline, not to be confused with a ridge.
The US Army states that A ridgeline is a line of high ground, usually with changes in elevation along its top and low ground on all sides from which a total of 10 natural or constructed terrain features are classified.Army, U. S. Map Reading and Land Navigation. Washington, DC, fm: 3-25. By comparison, a ridge is a sloping line of high ground.
Major terrain features include hills, saddles, gullies, ridges, and depressions, and they each have characteristic contour lines that make it easy to pick them out in the landscape.
- Hills, peaks, knolls, mountains: A hill, peak, knoll or mountain is an area of high ground. From a hilltop, the ground slopes down in all directions. A hill is shown on a map by contour lines forming concentric circles. The inside of the smallest closed circle is the hilltop.
- Hill = an area of high ground generally, a smaller and rounder than a mountain, and less steep.
- Knoll = small, rounded natural hill.
- Mountain = a very tall hill, generally with a minimum size of 600m, but varies around the world.
- Peak = a mountain with a pointed top.
- Munro = a Scottish mountain taller than 3,000 feet .
Closed contour loops represent hills or bumps along the ridgeline.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Six Essential Elements Of Geography
How Do I Know If I Have A Ring Or Radial Circuit
Undo the Live terminal and remove the two red wires now using a multi meter switch it to OHMS and place one of the leads on each of the red wires or use a continuity tester the meter should read Zero or very low resistance some meters will emit a bleep also this means that there is a circuit there and that it See also why cant you see stars on the moon
What Is A Spur In Rivers
What do you mean by spurs?1a : a pointed device secured to a rider’s heel and used to urge on the horse. b spurs plural : recognition and reward for achievement won his academic spurs as the holder of a chair in a university James Mountford. 2 : a goad to action : stimulus.
What is River Valley?
A river valley is a valley formed by flowing water.
What is a spur in geography?
A spur is a lateral ridge or tongue of land descending from a hill, mountain or main crest of a ridge.
What is spur in river?
Spurs are river engineering elements used to protect river banks from erosion and to concentrate flow to the river axis. Today, spurs are also employed for promoting environmental conditions along a river bank.
Read Also: Algebra And Geometry Practice Problems
What Is A Spur On A Contour Map
A spur is formed between two river valleys. In the case of a river valley the greatest height is to the outer side and the land sinks down towards the inner side where the riverbed is. In the case of a spur the greatest height is to the inner side and the land sinks down towards the outer side of the spur.
Subtle Featuresrecognising Subtle Features On Topographic Maps
There are subtleties to map reading that take time to develop. Some common things to watch out for include:
- Implied knoll: A bump or small hill that is too small to generate its own closed loop contour. Occurs in places where two ridge lines diverge and converge or on the top of a hill where the contour lines are furthest apart.
- Implied saddle: The opposite of an implied knoll. An implied saddle is a saddle that is not formed enough to have two parallel contours cross the ridgeline and connect.
- Minor gully: A dent in the side of a slope or ridge often too high for a proper water course to form.
- Minor spur or outcrop: a bump on the side of a ridge or slope thats too localised or flat to form a proper spur.
