Cited And Additional Bibliography:
1 StatisticsTimes.com. 2019. Countries by Population Density 2019. Statisticstimes.Com. 2019. http://statisticstimes.com/demographics/countries-by-population-density.php. UN .
2 Birth Rate Country Comparison. 2019. Www.Indexmundi.Com. January 1, 2019. https://indexmundi.com/g/r.aspx?t=0& v=25& I=en.
3 Death Rate Country Comparison. 2019. Www.Indexmundi.Com. January 1, 2019. https://indexmundi.com/g/r.aspx?t=0& v=26& I=en.
4 Population Country Comparison Total Fertility Rates. 2019. Www.Indexmundi.Com. January 1, 2019. https://indexmundi.com/g/r.aspx?v_31.
5 List of Countries by Net Migration Rate. 2020. Wikipedia. May 28, 2020. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_countries_by_net_migration_rate#cite_note-2.
GREY Perspective. n.d. Population Pyramid by GREY Perspective from the Noun Project. Accessed June 3, 2020. https://thenounproject.com/search/?q=population%20pyramid& i=2305354.
Grover, Drew. 2018. What Is the Demographic Transition Model? Population Education. November 16, 2018. https://populationeducation.org/what-demographic-transition-model/.
Population Pyramids of the World from 1950 to 2100. 2019. PopulationPyramid.Net. 2019. https://www.populationpyramid.net.
Previous/next navigation
How To Write An Introduction To Human Geography
Introduction to Human Geography Ques 1 . Describe Nature scopes and Approaches of Human Geography. Also give a brief account of different schools of Human Geography. Ans. Human Geography: Nature, Scope, Schools & Approaches. Human Geography: The study of man and his adjustments to natural environment is known as human geography.
Developmental And Reproductive Toxicity
Reproductive Inhibition
Fertility of breeding females may be adversely affected by xenobiotics with estrogenic activity. Sources of such xenobiotics to livestock include subterranean clover , and the mycotoxin zearalenone . Medicago sativa produces coumestrol, which has a weak estrogenic effect, and is suspected of causing infertility in livestock.
Abortifacient Agents
Consumption of Cupressus macrocarpa is well-recognized cause of bovine abortions in both Australia and New Zealand. Other abortifacients to which domestic animals may be exposed include ergot alkaloids .
Teratogenic and Fetotoxic Agents
Many xenobiotics cross the placenta, and some may cause developmental abnormalities in the embryo or fetus. As a generalization, if a xenobiotic has shown to be teratogenic or fetotoxic in one species, it is considered likely to cause deleterious effects in the embryos or fetuses of other species, although the target organ/s may not be the same, and the window of sensitivity is likely to differ.
There are relatively few teratogens known to affect the common domestic species. Dietary teratogens and fetotoxic xenobiotics relevant to Australia and New Zealand are presented in Table 5.4. This list should not be regarded as exhaustive.
Table 5.4. Dietary Teratogens and Fetotoxicants of Domestic Animals in Australia and/or New Zealand
| Teratogen or Fetotoxin |
|---|
Daniel Campbell, in, 2020
Also Check: How Much Physics Is On The Mcat
Key Factors Influencing Population Change
Three key factors to understand when trying to predict or analyze population change are the total fertility rate, infant mortality rate, and life expectancy at birth. Total fertility rate is the average number of children a woman would be expected to have during childbearing years . The global average for TFRs is about 2.5, but in less developed countries, it is as high as 5.0 or higher, and in more developed countries, it is as low as 2.0 or less. Fertility patterns can vary widely within countries. Racial and ethnic minorities may have higher fertility rates than the majority, and families with low incomes or low levels of education typically have more children than those that are affluent or well-educated. Women who work outside the home typically have fewer children than those who stay home, and rural families tend to have more children than city dwellers. In 2016, the number of births per 1,000 people worldwide was 20, with extremes ranging from a low of 8 or 9 , to 60 or more in a few West African nations .
