How The Brain Takes Out Its Trash While We Sleep
In 2013, layers were peeled back from two interrelated mysteries: the function of sleep, and how the brain removes its waste byproducts.
While its been known for some time that the brain doesnt directly use the bodys lymphatic system to dump its toxic waste, the mechanism that it does use wasnt identified until 2012. The research team that made this discovery was led by University of Rochester neurosurgeon, Maiken Nedergaard, who dubbed the brains waste-removal mechanism the glymphatic system.
The glymphatic system relies on cerebrospinal fluid to flush out neurotoxins via pathways separate from the lymphatic system. Among the toxins that are flushed is beta amyloid, a protein that’s found in clumps in the brains of Alzheimers sufferers.
In 2013, Nedergaards research team followed up on this discovery by identifying hidden caves that open in the brain while we sleep, allowing cerebrospinal fluid to flush out neurotoxins through the spinal column.
The implications of this research cant be overstated: failing to get enough sleep isnt just a bad idea for all of the reasons we already know, but over time it could also lead to neurological disorders like Alzheimers. If the studys findings are accurate, our brains need sleep to remove waste byproducts like beta amyloid that eventually become brain killers.
The study was published in the journal, Science.
The Two Hemispheres Of Our Brain
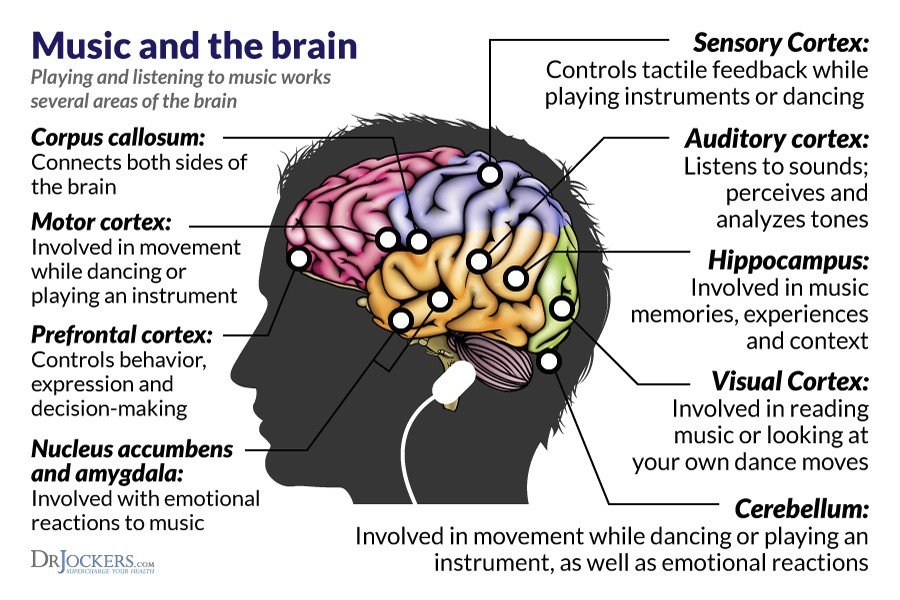
Our brain is divided into 2 halves, or hemispheres, that are connected to each other by the corpus callosum. These two hemispheres control the motion in and receive sensory inputs from the opposite side of our body. In other words, the left hemisphere controls the right side of our body and also receives sensory inputs from the right side of our body.
How Memories Are Stored In The Brain
While memories are usually described in terms of mental concepts, such as single packages of personal experience or specific facts, they are ultimately reducible to the workings and characteristics of the ever-firing cells of the brain. Scientists have narrowed down regions of the brain that are key to memory and developed an increasingly detailed understanding of the material form of these mental phenomena.
Also Check: Laws Of Exponents Worksheets 8th Grade
Recovery In The Addicted Brain
The more you use drugs, the more dependent your brain becomes on them. This makes it harder to recover from drug addiction.
