What Does Defense Mechanisms Mean In Psychology
defence mechanismpsychological mechanismDefence mechanismsmechanism
Also to know is, what are the 8 defense mechanisms in psychology?
Look into them and ask yourself if any of these apply to your behavior:
- Denial. Denial is one of the most common defense mechanisms.
- Repression. There is a fine line between denial and repression when it comes to defense mechanisms.
- Displacement.
Beside above, what are the 7 defense mechanisms? Terms in this set
- Repression. anxiety is reduced by banishing provoking thoughts
- Regression. anxiety is reduced by moving back to a previous psychosexual stage.
- Denial.
- Displacement.
Keeping this in consideration, what is Sigmund Freud’s defense mechanism?
Most notably used by Sigmund Freud in his psychoanalytic theory, a defense mechanism is a tactic developed by the ego to protect against anxiety. 2? Defense mechanisms are thought to safeguard the mind against feelings and thoughts that are too difficult for the conscious mind to cope with.
What are 5 common defense mechanisms?
Primitive Defense Mechanisms
- Denial. Denial is the refusal to accept reality or fact, acting as if a painful event, thought or feeling did not exist.
- Regression.
What Is Repression Psychology
Often times, whether in television, movies, or real life, you hear tales about individuals experiencing some type of trauma and later, having no memory that it happened. This often occurs to people who have been abused, neglected, in an accident, or part of another ordeal. One could have suffered years of abuse or may have been neglected for the greater part of their childhood. The person may have been in a natural disaster, such as a hurricane or earthquake, or may have just been at the wrong place at the wrong time during an act of terrorism. You often wonder about the truth behind these claims. Are they tales, or is there something more legitimate behind them?
Sigmund Freud was an Austrian neurologist denoted as the Father of Psychoanalysis. Freud pioneered psychoanalytic theory in the late 19th century. Psychoanalysis is a clinical approach for treating the human psyche and encompasses a theory of human behavior and personality. Psychoanalytic theory introduced the concept of defense mechanisms, or mental strategies that shield an individual from painful thoughts when they lack mechanisms of coping. A specific defense mechanism and cornerstone of psychoanalysis is the concept of repression. Repression psychology, sometimes termed as motivated forgetting, is the unconscious act of pushing distressing memories, thoughts, and emotions out of the conscious mind when one does not have the capacity to cope with them.
Repression In Contemporary Psychology
Contemporary psychologists most commonly use repression to refer to repressed memorieslife incidents that the individual cannot recall without the assistance of therapeutic tools such as hypnosis. Repressed memory therapy is extremely controversial. In the late 20th century, many therapists utilized hypnosis to help the people they worked with in therapy remember incidents of sexual abuse. In some cases, the abuse turned out to have never happened. People are highly suggestible under hypnosis, and in some cases therapists may have inadvertently suggested memories that never actually occurred.
Mainstream psychologists now argue that repressed memories are very uncommon, and some clinicians argue that once a memory is lost it cannot be recovered.
References:
You May Like: What Are The Three Types Of Research Methods In Psychology
Can Repressed Memories Be Recalled
Repressed memories may sometimes unexpectedly resurface triggered by something associated with them, such as a word, smell or an object. Or, it could be visiting a place or meeting a person that reminds one of a repressed memory.
Retrieving repressed memories may have a therapeutic effect for some people, but for some, especially if the memories are traumatic, it may actually make things worse.
Many therapists use methods such as hypnosis as therapy, to access repressed memories, but there is no scientific evidence to support the efficacy of such therapies.
The therapeutic value of retrieving repressed memories is a controversial concept that created a lot of interest in the late 1900s, when many adults reported memories of childhood abuse they hadnt been aware of until undergoing therapy.
The controversy arises because retrieved memories are not necessarily accurate or reliable. Eminent researchers like Elizabeth Loftus have demonstrated how easily the human mind forms false memories with suggestive questioning. Current scientific thought is that repression and retrieval of traumatic memories may happen, but extremely rarely.
What Does Repression Mean In Psychology
Repression is a defense mechanism in which a person distances themselves from negative thoughts and feelings by barring them from their consciousness. Essentially, its a psychological term for sweeping things under the rug. It happens without trying or realizing.
A person may repress the memories of certain traumatic events or some upsetting feelings, so that theyre completely unaware of their existence. Unlike with sublimation, where negative and inappropriate thoughts are channeled into a positive, productive behavior, repressed thoughts and emotions stay hidden under the surface. However, although they remain concealed from the person, they can still have a powerful damaging impact on all aspects of their life, including relationships.