Previous/next navigation
Total Period Fertility Rate
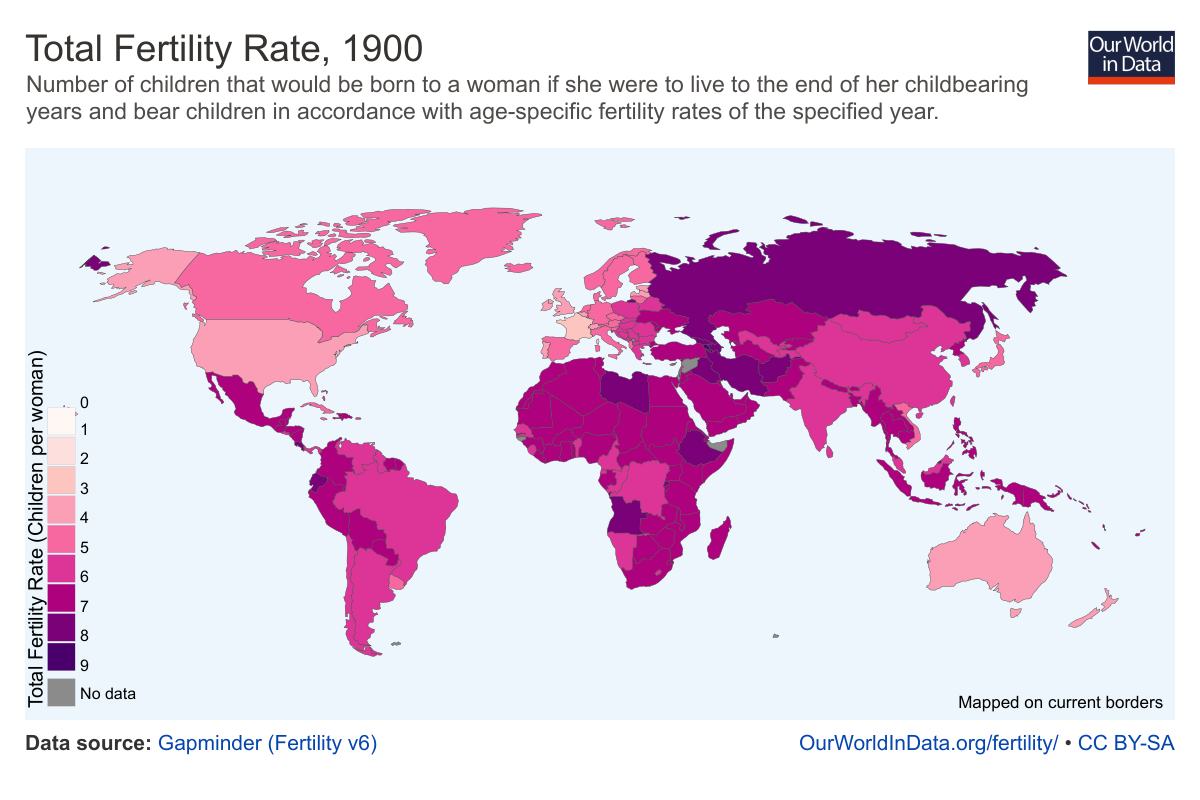
The TFR is a better index of fertility than the crude birth rate because it is independent of the age structure of the population, but it is a poorer estimate of actual completed family size than the total cohort fertility rate, which is obtained by summing the age-specific fertility rates that actually applied to each cohort as they aged through time. In particular, the TFR does not necessarily predict how many children young women now will eventually have, as their fertility rates in years to come may change from those of older women now. However, the TFR is a reasonable summary of current fertility levels. TFR and long term population growth rate, g, are closely related. For a population structure in a steady state, growth rate equals log/Xm, where Xm is the mean age for childbearing women.
The TPFR is affected by a tempo effectâif age of childbearing increases then while the age of childbearing is increasing, TPFR will be lower , and then the age of childbearing stops increasing, the TPFR will increase even though the life cycle fertility has been unchanged. In other words, the TPFR is a misleading measure of life cycle fertility when childbearing age is changing, due to this statistical artifact. This is a significant factor in some countries, such as the Czech Republic and Spain in the 1990s. Some measures seek to adjust for this timing effect to gain a better measure of life-cycle fertility.
