Development Studies Human Geography And Environmental Planning
- Development studies is a multidisciplinary branch of the social sciences which addresses a range of social and economic issues related to developing or low-income countries.
- Human geography studies the world, its people, communities and cultures, and differs from physical geography mainly in that it focuses on human activities and their impact – for instance on environmental change.
- Environmental planning explores the decision-making processes for managing relationships within and between human systems and natural systems, in order to manage these processes in an effective, transparent and equitable manner.
How Is Geography Used In Environmental Science
Study of Human Impact on the Environment
Geographers study the impact of humans on the environment. , geography is a bridge between the natural and social sciences, uniting the study of the natural environment and the study of human behavior. Geographers look at how human behaviors affect the environment.
Branches Of Social Sciences
If youre interested in this discipline but youre still unable to decide which subject to choose from different branches of social sciences, you dont have to wait up anymore. The below-provided list will help you find the best specialisation of Social Sciences you are more interested in:
Now, lets unravel the salient features of some of the sought-after branches of Social Science:
Read Also: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
Geography’s Relation With Physical And Social Science Disciplines
GeographysRelation with Physical and Social Science Disciplines
While defining geography, we have seen that somebranches of geography have strongest affiliations with subjects likemathematics and environmental sciences, while others have very close connectionwith history and sociology. Some subjects deal with distinctive type ofphenomena while geography examines several kinds of phenomena together. Thediagram gives clear idea about the relationship of geography withother disciplines.
Geography’s Ways Of Looking At The World
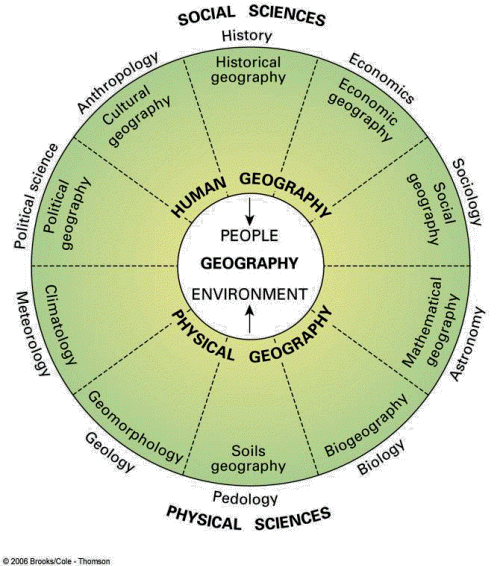
A central tenet of geography is that “location matters” for understanding a wide variety of processes and phenomena. Indeed, geography’s focus on location provides a cross-cutting way of looking at processes and phenomena that other disciplines tend to treat in isolation. Geographers focus on “real world” relationships and dependencies among the phenomena and processes that give character to any location or place. Geographers also seek to understand relationships among places: for example, flows of peoples, goods, and ideas that reinforce differentiation or enhance similarities. Geographers study the “vertical” integration of characteristics that define place as well as the “horizontal” connections between places. Geographers also focus on the importance of scale in these relationships. The study of these relationships has enabled geographers to pay attention to complexities of places and processes that are frequently treated in the abstract by other disciplines.
Integration in Place
Places are natural laboratories for the study of complex relationships among processes and phenomena. Geography has a long tradition of attempting to understand how different processes and phenomena interact in regions and localities, including an understanding of how these interactions give places their distinctive character.
Interdependencies Between Places
Suggested Citation:Rediscovering Geography: New Relevance for Science and Society
Interdependencies Among Scales
You May Like: Do You Capitalize Bachelor’s Degree In Psychology
Human Geography Space And Place
Historiographical studies of human geography outline a disjointed narrative: geography emerged in the early nineteenth century, characterized by environmental determinism and historicism. It became an arm of European imperialism, and fell into a crisis of disciplinary definition until the publication of Richard Hartshornes Nature of Geography in 1939. Hartshorne urged geographers to focus on spatial distributions rather than time. Though some had turned to social interests, the Second World War, the Cold War and McCarthyism in the United States presented significant obstacles. In the 1960s, geography was overcome by technical, statistical and quantitative study and did not return to qualitative methods and a humanistic focus until the 1970s.
Suggesting that places are fundamental in providing a sense of belonging for those who live in them, humanistic perspectives propose a definite but complex relationship between the character of specific places and the cultural identities of those who inhabit them. Against this, materialist perspectives propose that cultural battles create explicit inequalities in the way that space is occupied and used by members of different groups.
Keeping Up With The Journal Literature
Want an easy way to keep up with the journal literature for all facets of Geography? And you use a mobile device? You can install the BrowZine app and create a custom Bookshelf of your favorite journal titles. Then you will get the Table of Contents of your favorite journals automatically delivered to you when they become available. Once you have the ToC’s you can download and read the articles you want.
You can get the app from the App Store or Google Play.
Don’t own or use a mobile device? You can still use BrowZine! It’s now available in a web version. You can get to it here. The web version works the same way as the app version. Find the journals you like, create a custom Bookshelf, get ToCs and read the articles you want.