References
Also Check: What Is Red Shift In Physics
Choose The Right Synonym For Spur
Noun
motive, impulse, incentive, inducement, spur, goad mean a stimulus to action. motive implies an emotion or desire operating on the will and causing it to act. a motive for the crime impulse suggests a driving power arising from personal temperament or constitution. buying on impulseincentive applies to an external influence inciting to action. a bonus was offered as an incentiveinducement suggests a motive prompted by the deliberate enticements or allurements of another. offered a watch as an inducement to subscribe spur applies to a motive that stimulates the faculties or increases energy or ardor. fear was a spur to action goad suggests a motive that keeps one going against one’s will or desire. thought insecurity a goad to worker efficiency
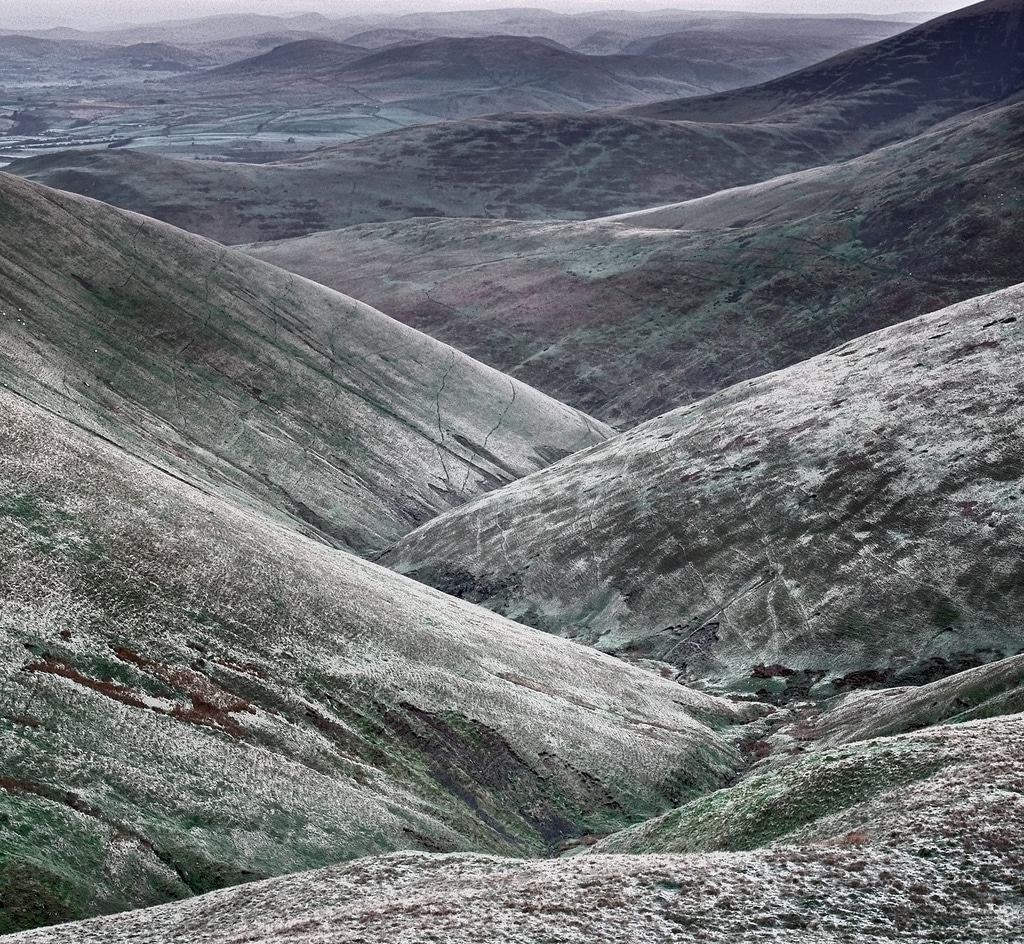
Landforms In The Upper Course Of A River
The diagram below shows the typical characteristics of the upper course of a river valley.
The characteristics of a v-shaped valley
Typical features of the upper course of a river:
Landforms and processes in the upper stages of a river
Cauldron Snout on the River Tees. Vertical erosion has led to the formation of this landform.
Also Check: How To Solve Any Organic Chemistry Reactions
Understanding How Elevation And Slope Are Depicted On Topographic Maps
Elevation and slope are the two elements that determine how landforms physically appear and connect.
ElevationThe contour interval the elevation between contours is the vertical distance between adjacent contour lines. On 1:25,000 maps usually used by bushwalkers, contours are either 10 or 20 m apart.
For measuring between contour lines see here.
Slope The rate of rise or fall of a terrain feature is known as its slope. The speed at which a bushwalking group can move is affected by the slope of the ground or terrain features. This slope can be determined from the map by studying the contour linesthe closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope the farther apart the contour lines, the gentler the slope. Totally flat ground has no contour lines.
Four types of slopes that concern bushwalkers are gentle, steep, concave, and convex.
Are There Contour Lines Mountains Or Depressions
When you have a closed contour like the one below, this means there is a hill/mountain or depression.
You dont really know unless there is a label on the contour line. In the example below, weve added labels and it should be clear that its a depression.
And this isnt just any depression. This is the massive meteor crater that struck Arizona a long time ago.
On some maps, cartographers use teeth marks or hachures for depressions at craters or volcanoes because it marks the elevation going up or down.
READ MORE:A Topographic Profile of Arizonas Massive Meteor Crater
Don’t Miss: Why Do Americans Stink At Math