Recommended Reading: How To Calculate Net Force
What Is The Global Average Tfr
According to World Bank data, the global fertility rate was 2.4 children per woman in 2019. This rate is approximately half of what it was in 1950 , and more economically developed countries such as Australia, most of Europe, and South Korea, tend to have lower rates than do less-developed or low-income countries.
Why Spatial Analysis Is Important
Spatial analysis allows you to solve complex location-oriented problems and better understand where and what is occurring in your world. It goes beyond mere mapping to let you study the characteristics of places and the relationships between them. Spatial analysis lends new perspectives to your decision-making.
Also Check: Core Connections Algebra Chapter 1 Answers
Why Do Females Live Longer
Yet women continue to live longer than men, suggesting the biological differences also have a role. Experts shave said the gap is due to a combination of biological and social differences. Mens hormone testosterone is linked to a decrease in their immune system and risk of cardiovascular diseases as they age.
Rate Of Natural Increase
- The rate of natural increase is also an annual statistic which estimates the percentage of population growth of a country for each year.
- To find the RNI, youll need the CBR and CDR and heres the formula: RNI = /10
- Additionally, it is also possible to have a negative RNI, as the rate of deaths can outnumber the rate of live births in a country, especially for the highly developed ones.
- For instance, Russia is undergoing a population decline, as seen with its own negative RNI, which is due to a large elderly population and fewer number of women wanting to have children in Russia.
- The RNI is also indicative of a countrys development and current population situation.
- However, it does NOT take into account immigration/emigration. Thus, the RNI doesn’t accurately predict population growth, so it is only an estimate.
Also Check: Geometry Dash World Vault
How Do You Write A Geographic Analysis
Writing reports or essays for Geography 360
Whats The Replacement Rate For Women In The World
If a larger percentage of female are born than males, it will reduce the replacement level. The widely accepted replacement level rate is 2.1 births per female for industrialized countries. If there were no deaths before age 45, then the replacement rate would be 2.0.
What is replacement rate in human geography? Replacement rate is the number of children that a couple would have to have over the course of their reproductive years in order to replace themselves. Countries that have a higher total fertility rate compared to their replacement ratethe population growth will be positive. What is CBR in
Read Also: Glencoe Geometry Concepts And Applications Practice Workbook Answers
How Is The Replacement Rate Related To Population Growth
Replacement rate is the number of children a woman needs to have in order to maintain the current population levels of her family, or what is known as zero population growth. In other words, replacement-level fertility exactly replaces a woman and her partner for a net loss of zero when she and the father of her children die.
Distribution Of The Worlds Population
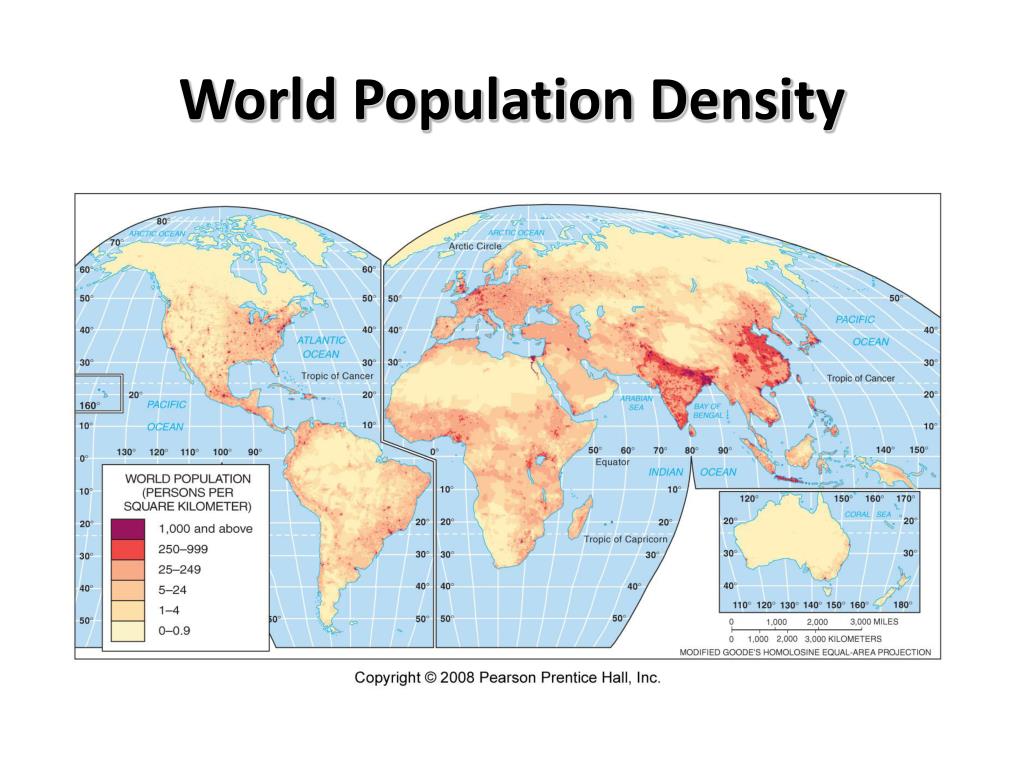
