Analytical Methods For Detecting Adulterant: An Overview
The SAMHSA guidelines indicate that initial screening of nitrite can be performed by a nitrite colorimetric test or general adulterant colorimetric test but the confirmation must be conducted using multiwavelength spectrophotometry, capillary electrophoresis, or ion chromatography. The initial presence of chromate may be detected by a general colorimetric chromium test or colorimetric test for oxidants but confirmatory test must be performed using atomic absorption spectrophotometry, multiwavelength spectrophotometry, ion chromatography, capillary electrophoresis, or inductively couple plasma MS. The presence of halogen should be screened by using a general oxidant colorimetric test but initial positive tests must be confirmed using multiwavelength spectrophotometry, ion chromatography, or inductively coupled plasma MS. The presence of glutaraldehyde can be determined by an aldehyde test but confirmation is needed and can be achieved by using GC/MS. The presence of pyridine at a concentration of 50 g/mL must also be confirmed. The presence of surfactant is verified by using a surfactant colorimetric test with an equal or greater than 100 g/mL dodecylbenzene sulfonate equivalent and confirmation at the same level by using a different analytical method, e.g., multiwavelength spectrophotometry.
Table 10.5. Criteria for diluted, substituted, adulterated, and invalid specimen urine specimen
| Specimen |
|---|
Geoffrey A. Cordell, in, 1999
Synthesis Of Analogs Starting From Diosgenin
Shawakfeh and coworkers described the preparation of several structurally simplified analogs of cephalostatin starting from diosgenin . In the first approach, CaCO3-buffered oxidation of 247 with PCC afforded the unsaturated ketone 248, which was brominated with PTAB in THF to produce the unsaturated 2-bromoketone 249. Treatment of 249 with NaN3, and KI in dimethylformamide , followed by reduction of the azide group and TsOH-catalyzed condensation afforded the symmetrical analog 250. Application of the protocol for the construction of the pyrazine core to the unsaturated diketone 251, obtained by Jones oxidation of diosgenin , afforded the analog 253 .90
Scheme 2.39. Synthesis of tridecacyclic pyrazines starting from diosgenin.
Hydrogenation of the unsaturated ketones 248 and 251 over Pd and application of the same protocol for the generation of the pyrazine core afforded the corresponding analogs 254 and 255 .
Figure 2.8. Tridecacyclic pyrazines bearing saturated A, A-rings.
Scheme 2.40. Synthesis of a 5,5,6,6-tetrahydroxy-tridecacyclic pyrazine starting from diosgenin.
Epoxidation of the unsaturated diketone 251 followed by the same synthetic sequence as shown in Schemes 2.39 and 2.40 afforded the epoxidized analog 261 .91
Scheme 2.41. Synthesis of a 5,6,5,6-diepoxy-tridecacyclic pyrazine starting from diosgenin.
Scheme 2.42. Synthesis of a 5,5-dihydroxy-6,6-dioxo-tridecacyclic pyrazine starting from diosgenin.
Amitava Dasgupta, in, 2017
Recent Advances In Application Of Pyridinium Chlorochromate In Organic Synthesis
Volume 13 , Issue 2 , 2016
Page:Pages: 35
Abstract
Pyridinium chlorochromate is an important reagent in organic synthesis used primarily for the selectiveoxidation of alcohols to give carbonyl compounds. Although a variety of related compounds are knownwith similar reactivity, PCC offers exclusively the advantage of the selective oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes,whereas many other reagents were less selective. Disadvantages of using PCC are the tedious reaction workup andits toxicity, very well compensated by selective oxidation, observed using this reagent as an oxidant. This usefuloxidant was first synthesized and used by E. J. Corey and J. William Suggs in 1972.
Title:Recent Advances in Application of Pyridinium Chlorochromate in Organic Synthesis
Volume: 13Issue: 2
Majid M. Heravi, Azadeh Fazeli and Zeinab Faghihi
Affiliation:
A printer is required for this course.
Instructor comments:
This information was provided to all CH 241 students in Fall 2021. For those who took Organic Chemistry I at another institution, this information will be particularly important.
There are five main items you need to purchase for the class:
I would recommend a physical text to all students taking the complete 241-2-3 series and/or those who will need to review Organic Chemistry at a later date . Once the 24 month period expires for the ebook, you will no longer have access.