Read Also: Eoc Fsa Warm Ups Algebra 1 Answers
Low Priority Of Social Science
The social sciences receive less funding than the natural sciences. It has been estimated that only 0.12% of all funding for climate-related research is spent on the social science of climate change mitigation. Vastly more funding is spent on natural science studies of climate change and considerable sums are also spent on studies of impact of and adaptation to climate change. It has been argued that this is a misallocation of resources, as the most urgent puzzle at the current juncture is to work out how to change human behavior to mitigate climate change, whereas the natural science of climate change is already well established and there will be decades and centuries to handle adaptation.
How Geography Is Related With Other Social Sciences
Physical versus of Human Geographygeography is related with other social sciences Geography and history historical events Geography and political scienceWorld citizenship Geography and economicsGeography Geography and geology ideographic traditiongeomorphology Geography and physics-Oceanography geography and its relation with other social sciencessocial scienceshow geography is related with other social sciences
Also Check: What Is Figure Ground Perception Psychology
Additional Fields Of Study
Additional applied or interdisciplinary fields related to the social sciences include:
The origin of the survey can be traced back at least early as the Domesday Book in 1086, while some scholars pinpoint the origin of demography to 1663 with the publication of John Graunt‘s Natural and Political Observations upon the Bills of Mortality. Social research began most intentionally, however, with the positivistphilosophy of science in the 19th century.
In contemporary usage, “social research” is a relatively autonomous term, encompassing the work of practitioners from various disciplines that share in its aims and methods. Social scientists employ a range of methods in order to analyse a vast breadth of social phenomena from census survey data derived from millions of individuals, to the in-depth analysis of a single agent’s social experiences from monitoring what is happening on contemporary streets, to the investigation of ancient historical documents. The methods originally rooted in classical sociology and statistical mathematics have formed the basis for research in other disciplines, such as political science, media studies, and marketing and .
Social research methods may be divided into two broad schools:
Some social theorists emphasize the subjective nature of research. These writers espouse social theory perspectives that include various types of the following:
Careers In Geography And Gis
Geography is not a discipline of endlessly memorizing capitals, countries, rivers, mountain ranges, and more. The discipline is about scientifically analyzing the spatial and temporal distribution, connections, and patterns of the physical and cultural environments we live within.
The following information on careers in geography is from the website of the Association of American Geographers , which is a resource for those interested in pursuing employment in the field of geography.
Many occupations require knowledge of and skills in geography. Geographers work in many different areas, such as environmental management, education, disaster response, city and county planning, community development, and more. Geography is an interdisciplinary field that offers diverse career opportunities.
Many geographers pursue rewarding careers in business local, state, or federal government agencies, nonprofit organizations and schools. Geographers with graduate degrees may become educators in higher education .
Also Check: Fsa Warm Ups Grade 5 Answer Key
Importance Of Social Science
Social Science is a vast discipline which aims to discover the human society and its different constructs and their connection with human relationships. At the same time, it also carries out extensive studies about the manner in which people tend to organize, behave and affect change in the world surrounding them. It tries to reveal underlying social issues that closely form our experiences, which subsequently can clarify a great deal about the functioning of our society. It lies purely within its realm to explain, for instance, the different reasons that contribute to the steep rise in the unemployment graph. It is a fulcrum of the very philosophy according to which governments function and formulate policies.
Class 12 Geography Chapter 1 Ncert Textbook Questions Solved

1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below:
Question 1.Which one of the following statements does not describe geography? an integrative discipline study of the inter-relationship between humans and environment subjected to dualism not relevant in the present time due to the development of technologyAnswer: not relevant in the present time due to the development of technology
Question 1.Which one of the following is not a source of geographical information? travellers accounts samples of rock materials from the moon ancient epics samples of rock materials from the moon
Question 1.Which one of the following is the most important factor in the interaction between people and environment? human intelligence
Which one of the following is not an approach in human geography? Areal differentiation
2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words:
Question 2.Define human geography.Answer:Human geography is defined as the relationship between the physical/ natural and the human worlds, the spatial distribution of human phenomenon and how they come about, the social and economic difference between different parts of the world. According to Ratzel Human geography is the synthetic study of relationship between human societies and earths surface.According to Ellen C. Semple Human geography is the study of the changing relationships between the unresting man and unstable earth
3. Answer the following questions in 150 words:
Read Also: Which Founding Contributors To Psychology
Is Geography A General Science
Indeed, geography degrees are some of the most varied out there its more apt to consider this as a broad academic field, rather than a single subject. In general, geography is considered a science which attempts to explain the world around us and the impact of both natural and manmade factors and events.
What Do Geographers Study
What is a Geographer? A geographer studies the earth and its land, features, and inhabitants. They also examine phenomena such as political or cultural structures as they relate to geography. Geographers study the physical or human geographic characteristics or both of a region, ranging in scale from local to global.