Economist Jeffrey Sachs, director of the Earth Institute at Columbia University, believes that there are two reasons why the global population and extreme poverty occur where they do:
- Capitalism distributes wealth to nations better than socialism or communism
- Geography is a significant factor in population distribution in relationship to wealth
For example, the population tends to be lower in extreme environments such as arid climates, rainforests, polar or mountainous regions. Another example is a nation that has a large body of water within its boundaries or has large mineral deposits or resources that are likely to have more wealth and a larger population.
Humans only occupy five percent of the Earths surface because oceans, deserts, rainforests, and glaciers cover much of the planet . The term for areas where humans permanently settle is ecumene. Population growth and technology dramatically increase the ecumene of humans, which affects the worlds ecosystems.
Additionally, regions that are too cold pose problems for large population clusters and food production. The cold Polar Regions have a short growing season, and many of the Polar Regions have limited amounts of moisture because they are covered by high- pressure systems . Thus, cold polar regions are defined by temperature and lack of moisture, despite access to snow, ice, and glaciers. Mountainous and highland regions lack population clusters due to steep slopes, snow and ice cover, and short growing seasons.
Read Also: Core Connections Algebra 2 Chapter 1 Answers
What Is The Lowest Birth Rate In The World
Cyprus has the lowest birth rate in the world Cyprus has the lowest fertility rate in the world, research just published in the Lancet has found. Cypriot women are having on average just one child in their lifetime, way below the replacement level of roughly 2.1. The numbers vary substantially across countries and over time.
What Is The Influence Of Tfr On Population
Generally speaking, when the TFR is greater than 2.1, the population in a given area will increase, and when it is less than 2.1, the population in a given area will eventually decrease, though it may take some time because factors such as age structure, emigration, or immigration must be considered.
Recommended Reading: 4 Goals Of Psychology Example
How Is Zero Population Growth Achieved In The Long Term
Ehrlich stated: The mother of the year should be a sterilized woman with two adopted children. In the long term, zero population growth can be achieved when the birth rate of a population equals the death rate, i.e. fertility is at replacement level and birth and death rates are stable, a condition also called demographic equilibrium.
What Is Total Fertility Rate In Human Geography
total fertility ratetotal fertility ratetotal fertility rate
. Just so, what is the meaning of total fertility rate?
Total fertility rate. Definition: The number of children who would be born per woman if she/they were to pass through the childbearing years bearing children according to a current schedule of age-specific fertility rates. The TFR is calculated as: TFR = ASFR a
Beside above, what are the measure of fertility? These measures are Child-women ratio Crude birth rate General fertility rate Age specific fertility rate Total fertility rate Gross reproduction rate Net reproduction rate and Cohort fertility rate.