Recommended Reading: Who Are Paris Jackson’s Biological Parents
In Freuds View How Did Repression Harm Mental Health
Freud believed that repressed material, though unconscious, was still present and could resurface in disturbing forms. As well as a lack of insight and understanding, the inability to process and come to terms with repressed material could lead to psychological problems such as poor concentration, irritability, anxiety, insomnia, nightmares, and depression. He believed that maladaptive and destructive patterns of behavior such as anger and aggression could emerge due to reminders of the repressed material.
Is It Possible To Release Them
If you have trouble expressing or regulating your emotions, talking to a mental health professional is a good first step.
A therapist can help you explore potential causes of repressed emotions and offer guidance and support as you begin to address these reasons.
Therapy also provides a safe space to:
- work on naming and understanding your feelings
- increase your comfort level around talking about emotions
- learn more helpful methods of emotional regulation
Emotionally focused therapy is one approach that may have particular benefit for emotional repression. EFT emphasizes emotional expression as one of the most important components of your personal experience and your ability to relate to others.
According to EFT theory, people who have a hard time accessing and understanding their feelings typically also struggle to enjoy meaningful relationships with others. This approach is often used in couples counseling, but it can also help you work through childhood trauma, depression, anxiety, and other mental health symptoms.
You May Like: Unit 1 Test Geometry Basics Answers Key
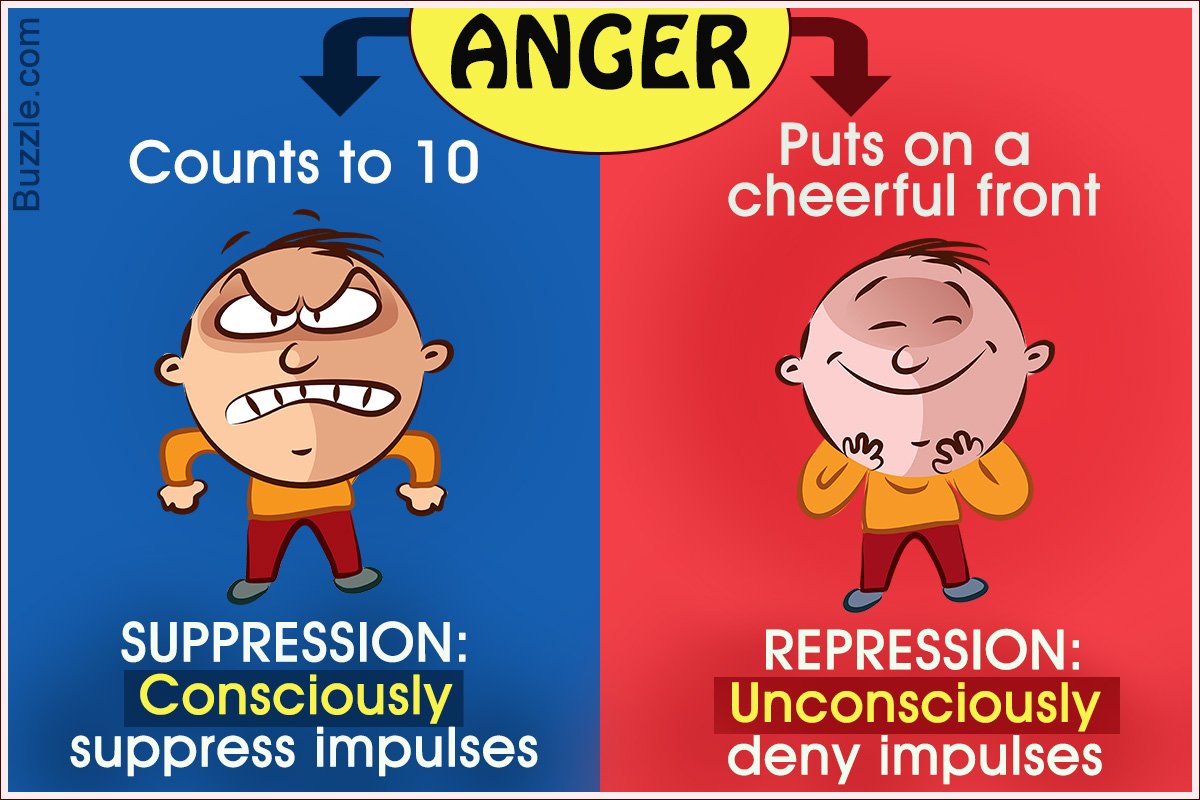
Psychological Repression Is A Defense Mechanism In Which We Unconsciously Push Away Painful Or Traumatic Memories Thoughts Or Desires
This also includes aggressive or sexual urges. We repress these unpleasant thoughts and memories so that we can lead a relatively normal life. Psychological repression is an unconscious act. If we consciously push distressing thoughts to the back of our minds, this is called suppression.