When you stop taking drugs, your brain has to re-adjust to functioning without the drug. It will eventually turn the volume back up and allow you to feel natural pleasure again, but this will take time. In the first weeks or months of recovery, many people feel sad, hostile, restless or irritable.
Some studies have shown that meditation can help naturally increase the brains dopamine levels in recovery. For example, a 2002 study found that meditation boosted participants dopamine levels by as much as 65 percent.
With or without meditation, the addicted brain should adjust in weeks to months of recovery. Still, you may always struggle with cravings and triggers. Cravings should weaken over time, but the brain will always remember the pleasurable high feeling you got from the drug.
Addiction makes changes to a users brain, and some may be permanent. This is why its so dangerous for an addict to use again if even just one more time.
The Brain And The Ap Psychology Exam

The brain is the basis for the entire course, so you should anticipate seeing multiple choice questions on various aspects and structures of the brain.
Here is asample question from AP® Central that would be similar to what you could see on the AP® Psychology exam:
Damage to the cerebellum would most likely result in which of the following problems?
a) Aphasia
c) A loss of vision
d) A loss of motor coordination
e) A change in personality
The cerebellum , plays a role in your motor control and movement, which would make the answer D. Multiple choice questions on the brain in the exam will most likely be similar to this one the exam tests how well you can understand and relate the structures of the brain to their functions.
Also Check: What Is An Example Of Movement In Geography
How Does The Brain Work
The brain sends and receives chemical and electrical signals throughout the body. Different signals control different processes, and your brain interprets each. Some make you feel tired, for example, while others make you feel pain.
Some messages are kept within the brain, while others are relayed through the spine and across the bodys vast network of nerves to distant extremities. To do this, the central nervous system relies on billions of neurons .
You Can Make Your Brain Think Time Is Going Slowly By Doing New Things
Ever wished you didnt find yourself saying Where does the time go! every June when you realize the year is half-over? This is a neat trick that relates to how our brains perceive time. Once you know how it works, you can trick your brain into thinking time is moving more slowly.
Essentially, our brains take a whole bunch of information from our senses and organize it in a way that makes sense to us, before we ever perceive it. So what we think is our sense of time is actually just a whole bunch of information presented to us in a particular way, as determined by our brains:
When our brains receive new information, it doesnt necessarily come in the proper order. This information needs to be reorganized and presented to us in a form we understand. When familiar information is processed, this doesnt take much time at all. New information, however, is a bit slower and makes time feel elongated.
Even stranger, it isnt just a single area of the brain that controls our time perceptionits done by a whole bunch of brain areas, unlike our common five senses, which can each be pinpointed to a single, specific area.
When we receive lots of new information, it takes our brains a while to process it all. The longer this processing takes, the longer that period of time feels:
The same thing happens when we hear enjoyable music, because greater attention leads to perception of a longer period of time.
Don’t Miss: Hawkes Learning Systems Prealgebra And Introductory Algebra Answers
Psychology In Everyday Life: Why Are Some People Left
Across cultures and ethnic groups, about 90% of people are mainly right-handed, whereas only 10% are primarily left-handed . This fact is puzzling, in part because the number of left-handers is so low, and in part because other animals, including our closest primate relatives, do not show any type of handedness. The existence of right-handers and left-handers provides an interesting example of the relationship among evolution, biology, and social factors and how the same phenomenon can be understood at different levels of analysis .
At least some handedness is determined by genetics. Ultrasound scans show that nine out of 10 fetuses suck the thumb of their right hand, suggesting that the preference is determined before birth , and the mechanism of transmission has been linked to a gene on the X chromosome . It has also been observed that left-handed people are likely to have fewer children, and this may be in part because the mothers of left-handers are more prone to miscarriages and other prenatal problems .
But culture also plays a role. In the past, left-handed children were forced to write with their right hands in many countries, and this practice continues, particularly in collectivistic cultures, such as India and Japan, where left-handedness is viewed negatively as compared with individualistic societies, such as Canada and the United States. For example, India has about half as many left-handers as the United States .
