# 57 Assimilation And Role Of The Liver
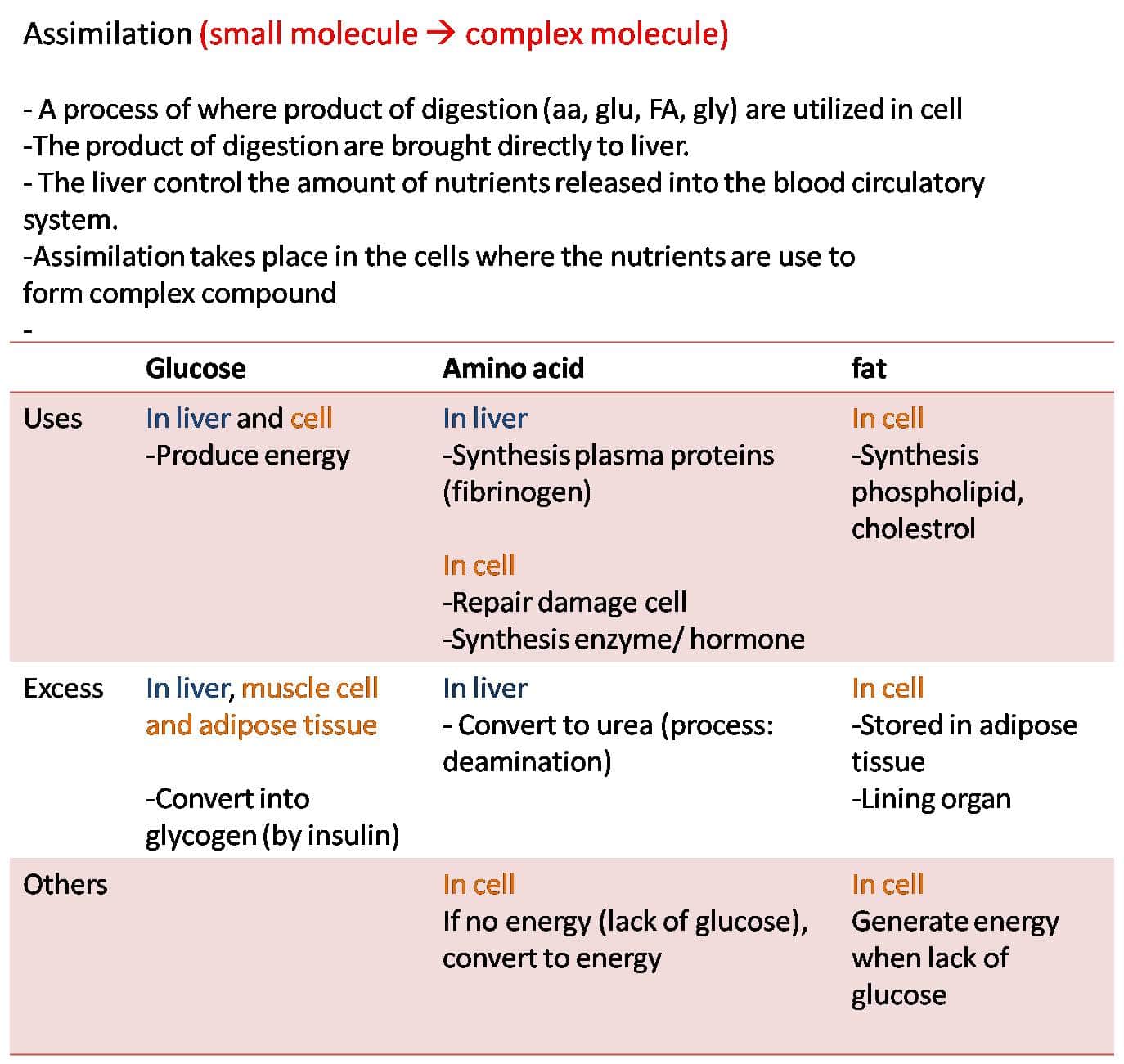
Assimilation digested food moleculesthe cellsRole of liver in the metabolism of glucose and amino acids
- Excess glucose in the blood arriving at the liver is converted into glycogen for storage, or broken down through respiration, producing energy for other purposes.