Sigmund Freud was the first person to talk about psychological repression. He believed that many of our physical and mental problems are caused by deeply repressed internal conflicts. Freud used psychoanalysis to uncover these repressed thoughts and feelings.
Freud reasoned that although painful thoughts and disturbing memories were out of the conscious mind, they still had the capacity to cause neurotic behaviour. This is because they remained in the unconscious mind.
Why Does Repression Happen
Repression of memories is thought to happen because they are too overwhelming and distressing to process and come to terms with. Also known as dissociative amnesia, repression of memories may happen because an individual dissociates themselves while undergoing trauma, to be able to survive through it.
Repression of emotions, on the other hand, often happens because expressing them may be perceived as unacceptable behavior socially and culturally. For instance, in many cultures, men are discouraged from expressing sadness or fear, because they are seen as signs of weakness. Anger is a negative emotion that is often repressed.
Also Check: Algebra 1 Honors Eoc Practice Test
Religious Persecution As A Means Of
Religious persecution as a means of repression has been a problem for centuries, and in modern times it is particularly rampant in the country of Nigeria, where thousands of Christians and Muslims have been murdered for their faith. Not one person has been convicted and sentenced in Nigeria for any of these murders during the ten years since the extreme violence initially broke out.
Nigeria is far from alone on this issue. Over two dozen countries participate in religious persecution as a means of repression. For instance, in Egypt, members of the Bahai faith, as well as Muslims, have not only been imprisoned for their religious beliefs but have also been fired from their jobs, kicked out of college, and prohibited from obtaining bank accounts, drivers licenses, and even copies of their own birth certificates.
Further examples of religious persecution as a means of repression can be found in Saudi Arabia, China, India, Afghanistan, Russia, Cuba, Turkey, Venezuela, and Somalia, to name a few. Both China and Iran made headlines for their extreme methods of repressing religion. China implemented tougher security measures and tighter restraints on Islamists in an effort to curb any potential violence that those who followed the religion might engage in and Iran labeled anyone who dared to disagree with domestic politics an enemy of God which is a capital offense in Iran .
Defense Mechanisms: Neuroscience Meets Psychoanalysis
Suppression and dissociation, two psychoanalytic defense mechanisms, are now studied by modern neuroscience
Nothing is so difficult as not deceiving oneself. Ludwig Wittgenstein
How much of what you consciously experience in your daily life is influenced by hidden unconscious processes? This mystery is one of the many that continue to confound our understanding of ourselves. We do not know how conscious impulses, desires or motives become unconscious or, conversely, how unconscious impulses, desires or motives suddenly become conscious.
Advances in technologies such as functional magnetic resonance imaging permit scientists to directly measure brain activity. This ability has led to a revival and reconceptualization of key psychoanalytic concepts, based on the idea of inner forces outside our awareness that influence our behavior. According to psychodynamic theory, unconscious dynamic processes defensively remove anxiety-provoking thoughts and impulses from consciousness in response to our conflicting attitudes. The processes that keep unwanted thoughts from entering consciousness are known as defense mechanisms and include repression, suppression and dissociation.
Evidence of SuppressionLinking suppression to widely accepted brain mechanisms involved in behavioral control moves this concept from the domain of the psychoanalysts couch to the physical realm of the brain.
Note: This article was originally printed with the title, “Neuroscience Meets Psychoanalysis”.
Don’t Miss: Calculate Ihd
What Is An Example Of Denial
Many people use denial in their everyday lives to avoid dealing with painful feelings or areas of their life they donât wish to admit.
For example, a husband may refuse to recognise obvious signs of his wifeâs infidelity. A student may refuse to recognise their obvious lack of preparedness for an exam!
What Can Trigger Repressed Memories

A repressed memory may sometimes be triggered by a stimulus and cause the person to experience a range of physical and psychological difficulties. Triggers can widely vary. They can be anything that the person associated with the traumatic event from their past, including various sensations, like smells, sounds, or sights.
The reaction to the trigger is also individual. For example, it can set off a panic attack, a violent outburst, or severe generalized anxiety. It is helpful for people to recognize their triggers and learn how to retrain themselves to gain control over them, which they can do with adequate psychological support.
Also Check: Did Michael Jackson Have Biological Kids
Psychological Repression And The Case Of Anna O
Freuds first case of psychological repression was a young woman called Anna O . She was suffering from hysteria. She showed signs of convulsions, paralysis, loss of speech, and hallucinations.
There did not appear to be a physical cause for her ailments. She then underwent psychoanalysis. It transpired that she had developed certain hysterical symptoms shortly after caring for her sick father. Once she had uncovered these anxious thoughts, the hysteria vanished.
Other examples of psychological repression:
- A child suffers abuse at the hands of his parents then represses the memories. When this person then goes on to have their own children, they have trouble bonding with them.