Hereof, what is fertility rate in geography?
The Pampas supports both farming and ranching. Human Fertility. For demographerspeople who study population statisticsfertility means the number of live births occurring in a population. The general fertility rate is the number of live births per 1,000 women of childbearing age in a given year
What does a total fertility rate of 2.1 indicate?
Generally speaking, when the TFR is greater than 2.1, the population in a given area will increase, and when it is less than 2.1, the population in a given area will eventually decrease, though it may take some time because factors such as age structure, emigration, or immigration must be considered.
You May Like: Is Physics Harder Than Math
G The Demographic Transition Model
Aging Populations: A Comparison Between Japan And Germany
When comparing population trends of Japan and Germany, numerous similarities stand out. Both countries have an identical total fertility rate per woman of 1.4 with a population growth rate of -0.2 percent . While both countries have high life expectancies, Japans eighty-five-year life expectancy is among the worlds longest, leading to a higher elderly dependency ratio in 2017 . Similarities between the countries related to below-replacement-rate population growth, aging-related pension and health care challenges, and pronatal policies place the countries on a similar population trajectory. When analyzing historical, economic, and social/cultural factors behind demographic similarities, different paths toward population decline emerge. Additionally, the countries vary in their views of international migration as a population stimulus. The analysis provides classroom activities that directly align with the College Board AP Human Geography course description. The comparison and suggested classroom activities could also augment any course addressing current demographic issues at the high school or undergraduate levels.
GERMANY
CONCERNS, RELATED TO THE SOCIAL SYSTEM
GERMANYS PRONATAL POLICY
GERMAN PERSPECTIVES TOWARD MIGRATION
JAPAN
ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL FACTORS BEHIND DECLINE
IMPACTS OF POPULATION DECLINE
JAPANS PRONATAL POLICY
CLASSROOM USE
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS
AP HUMAN GEOGRAPHY FAQS OR ESSAY QUESTIONS
You May Like: What Influence Did Geography Play In The Development Of Greek Society
What Is Tfr In Human Geography
Sex ratio The number of males per 100 females in the population. Total fertility rate The average number of children a woman will have throughout her childbearing years. Zero population growth A decline of the total fertility rate to the point where the natural increase rate equals zero.