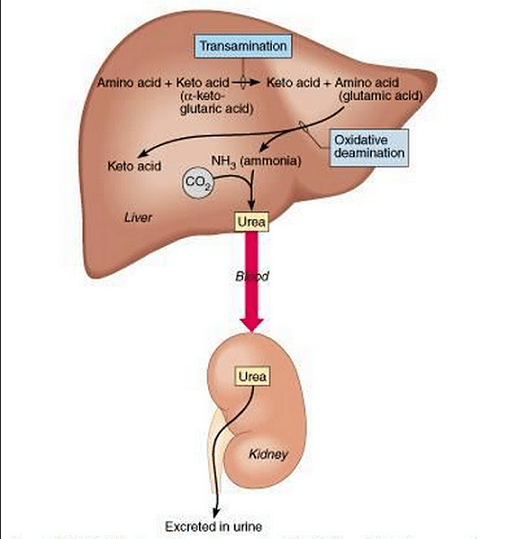
- Amino acids cannot be stored in our body, so any that is excess has to be dealt with in the liver. – Some amino acids are transaminated to produce a different amino acid. – The rest are deaminated to produce ammonia and a keto acid. + NH3 is converted into urea, which is transported to the kidneys and excreted. + The keto acid is used primarily as energy for liver cells
Deaminationnitrogen-containingureaenergy
Examples Of Assimilation In A Sentence
assimilationThe Christian Science MonitorassimilationWashington PostassimilationThe New York Review of Booksassimilation Forbesassimilation WSJassimilation Washington Postassimilation VarietyassimilationNew York Times
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘assimilation.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
Metabolism: The Unity Of The Two Processes
Metabolism is the unity of the twoprocesses: assimilation and dissimilation. Assimilation is the sum of all the processes of creating living matter: the absorption of cells by substances entering the body from the environment, the formation of more complex chemical compounds from simpler ones, and so on. Assimilation in biology is a process in which cells using different materials are transformed into living matter. Dissimilation is destruction of living matter, decay, splitting of substances in cellular structures, in particular, in protein compounds. Assimilation and dissimilation are inextricably linked. Assimilation is accompanied by an increase in the processes of destruction, which, in turn, prepare the soil for assimilation.
Don’t Miss: How Do We Know That Clocks Are Hungry Math Answer
Assimilation In Biology Is What Examples Of Assimilation And Dissimilation In Nature
Assimilation in biology is a process thatplays an important role in the digestive system of a living organism. What is it? Let’s say you ate food today to get some energy. But have you ever thought about how food gets from a plate to cages? After you have eaten something, your body begins to break down food during digestion, absorbs nutrients and distributes them to cells during assimilation, where they are used for growth and recovery.
Examples Of Biological Assimilation
The main source of energy for all living things onthe planet is solar radiation. All organisms living on the Earth can be divided into autotrophic and heterotrophic. The first group is predominantly green plants capable of converting radiant energy from the sun and producing photosynthesis of organic compounds from inorganic substances.
Other living organisms, not including somemicroorganisms that can receive energy by means of chemical reactions, absorb the already formed organic matter and use it as an energy source or as a structural material for the creation of organs. The time when the most active and intensive assimilation in biology takes place is the young age in animals and the growing season in plants.
Recommended Reading: Teorema Fundamental Del Algebra Gauss
Solved Questions For You
Q: Why are villi present in the small intestine and not in the stomach?
Ans: The small intestine is mainly responsible for the absorption process. The villi and microvilli increase the surface area of absorption. The stomach, on the other hand, is an organ that primarily stores food temporarily along with the digesting proteins. Hence the small intestine has villi and not the stomach.
What Is The Difference Between Absorption And Assimilation
Absorption is the process of taking simple molecules, which are produced as a result of digestion into the body from the intestinal cavity.
On the other hand, assimilation is the process of making new compounds from the absorbed molecules, which are necessary for normal cell functioning or to produce energy. Thus, this is the key difference between absorption and assimilation.
When considering the locations where they occur, absorption takes place mainly in the small intestine while assimilation takes place in the liver. Hence, this is another difference between absorption and assimilation.