Link Between Biopsychology And Human Behavior
Researchers also became interested in understanding how different parts of the brain control human behavior. One early attempt at understanding this led to the development of a pseudoscience known as phrenology. According to this view, certain human faculties could be linked to bumps and indentations of the brain which could be felt on the surface of the skull.
While phrenology became quite popular, it was also soon dismissed by other scientists. However, the idea that certain parts of the brain were responsible for certain functions played an important role in the development of future brain research.
The famous case of Phineas Gage, a railroad worker who suffered a devastating brain injury, also had an influence on our understanding of how damage to certain parts of the brain could impact behavior and functioning.
Don’t Miss: Segment Addition Postulate Practice
Psychology And The Brain
Psychology is commonly defined as the scientific study of behavior and mental processes. It has existed since the late 19th century, with 1879 often being given as a starting date because that was when the first psychological research lab was founded. Many schools of thought within the field have come and gone since then some, like behaviorism, have persisted and evolved if they stood up to scientific study others, like phrenology, have faded as they have lost credibility.
One approach has only begun to gain ground over the 20th and 21st centuries as scientific research and technology have improved: the study of the brain. Neuroscience is a relatively new field, but the more research that is done, the more it appears that much of human behavior and mental processesthe key interests for psychological studyare intimately intertwined with activity in the brain. Understanding the brain is important no matter what type of psychology you will be involved with, because its effects permeate all human behavior.
How Drugs Cause A High
Most drugs also lead to an increase of dopamine in the brain. But its different than with ice cream. The brain releases a controlled amount of dopamine when you experience natural pleasures. Drugs cause an unnatural dopamine surge. This causes the euphoric high that keeps drug users coming back for more.
But theres more to what drugs do to the addicted brain than a simple dopamine surge. In fact, drugs alter how the entire pleasure center of the brain works. Once the brain experiences the dopamine surge, the hippocampus creates memories of the pleasure, and the amygdala creates a conditioned response to stimuli.
Different drugs work in the brain in different ways. For example, heroin and LSD mimic the effects of a natural neurotransmitter like dopamine. PCP blocks the brains receptors to stop messages from getting through. Cocaine interferes with the neurons that bring neurotransmitters back to the neurons they came from. And methamphetamines cause the brain to release more neurotransmitters.
Don’t Miss: Do You Capitalize Bachelor’s Degree In Psychology
Energetic Organization As The Cause Of Consciousness
In theory, we could account for all the highly complex processes occurring in the brain in terms of energy, forces and work, that is, as physical, chemical and biological processes. But the seemingly unassailable problem of how any of these processes might cause consciousness remains. The principle outlined here that there is something it is like, intrinsically to undergo differences due to the antagonistic action of energy, forces and work may offer a toehold in the slippery face of the problem. There is something it is like, intrinsically, to be a tense muscle that is different from being a relaxed muscle. There is something it is like, intrinsically, to be networks of neurons in fantastically complex states of actualized differentiation from other networks, with action potentials propagating through vast arrays of fibers. But all this something is it like-ness is not in itself sufficient for consciousness. Muscles are not conscious, and networks of neurons are active in the brain when we are in dreamless sleep or under anesthesia. What is it about the organization of energetic processes in the brain, as discussed in Section Consciousness and the Organization of Energetic Processing in the Brain, which determines the level of consciousness we experience?
The Peripheral Nervous System
In addition to the central nervous system there is also a complex network of nerves that travel to every part of the body. This is called the peripheral nervous system and it carries the signals necessary for the body to survive . Some of the signals carried by the PNS are related to voluntary actions. If you want to type a message to a friend, for instance, you make conscious choices about which letters go in what order and your brain sends the appropriate signals to your fingers to do the work. Other processes, by contrast, are not voluntary. Without your awareness your brain is also sending signals to your organs, your digestive system, and the muscles that are holding you up right now with instructions about what they should be doing. All of this occurs through the pathways of your peripheral nervous system.