Read Also: What Does Biotic And Abiotic Mean
What Does Pcc Stand For In Organic Chemistry
Chromic Acid is commonly represented by any of these three in an undergraduate organic chemistry course. PCC stands for pyridinium chlorochromate but its acronym is much more commonly used. PCC is prepared from a combination of chromium trioxide, pyridine, and concentrated hydrochloric acid. Chromic Acid is the stronger of the two oxidizing agents.
Jones Reagent Versus Pcc
In organic chemistry students will learn both Jones and PCC reagents and will need to know how to differentiate between the two. Both reagents oxidize alcohols. Only secondary and primary alcohols can be oxidized, since oxidizing tertiary alcohol will lead to a carbon with five bonds which is impossible. Both Jones reagent and PCC turn a secondary alcohol into a ketone, going from C-OH to C=O. The difference comes to the primary alcohols. PCC turns a primary alcohol into an aldehyde . However, Jones reagent is strong and oxidizes primary alcohol further to carboxylic acids .
What other reagents produce C=O? Ozonolysis . Ozonolysis is done on alkenes. It can be under reductive and oxidative conditions. Under reductive conditions, O3/DMS, all we need to do is break the double bond and attach an O on each side. Therefore, reductive ozonolysis will create ketones and aldehydes. Ozonolysis under oxidative contusions, on the other hand, will lead to carboxylic acids instead of aldehydes.
DMP is the final reagent we will discuss here. DMP is used to oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes and secondary alcohols to ketones. Therefore DMP is similar to PCC in the end results it gives.
Let Transformation Tutoring help you ace your organic chemistry class and find passion and love for the subject. Our organic chemistry tutors in Brooklyn, NYC, and online are here to help you and talk to you. Please call 646-407-9078 and we will gladly discuss your needs.
Read Also: Bridge To Algebra Answer Key
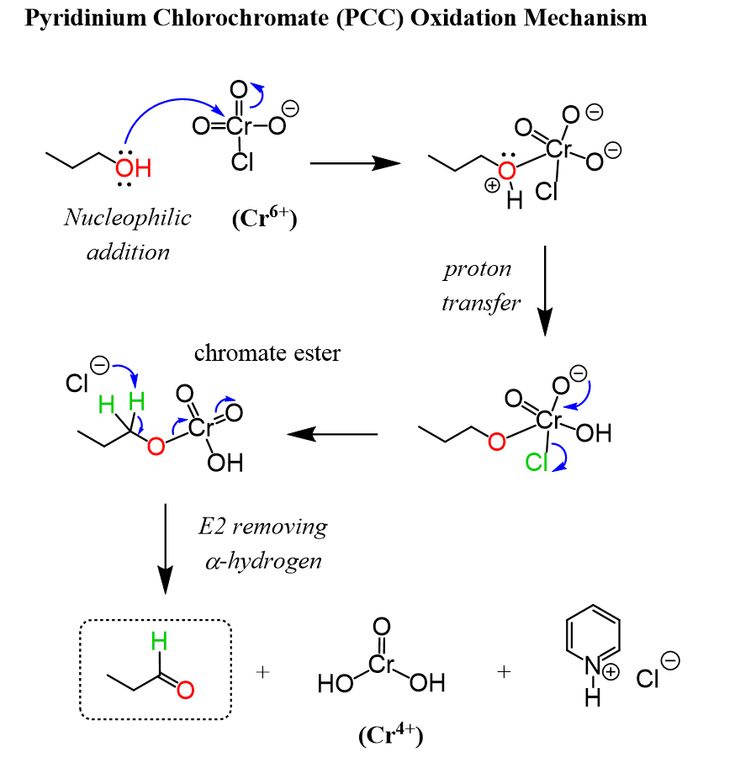
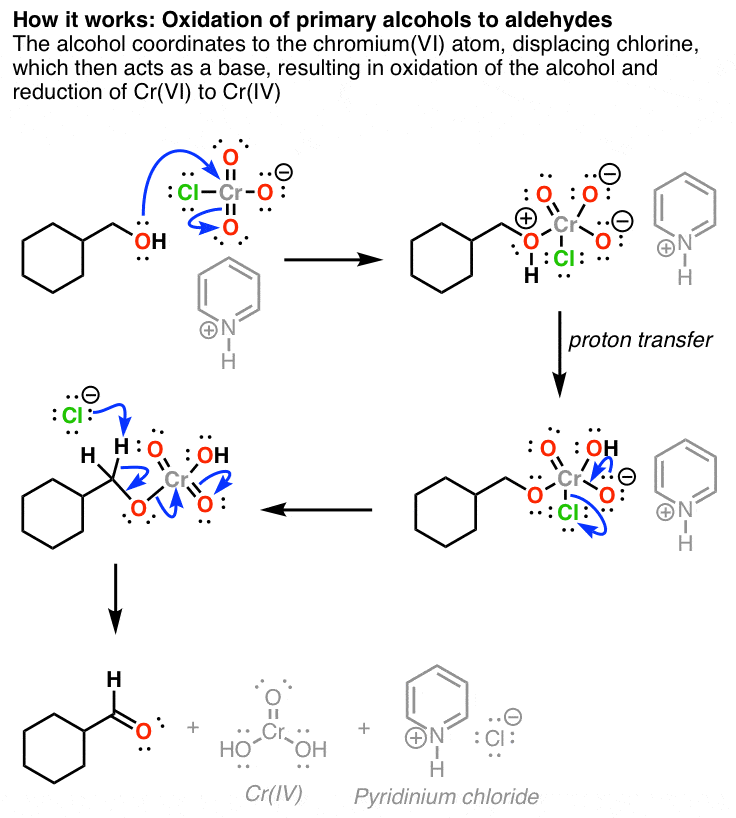
Mechanism For The Oxidation Of Primary Alcohols To Aldehydes With Pyridinium Chlorochromate
How does it work? Oxidation reactions of this sort are actually a kind of elimination reaction. Were going from a carbon-oxygen single bond to a carbon-oxygen double bond. The elimination reaction can occur because were putting a good leaving group on the oxygen, namely the chromium, which will be displaced when the neighboring C-H bond is broken with a base.