Furthermore, during the absorption, nutrients are adding into the bloodstream but, during the assimilation, molecules are taken out of the bloodstream by different cells. Thus, it is also a difference between absorption and assimilation.
Read Also: Geometry Definition Of Acute Angle
What Happens After Eating
To understand what is the assimilation of food andassimilation in biology, let’s first see how we digest conventional food. Let’s take an example like a cheeseburger. During chewing, the soaking, grinding and turning of food into a bolus takes place, which then moves through the esophagus to the stomach, where already strong acids and enzymes break it into parts.
Carbohydrates and proteins beginto be digested before everyone else. Further in the small intestine, fats begin to break up to their individual components, called fatty acids. At the moment, the cheeseburger’s digestion is complete. Now it’s time to digest the nutrients that have entered your body.
Fusion Of Multisource Evidence In Systems Biology
Advanced statistical techniques are necessary to fuse data from multiple sources. A data fusion-based risk assessment framework for human health was proposed in accordance with DempsterShafer theory and systems biology principles to achieve excellent evidence fusion . The same evidence fusion theory has been applied to design and fuse multisensory evidence for engine fault diagnosis . A framework with multiscale processes and multiple model choices, such as ordinary or partial differential equations, has been recommended for biological applications .
Prediction functions well with the correct system model. Among the most common and traditional models are linear regression and linear time series types. However, linear and time-invariant systems are part of a small portion of the actual world phenomena. Moreover, most systems change with time, and outputs are not linearly proportional to inputs. Some systems can be easily discussed with a simple transformation. For instance, neural network transformation has been implemented to bypass nonlinear problems and perform effective inferences based on extracted features . Models and methods in discovering biomarkers have been reviewed to predict clinical outcomes in the cardiovascular field . Mathematical modeling has been applied to predict atherosclerosis .
You May Like: What Is The Hardest Level In Geometry Dash
How Assimilation Is Measured
Social scientists study the process of assimilation by examining four key aspects of life among immigrant and racial minority populations. These include socioeconomic status, geographic distribution, language attainment, and rates of intermarriage.
Socioeconomic status, or SES, is a cumulative measure of one’s position in society based on educational attainment, occupation, and income. In the context of a study of assimilation, a social scientist would look to see if SES within an immigrant family or population has risen over time to match the average of the native-born population, or whether it has stayed the same or declined. A rise in SES would be considered a mark of successful assimilation within American society.
Geographic distribution, whether an immigrant or minority group is clustered together or dispersed throughout a larger area, is also used as a measure of assimilation. Clustering would signal a low level of assimilation, as is often the case in culturally or ethnically distinct enclaves like Chinatowns. Conversely, a distribution of an immigrant or minority population throughout a state or across the country signals a high degree of assimilation.
What Happens To The Digested Food In The Small Intestine
The small intestine has special cells that help absorb nutrients from the intestinal lining into the bloodstream. It has many physiological features that help in this absorption process. It is a long convoluted tube-like organ, which is around ten feet in length and has a diameter of one inch. There is a thin membrane called the mesentery that surrounds the small intestine and anchors it in place.
Many blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, nerves pass through the mesentery. They provide support to the tissues of the small intestine and also help in the transport of nutrients from intestines to the rest of the body.
The small intestine is divided into three regions:
- Duodenum- It is the first section which connects to the pyloric sphincter of the stomach. It is the shortest region of the intestine. The chyme gets mixed with bile and pancreatic juice here.
- Jejunum It is the middle section and is the primary site of nutrient absorption. This region measures around 3 feet in length.
- Ileum It is the final section of the small intestine that empties into the large intestine. At a length of 6 feet, it completes the absorption of the remaining nutrients.
Read Also: Bju Algebra 1 3rd Edition
Genetic Assimilations Role In Diversifying Evolution
Genetic assimilation has long been regarded as potentially crucial in the origins of novel traits . With genetic assimilation, the origin of a new, canalized trait does not require new genes instead, selection can promote the origins of a novel trait by acting on existing genetic and epigenetic variation in a population . In other words, a plastic trait can be converted into a canalized trait through evolutionary adjustments in the regulation of a traits expression.