You May Like: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet
Tamilrulers And Geographic Knowledge
History reveals to us that how the Great rulers like Raja Raja Cholaor Rajendra Chola had trade relations with other countries of the world,especially South Asian countries by understanding the relief, seasons, oceancurrent movements etc., The sailors would have been experts in every aspect ofgeography to move their troops, sail overseas and trade with all known nationsof that time. They also utilised the ocean currents to transport teak and othervaluable timbers from Indonesia, Myanmar, and other countries to South India.
Economics Management And Business Studies
- Economics seeks to understand how individuals interact within the social structure, to address key questions about the production and exchange of goods and services.
- Management and business studies explores a wide range of aspects relating to the activities and management of business, such as strategic and operational management, organisational psychology, employment relations, marketing, accounting, finance and logistics.
Don’t Miss: Is Paris Jackson Michael Jackson’s Biological Child
Society For Conservation Biology
Department of Geography and Regional DevelopmentUniversity of Arizona
The fields of human and physical geography, though they developed together over centuries since antiquity, have recently become distinct subfields with human geography dedicated to the study of human activity, culture, politics and economics within its spatial and environmental context. Within human geography a range of subfields are dedicated to elements of the environment/society interface, including risk and hazards science, cultural and political ecology, water resource geography, land use and cover change science, and the human dimensions of global change. All of these share an integrative perspective on the mutual influences between humans and non-human systems and actors.
Environment/society research and theory in human geography
Human Geography and Conservation
Though the field of human geography is therefore diverse and dynamic, the last hundred years has provided a template of somewhat common understandings, all relevant for contemporary conservation problems:
While some of the work operates in direct support of conservation efforts providing ethnographic and spatial data for informed planning, a significant body of work seeks to critically evaluate the problems and limits of conservation efforts, assessing both direct interventions as well as the assumptions and philosophies underlying them.
Useful references on environment/society traditions in Human Geography
Social Policy And Social Work
- Social policy is an interdisciplinary and applied subject concerned with the analysis of societies’ responses to social need, focusing on aspects of society, economy and policy that are necessary to human existence, and how these can be provided.
- Social work focuses on social change, problem-solving in human relationships and the empowerment and liberation of people to enhance social justice.
Don’t Miss: Geometry Dash Hack No Survey
Why Is Geography An Environmental Geography
Environmental geography represents a critically important set of analytical tools for assessing the impact of human presence on the environment by measuring the result of human activity on natural landforms and cycles. By its very nature geography is a discipline that seeks to integrate and synthesize knowledge.
Is Geography A Bsc Or Ba
Conclusion. The major difference between the two is the area of focus, while a Bachelor of Arts in Geography guides a student down more of a Humanities and Social Science role, a Bachelor of Science guides students down physical and natural sciences which then branches on to various sub-fields in Geography.
You May Like: Which Founding Contributors To Psychology Helped Develop Behaviorism
Why Choose This Course
UOW Social Sciences is an innovative discipline giving you expertise in research, and practical knowledge of social systems and practices in diverse environments. Our Social Science academics are at the forefront of their specialisations. They’re accredited professionals, published authors and respected researchers who are connected to their professional research networks. They take all this experience with them to the classroom to enrich and guide your learning experience.
Geography: Science Or Social Science
Geography a word derived from the Greek word geographia which means earth description has been long considered as one of the fundamental subjects in education system right from the beginning of the system. A subject that is unique in bridging the social and physical aspects of the globe.
Stories about princes being taught geography when they were young, be it Alexander from Greece or Ashoka from India are well known. It is one of the most important subjects that an educated person and more importantly a future king needed to know. Geography knowledge was seen as a vital to survival and success.
Coming back to the Present 2013! We see GIS and Location based applications being used ubiquitously.
In India, GIS is being actively employed by the electricity department to keep track of their installations and to help in maintenance. The cops in the country are now getting GPS fitted vehicles to keep track of their resources and help maintain Law and Order. These are just well known applications of Geography.
Ill leave the how to improve Geography awareness question to the experts, the question that I have in mind
Are we correct in categorizing Geography as a social science and not as a Science?
A subject that studies physical phenomenons and interaction between different elements cannot be limited to be called Social Science. Geography is not just a Social Science, it is Science with a social element to it.
Recommended Reading: Do I Capitalize Bachelor’s Degree In Psychology
Space Place And Scale In Past And Present
Underpinning many articles in Past and Presents earliest issues is an unspoken agreement with the nation-state as container of historical process. These articles often expose this tendency within their title, including the name of the nation along with an indication of the period studied. While this tendency reflects practical intra-disciplinary divisions , it also reveals a tacit agreement that national borders delimit bounded spaces within which social and economic practices unravel.
Nonetheless, in these early issues of Past and Present, there are deviations from this pattern. The most obvious divergences occur in articles focused on the pre-national period in Europe, which refer, instead, to regional designations of space. In these articles, the focus is on the process studied, often interpreted through the lens of social class. These studies do not emphasize local meaning, but instead treat the space within which processes occur as absolute. Eric J. Hobsbawms work in this early period deserves special mention, as his work focused on social processes that crossed national borders, giving more importance to the role of class than to the national space within which it existed.
As such,