- A woman who nearly drowned as a very young toddler may develop a fear of swimming or water. She might have no idea where the phobia came from.
- A student might insult their teacher because they remind him of an abusive parent. He has no memory of the abuse.
- Freudian slips are thought to be good examples of psychological repression. So any errors or slip-ups in a persons speech should be noted.
Psychological repression is a necessary defense mechanism. It shields us from experiencing distressing thoughts on a daily basis. However, Freud believed that problems would occur whenever repression developed under a persons superego in our unconscious mind. If this happened, it could lead to anxiety, antisocial or self-destructive behaviours.
How Do I Deal With An Emotionally Repressed Partner
Emotional repression can take a toll on your romantic relationships. It can result in relationship avoidance, where you are afraid to open up and commit to your partner. If your significant other has repressed feelings, they may have trouble talking about their emotions or realizing what emotion governs their behavior at a given time. Its hard seeing a partner suffering without being able to help them.
Here are a few things that can be helpful:
Also Check: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet
What Causes Regressive Behaviour
Regression is typical in normal childhood, and it can be caused by stress, by frustration, or by a traumatic event. Children usually manifest regressive behavior to communicate their distress. Addressing the underlying unmet need in the child usually corrects the regressive behavior.
Last Review : 15 days ago.
Dont forget to share this post !
References
Everything You Need To Know About Repression
Have you ever felt a strong, almost instinctual, urge to avoid something that other people seem to be okay with? Does it occur time and again in the same place or in a similar situation? This feeling may be a sign that you are dealing with repression. A term originally coined by Sigmund Freud, relating to a form of forgotten memory that is awakened by an outside force, with meaning that has evolved over time just as psychology has.
Read Also: Lesson 9.5 Distance In Coordinate Geometry Answers
What Is An Example Of Repression
Repression may sometimes be confused with suppression, but there is a distinction. Suppression refers to a person consciously pushing away distressing thoughts in order to focus on reality and activities of daily life.
Repression, on the other hand, is unconscious blanking of distressing memories by the brain, a way to cope with painful emotions.
Following are some examples of repression:
- Memories of childhood abuse are often repressed. An individual may not remember the abuse in adulthood, but it can lead to anxiety and difficulty in forming relationships as an adult.
- Phobias, such as the fear of certain animals, are likely the result of a painful encounter with those animals in childhood. The person may not remember the experience, but continues to have an inexplicable fear.
- Slips of the tongue, known as Freudian slips, when people accidentally say something when they want to say something else, may possibly reflect repressed thoughts.
Opd Interview And Stimulus Generation
Participants were asked to write down six emotionally negative and six emotionally positive life events that they could recollect very vividly and that still elicited strong emotions. Then they mailed their document to the interviewer, a trained psychodynamic psychotherapist . The OPD interview was based on the information about these life events. The system of OPD comprises a semi-structured interview based on five axes: axis I , axis II , axis III , axis IV , and axis V . In our study, axes II and III were most relevant for the generation of individualized cue sentences. OPD is an open psychodynamic interview in nature but provides flexible guidelines to ensure that the relevant information is obtained. Details can be found in the recent OPD manual . The interviewer distinguished conflict-related life events from non-conflict related negative and positive life events, and assigned the conflict-related life events to one or more conflict dimensions of the OPD conflict scale . Such conflicts would be expected even in our sample of healthy participants, because the existence of a conflict theme does not necessarily lead to clinically relevant symptoms. More often a conflict leads to sub-clinical tensions and distress, or it becomes integrated into ones everyday life.
TABLE 1. Overview of OPD conflicts .
We did not include neutral sentences in the study design because we wanted to contrast sentences with a similar emotional and cognitive load.
Also Check: College Algebra 6th Edition Mark Dugopolski Pdf
Life Events Conflicts And Free Associations
The OPD interview allowed us to identify typical psychodynamic conflicts. Table 3 gives an overview of the frequency of typical conflict categories , and the number of conflicts per subject. For 19 subjects, 2 conflict themes were found, and for 1 subject, 3 conflict themes were identified. In total, 6 of 7 OPD conflict themes occurred at least once in our sample. We did not find any participants with an identity conflict. Though these conflict themes might appear to some psychoanalytically trained readers more related to early personality than neurotic disorders, it should be noted, that the OPD conflict categories are principally detached from deficits on a structural level. Thus, every conflict theme can be associated with a neurotic or a more disintegrated personality structure. Additionally, in contrast to some views in psychoanalytic theory, repression is defined broadly in our study and hence not only related to neurotic oedipal conflicts.
TABLE 3. Frequency of conflict themes and number of conflict themes per subject .
In the following section we would like to give a brief impression of the experimental stimuli by depicting negative life events, stimulus sentences, and free associations from three subjects.