The first step is attack of oxygen on the chromium to form the Cr-O bond. Secondly, a proton on the OH is transferred to one of the oxygens of the chromium, possibly through the intermediacy of the pyridinium salt. A chloride ion is then displaced, in a reaction reminiscent of a 1,2 elimination reaction, to form what is known as a chromate ester.
The C-O double bond is formed when a base removes the proton on the carbon adjacent to the oxygen. The electrons from the C-H bond move to form the C-O bond, and in the process break the O-Cr bond, and Cr becomes Cr in the process 2 ).
Real life notes: If you end up using PCC in the lab, dont forget to add molecular sieves or Celite or some other solid to the bottom of the flask, because otherwise you get a nasty brown tar that is a real major pain to clean up. The toxicity and mess associated with chromium has spurred the development of other alternatives like TPAP, IBX, DMP, and a host of other neat reagents you generally dont learn about until grad school.
References and Further Reading
Also Check: Qualitative Data Definition Ap Human Geography
Alkyl Iodides From Alkanes
N-Iodosuccinimide can be used to iodinate enol esters < 53JA3493, 55JA3826> and enol silanes < 84TL233> , although in the latter case a combination of N-chlorosuccinimide and sodium iodide is used. Finally, iodide ion in combination with either m-chloroperbenzoic acid or KIO3 yields -iodocarbonyl compounds from enol silanes or aryl ketones, respectively < 87JOC3919, 92BCJ1731> .
Also Check: Jonathan Tennent Child Of Rage
What Gets Stored In A Cookie
This site stores nothing other than an automatically generated session ID in the cookie no other information is captured.
In general, only the information that you provide, or the choices you make while visiting a web site, can be stored in a cookie. For example, the site cannot determine your email name unless you choose to type it. Allowing a website to create a cookie does not give that or any other site access to the rest of your computer, and only the site that created the cookie can read it.
Oxidation Of Primary Alcohols To Aldehydes With Pyridinium Chlorochromate And Oxidation Of Secondary Alcohols To Ketones
Here are two examples of PCC in action. If you add one equivalent of PCC to either of these alcohols, you obtain the oxidized version. The byproducts are Cr as well as pyridinium hydrochloride.
One has to be careful with the amount of water present in the reaction. If water is present, it can add to the aldehyde to make the hydrate, which could be further oxidized by a second equivalent of PCC were it present. This is not a concern with ketones, since there is no H directly bonded to C.