Phenotypic plasticity, followed by genetic assimilation, might also promote adaptive radiation, influencing both the likelihood of occurrence and the patterns of diversity that emerge . In adaptive radiation, a single ancestral lineage diversifies rapidly in response to divergent selection pressures across numerous environments . According to the flexible stem hypothesis , an adaptive radiation arises when ecological circumstances favour diversification in an ancestral taxon that expresses phenotypic plasticity in the types of traits that characterize the adaptive radiation. Under such circumstances, when individuals are exposed to the same selective environments, plasticity in the ancestral lineage repeatedly reveals the same sets of phenotypes. This model might explain replicate adaptive radiations in a number of systems . However, further study is needed to test this model more rigorously.
What Is An Example Of Assimilation In Society
One of the most obvious examples of assimilation is the United States’ history of absorbing immigrants from different countries. From 1890 to 1920, the United States saw an influx of many immigrants from European and Asian countries. The desire to come to the United States was primarily for economic purposes.
Don’t Miss: What Is Theoretical Orientation In Psychology
Molecular Insights Into Biological Carbon Assimilation
Scientists have unveiled the molecular structure of a membrane transporter that is responsible for carbon assimilation in cyanobacteria major contributors to photosynthesis and global carbon fixation.
The study by researchers at the University of Liverpools Institute of Integrative Biology and Chinese Academy of Sciences has been published online in Nature Plants.
The conversion of carbon dioxide and water into sugar is one of the most important biological processes for life on earth. Up to 90% of carbon dioxide exists in the form of bicarbonate in the ocean, which covers 71% of the Earths surface.
To improve carbon assimilation, cyanobacteria, the most common bacteria in the ocean, use specific transport proteins in cellular membranes to pump HCO3 into the cell. The enriched HCO3 inside the cyanobacterial cell is then used by an enzyme known as Rubisco, which is encapsulated within a protein-based organelle called the carboxysome.
The researchers used state-of-the-art protein crystallisation and cryo-electron microscopy to obtain the three-dimensional structure of a key HCO3 transporter , and explored the locations of the transporters in cells using fluorescence microscopy, with the support of the Universitys Centre for Cell Imaging.
Research reference:
Assimilation Of Food In Human Beings
In this article we will discuss about the Assimilation of Food in Human Beings.
Meaning of Assimilation of Food:
The absorbed food materials are transported by blood and lymph. Lymph is finally transferred to the blood circulation. The blood transports absorbed food materials to different body cells where food materials become integral component of the living protoplasm and are used for energy, growth and repair. This is called assimilation of food.
Assimilation of Proteins, Carbohydrates and Fats:
Proteins:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Amino acids are not stored but are taken up by the cells in connection with the synthesis of proteins. Proteins are used for growth, repair, etc.
Excess amino acids can be converted into glucose and then to fat and are thus stored. This is an irreversible reaction. Amino acids can also be converted to glucose and used as fuel for the cell. During their conversion to glucose the amino acids are deaminated .
The liver is chief site for deamination, i.e., a process by which the amino group is removed from the amino acids resulting in the production of ammonia. The ammonia is soon converted into urea, which is filtered from the blood in the kidney.
Carbohydrates:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The excess of the monosaccharides the glucose, fructose and galactose are usually stored in the liver and muscle cells in the form of glycogen . Whenever, there is a deficiency of glucose in the blood the glycogen is converted into glucose .
Fats:
Egestion :
Meaning of Egestion:
You May Like: What Is Ph In Biology
Data Assimilation In Biology And Medicine
Unobservable data can be readily estimated by Bayesian methods, forward system equations, and few observations, even without detailed parameters, which are then gradually estimated through assimilation. Moreover, the technique applies sparsely observed information to estimate system internal states by acquiring assumptions based on system behaviors typically governed by a set of predefined spatio-temporal equations. Assimilation application can significantly reduce the requirement of measurement .