Read Also: Kendall Hunt Geometry Answer Key
Age And Working Memory
Nevertheless, having established a clear working memory circuitry in the brain, differences in brain activations, neural patterns or working memory performances are still apparent in different study groups, especially in those with diseased or aging brains. For a start, it is well understood that working memory declines with age . Hence, older participants are expected to perform poorer on a working memory task when making comparison with relatively younger task takers. In fact, it was reported that decreases in cortical surface area in the frontal lobe of the right hemisphere was associated with poorer performers . In their study, healthy elderly people with an average age of 70 took the n-back working memory task while magnetic resonance imaging scans were obtained from them . The outcomes exhibited that a decrease in cortical surface areas in the superior frontal gyrus, pars opercularis of the inferior frontal gyrus, and medial orbital frontal gyrus that was lateralized to the right hemisphere, was significantly detected among low performers, implying an association between loss of brain structural integrity and working memory performance . There was no observed significant decline in cortical thickness of the studied brains, which is assumed to implicate neurodegenerative tissue loss .
TABLE 2. Working memory studies in relation to age.
General Discussion And Future Direction
On the other hand, even though the roles of the prefrontal cortex in working memory have been widely established, region specificity and localization in the prefrontal cortex in relation to the different working memory domains such as manipulation or delayed retention of information remain at the premature stage . It has been postulated that the neural mechanisms involved in working memory are of high-dimensionality and could not always be directly captured and investigated using neurophysiological techniques such as fMRI, EEG, or patch clamp recordings even when comparing with lesion data . According to DEsposito and Postle , human fMRI studies have demonstrated that a rostral-caudal functional gradient related to level of abstraction required of working memory along the frontal cortex might exist. Other functional gradients relating to different aspects of working memory were similarly unraveled . These proposed mechanisms with different empirical evidence point to the fact that conclusive understanding regarding working memory could not yet be achieved before the inconsistent views are reconciled.
Don’t Miss: Segment Addition Postulate Coloring Activity
Mechanisms Of Stress Effects On The Immune System
Virtually nothing is known about the psychological pathways linking stressors with the immune system. Many theorists have argued that affect is a final common pathway for stressors , yet studies have enjoyed limited success in attempting to explain peoples immune responses to life experiences on the basis of their emotional states alone . Furthermore, many studies have focused on the immune effects of emotional valence , but the immune system may be even more closely linked to emotional arousal , especially during acute stressors . Finally, it is possible that emotion will prove to be relatively unimportant and that other mental processes such as motivational states or cognitive appraisals will prove to be the critical psychological mechanisms linking stress and the immune system .
Future studies could also benefit from a greater emphasis on behavior as a potential mechanism. This strategy has proven useful in studies of clinically depressed patients, in which decreased physical activity and psychomotor retardation , increased body mass , disturbed sleep , and cigarette smoking have been shown to explain some of the immune dysregulation evident in this population. There is already preliminary evidence, for instance, that sleep loss might be responsible for some of the immune system changes that accompany stressors .
Who Is Vulnerable To Stress
If the stress response in the immune system evolved, a healthy organism should not be adversely affected by activation of this response because such an effect would likely have been selected against. Although there is direct evidence that stress-related immunosuppression can increase vulnerability to disease in animals , there is little or no evidence linking stress-related immune change in healthy humans to disease vulnerability. Even large stress-induced immune changes can have small clinical consequences because of the redundancy of the immune systems components or because they do not persist for a sufficient duration to enhance disease susceptibility. In short, the immune system is remarkably flexible and capable of substantial change without compromising an otherwise healthy host.
However, the flexibility of the immune system can be compromised by age and disease. As humans age, the immune system becomes senescent . As a consequence, older adults are less able to respond to vaccines and mount cellular immune responses, which in turn may contribute to early mortality . The decreased ability of the immune system to respond to stimulation is one indicator of its loss of flexibility.
Read Also: Unit 1 Test Geometry Basics Answers Key