Recommended Reading: Difference Between Human Geography And Physical Geography
Pcc Is Launching Greenline A High
Duisburg, July 24, 2020. The chemical companies of the PCC Group have developed a product portfolio of sustainable chemicals under the brand name GREENLINE. Green chemistry includes chemical products and applications that can be used to reduce or even eliminate environmentally harmful substances. PCCs green chemistry range includes high-quality products that are sustainable in many ways, for example chemicals that increase the effectiveness of detergents at low temperatures and thus reduce energy consumption. Other chemicals are particularly suitable as input to manufacture organic and ecological products. Our sustainable products for the construction industry include raw materials and chemical additives that are particularly environmentally friendly and that, when used in building materials, significantly reduce the energy consumption of buildings. The new Green Chemistry section on the large product portal in our Chemicals division provides an overview of our range.
Ch242 Organic Chemistry Ii
Introduces radical reactions substitution and elimination reaction mechanisms structure and chemistry of alcohols, ethers, epoxides and their sulfur analogues organometallic compounds arenes and aromaticity structure and chemistry of aromatic compounds NMR, UV-VIS and Mass Spectroscopy and special topics as time and interest permit. Prerequisite: CH 241. Audit available.
- you will need the CRN to register.
- Fees:
This page includes one section only, more sections may exist for this class.
Recommended Reading: Algebra 2 Domain And Range Worksheet Answer Key
Why Is Pcc Toxic
However, PCC was probably avoided due to its toxicity from Chromium . Similar to the problem with PCC, it is also toxic due to the presence of Chromium , if using chromium trioxide. A reaction with Jones reagents also occurs in acidic conditions, which could cause damage as well if handled improperly.
Are Hydrogen And Hydronium The Same
What is the difference between Hydrogen Ion and Hydronium Ion? Hydrogen ion is shown by the symbol H+ and hydronium ion is denoted by the symbol H3O+. Hydrogen ion is obtained by removing an electron from the hydrogen atom. Since this is so reactive, in aqueous medium it combines with water, to form a hydronium ion.
Read Also: Domain And Range Worksheet 2 Answer Key Algebra 1
Don’t Miss: Beth Thomas Psychopathic Child
Why Is Pyridinium Chlorochromate Selective Compared To Chromate Dichromate Etc
One can use PCC to oxidise an alcohol selectively up one level to an aldehyde/ketone, without further oxidation to a carboxylic acid.Why is pyridinium important to this selectivity?
I understand that usually PCC is dissolved in dichloromethane and not in anything like THF, and this prevents the formation of a hydrate, which can then act like an alcohol in its oxidation to a carboxylic acid, but I cant figure out why its important that pyridinium is used.
Though pyridinium chlrochromate is a salt, the pyridnium cation is easily dissolved by a wide variety of organic solvents. As such, the chlorochromate anion then becomes dissolved in the organic solvent, and can oxidize $1º$ and $2º$ alcohols present in solution to carbonyls. Oxidation of carbonyls to carboxylic does not occur when using PCC for the very reason you said yourselfno water is present to hydrate the carbonyl species to its geminal diol to allow for further reaction.
Other benefits of PCC include that it is not particularly hygroscopic, is commercially available, and can be stored for some time, though other methods are generally preferred as the reaction workup for PCC can be tedious and the chromium species produced is toxic.
Can Toluene Be Oxidized To Benzoic Acid Using Pyridinium Chlorochromate
PCC is generally regarded as a milder oxidizing agent, used to effect selective oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes or ketones . While over-oxidation to a carboxylic acid from a primary alcohol is definitely possible, PCC should not react with a simple unfunctionalized benzylic carbon.
However, oxidation at the benzylic position is easily achieved with more aggressive oxidizing agents. In particular, chromic acid as well as aqueous potassium permanganate will fully oxidize virtually any benzylic carbon all the way to the carboxylic acid, providing the benzylic carbon has at least one hydrogen. Of course, the rest of the chain is completely cleaved in the process.
Edit: Out of curiosity, I consulted my copy of Marchs Advanced Organic Chemistry to determine if any other common reagents were able to effect the same benzylic oxidation. Nitric acid is listed along with the two methods I described above. Naturally, a survey of various more exotic methods is also given. Intriguing was the use of sodium hypochlorite in acetonitrile, or NBS in aqueous sodium hydroxide under photochemical conditions, for the specific complete oxidation of aryl methyl groups.