Although well-developed diagnostic decision support systems have been established for general usage, accumulated experiences are helpful for more elaborate applications upon establishing the forward path of system dynamics. New algorithms are necessary for fusing data when observations are collected from different models of system dynamics . Scientific knowledge and applications are important in the success of related developments because system dynamics modeling is crucial in data assimilation. However, a simple linear regression between causes and effects is insufficient for biological and medicinal applications.
The purposes of medical data assimilation and medical decision support system are different. Data assimilation may create millions of systems for different patients and can be applied to collect personal data, establish models, and obtain new evidence. Moreover, it seldom applies the logic that most people act in such manner that others may follow the same way.
Potential Mechanisms Of Genetic Assimilation
For genetic assimilation to take place, the reaction norms that underlie a phenotypes expression in a population must undergo an evolutionary shift, such that genotypes that express a phenotype robustly across a range of different environments become fixed in the population . Experimental evidence indicates that such changes in reaction norms may be driven by variation in signalling pathways that mediate the relationship between genotype, environment and phenotype. One way such variants might act is by changing developmental thresholds for environmentally influenced hormones and other key signalling molecules .
Although there have yet to be case studies reported in which genetic assimilation has been linked to specific genetic changes , work on related topics including the molecular basis of gene expression variation, genotypeenvironment interaction, and robustness provides valuable insights into possible causes of genetic assimilation. As with phenotypic plasticity in general, genetic variants that alter gene regulation are likely important contributors to genetic assimilation . Populations commonly harbour large numbers of genetic variants that affect gene expression . Additionally, many new mutations that arise within populations impact gene regulation . Thus, ample genetic diversity in gene expression exists within populations that affects gene regulation and may serve as a reservoir of cryptic phenotypic effects .
You May Like: How Hard Is College Chemistry
Dissimilation In Plant And Animal Organisms
Dissimilation in plants occupies a centrala place in the metabolism of a number of processes, including respiration and glycolysis. The release of energy and the resultant result of these processes is necessary for the existence of vital signs. Among the final products of dissimilation, the leading positions are occupied by water, gaseous carbon dioxide and ammonia.
If the animals have these products in the processthe accumulations are released from the outside, then in plants carbon dioxide and ammonia are used for the biosynthesis of organic matter and are the source material for assimilation. The intensity of dissimilation processes in plants varies depending on the stage of ontogenesis of the organism and depends on some other factors.
What Is Assimilation In Biology
Assimilation in biology is the process through which an organism incorporates nutrients from outside its body to the more complex structures needed inside of it. The most simple of life forms, a single-cell organism, does this via direct intake through the cell wall. In multicellular organisms, such as plants and animals, the process is different and becomes more elaborate in more complex life forms.
You May Like: What Is Cleavage In Biology
What Is The Difference Between Acculturation Assimilation And Amalgamation
Acculturation is one of several forms of culture contact, and has a couple of closely related terms, including assimilation and amalgamation. Although all three of these words refer to changes due to contact between different cultures, there are notable differences between them.Acculturation is often tied to political conquest or expansion, and is applied to the process of change in beliefs or traditional practices that occurs when the cultural system of one group displaces that of another.Assimilation refers to the process through which individuals and groups of differing heritages acquire the basic habits, attitudes, and mode of life of an embracing culture.Amalgamation refers to a blending of cultures, rather than one group eliminating another or one group mixing itself into another .
How Assimilation Differs From Acculturation
Often, assimilation and acculturation are used interchangeably, but they mean rather different things. While assimilation refers to the process of how different groups become increasingly similar to one another, acculturation is a process through which a person or group from one culture comes to adopt practices and values of another culture, while still retaining their own distinct culture.
So with acculturation, one’s native culture is not lost over time, as it would be throughout the process of assimilation. Instead, the process of acculturation can refer to how immigrants adapt to the culture of a new country in order to function in everyday life, have a job, make friends, and be a part of their local community, while still maintaining the values, perspectives, practices, and rituals of their original culture. Acculturation can also be seen in the way that people from the majority group adopt cultural practices and values of members of minority cultural groups within their society. This can include the uptake of certain styles of dress and hair, types of foods that one eats, where one shops, and what kind of music one listens to.
You May Like: Beginning And Intermediate Algebra Sherri Messersmith