You May Like: Linear Algebra Span Definition
Setting Your Browser To Accept Cookies
There are many reasons why a cookie could not be set correctly. Below are the most common reasons:
- You have cookies disabled in your browser. You need to reset your browser to accept cookies or to ask you if you want to accept cookies.
- Your browser asks you whether you want to accept cookies and you declined. To accept cookies from this site, use the Back button and accept the cookie.
- Your browser does not support cookies. Try a different browser if you suspect this.
- The date on your computer is in the past. If your computer’s clock shows a date before 1 Jan 1970, the browser will automatically forget the cookie. To fix this, set the correct time and date on your computer.
- You have installed an application that monitors or blocks cookies from being set. You must disable the application while logging in or check with your system administrator.
Pyridinium Chlorochromate And Dichromate
An alternative to the chromium trioxidepyridine complex is provided by pyridinium chlorochromate and pyridinium dichromate .137 These reagents, now ubiquitous for chromate-based oxidation of alcohols, overcome the hygroscopic nature of the chromium trioxidepyridine complex138 and are prepared by a less hazardous procedure 139 both are commercially available as are several other derivative reagents.
Pyridinium chlorochromate has been shown to be of particular value in the allylic oxidation of compounds containing an activated methylene group, such as 5,6-dihydropyrans .140
Indeed, Parish141 claims that PCC is the reagent of choice in the allylic oxidation of 5-steroids . The reactions were carried out using PDC in pyridine solution at 100 °C, PCC in refluxing benzene solution, and PCC in DMSO solution at 100 °C. These solvent systems are claimed to be superior to the more usual methylene chloride.138,142
One drawback associated with this type of chromium species is the frequent requirement for a large excess of reagent. Recent attempts to combat this problem have involved the use of a PCCcelite mixture in benzene solution under reflux143 and more successfully a t-butyl hydroperoxidepyridinium dichromate mixture .144
Kristine L. Teppang, Jerry Yang, in, 2020
Read Also: Does The Mcat Give You Equations
You May Like: Kw Value Chemistry
What Is Pcc In Organic Chemistry
Answer:
Pyridinium chlorochromate is a yellow-orange salt with the formula +. It is a reagent in organic synthesis used primarily for oxidation of alcohols to form carbonyls. A variety of related compounds are known with similar reactivity.
Pyridinium chlorochromate is a yellow-orange salt with the formula +. It is a reagent in organic synthesis used primarily for oxidation of alcohols to form carbonyls. A variety of related compounds are known with similar reactivity.Appearance: yellow-orange solid
Pyridinium chlorochromate is a yellow-orange salt with the formula +. It is a reagent in organic synthesis used primarily for oxidation of alcohols to form carbonyls. A variety of related compounds are known with similar reactivity.Appearance: yellow-orange solidChemical formula: C5H6ClCrNO3
Pyridinium chlorochromate is a yellow-orange salt with the formula +. It is a reagent in organic synthesis used primarily for oxidation of alcohols to form carbonyls. A variety of related compounds are known with similar reactivity.Appearance: yellow-orange solidChemical formula: C5H6ClCrNO3Solubility in other solvents: soluble in acetone, acetonitrile, THF
Pyridinium chlorochromate is a yellow-orange salt with the formula +. It is a reagent in organic synthesis used primarily for oxidation of alcohols to form carbonyls. A variety of related compounds are known with similar reactivity.
Appearance: yellow-orange solid
You May Like: Fsa Algebra 1 Eoc Algebra And Modeling Answer Key
What Does Pcc Do In Organic Chemistry
PCCdoesPCC
. Simply so, what is PCC used for in organic chemistry?
Pyridinium chlorochromate is a yellow-orange salt with the formula +. It is a reagent in organic synthesis used primarily for oxidation of alcohols to form carbonyls. A variety of related compounds are known with similar reactivity.
Similarly, what is the structure of PCC? C5H5NHClCrO3
In respect to this, is PCC a reducing agent?
Pyridinium chlorochromate is a weak oxidizing agent and is often used to oxidize alcohols into carbony compounds. All of the other compounds are similar in that they function as reducing agents.
What does the Jones reagent test for?
Jones reagent is a solution of chromium trioxide in aqueous sulfuric acid. Using acetone as a reaction solvent, the reagent is usually used for the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to carboxylic acids and ketones, respectively.
Read Also: Algebra 1 Eoc Practice Worksheets