What Is Total Fertility Rate
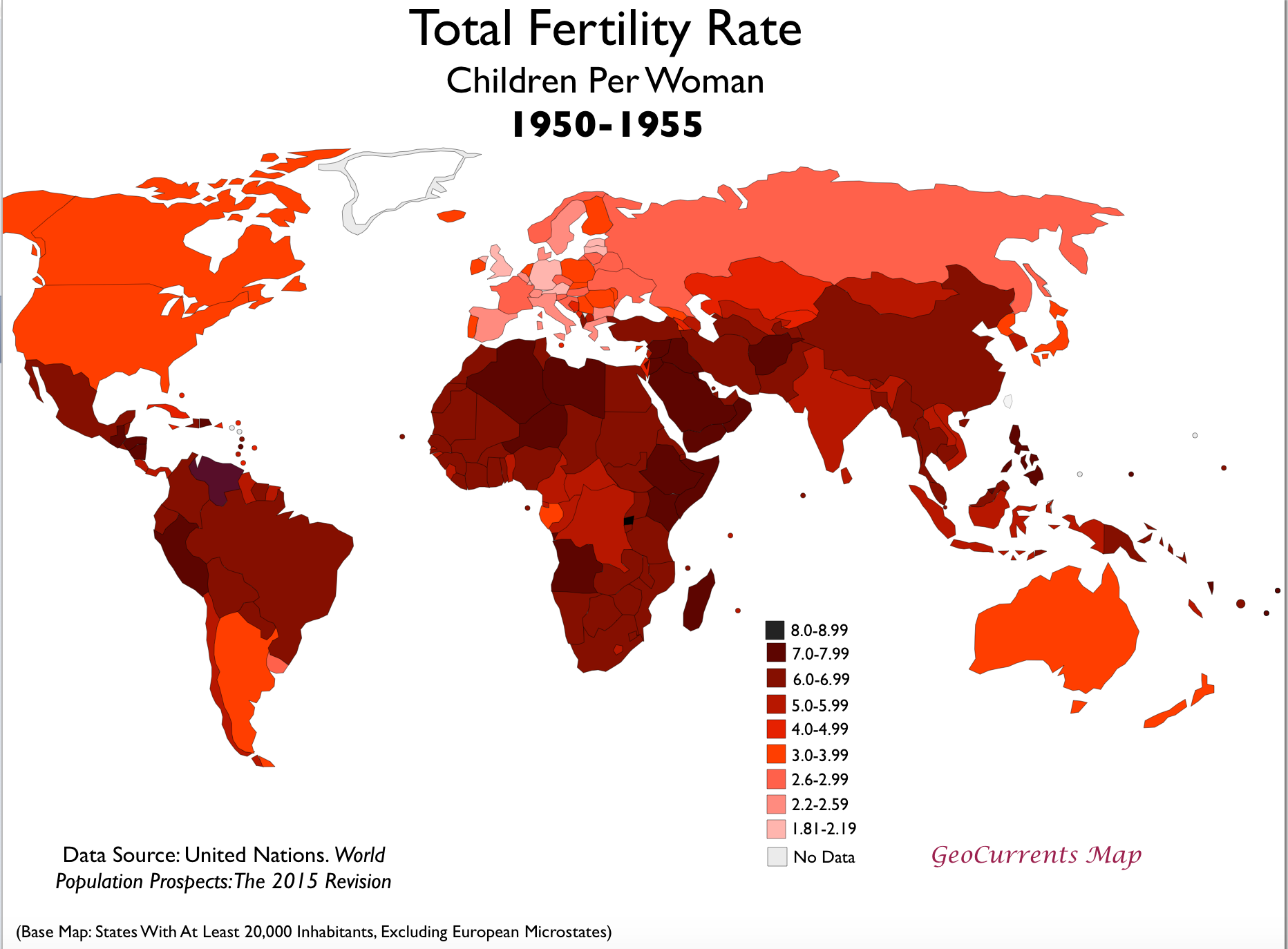
December 30, 2014
According to the Population Reference Bureau, Total Fertility Rate is defined as, the average number of children a women would have assuming that current age-specific birth rates remain constant throughout her childbearing years. Simply put, total fertility rate is the average number of children a woman would have if a she survives all her childbearing years. Childbearing years are considered age 15 to 49.
The total fertility rate can be calculated using age-specific birth rates. An age-specific birth rate is the number of babies born within a 5-year increment during reproductive years. The TFR is the calculation of adding up all the age-specific birth rates for a population and multiplying by five. While the TFR gives a good picture of current fertility rates of a place or a population, the TFR wont actually predict how many children a woman will have because its an average different things will factor into this for different women location, decisions to wait to have children, etc.
Check out the World Population Data Sheet to see total fertility rates around the world, by region and country.
Image Source: Population Bulletin Vol. 62, No. 1 March 2007.
Recommended Reading: Does Michael Jackson Have Biological Children
History Of Total Fertility Rate And Projections For The Future
From around 10,000 BC to the beginning of the Industrial Revolution fertility rates around the world were high by todayâs standards, but the onset of the Industrial Revolution, around 1800, brought about what has come to be called the Demographic Transition, and TFR began a long-term decline in almost every region of the world, a decline that continues to this day.
Before 1800
Because all nations before the Industrial Revolution were caught in what is now labeled the âMalthusian Trapâ, improvements in standards of living could only be achieved by reductions in population growth through either increases in mortality rates or reductions in birth rates.:76However, at the same time, other realities such as child mortality, that could reach 50%, and the need to produce workers, male heirs, and old-age care givers required fertility rates to be high by todayâs standards.
For example, fertility rates in Europe in the years before 1800 ranged from 4.5 to 6.2 . :76 The Total Fertility Rate in America in 1800 was 7.0. Fertility rates in Asia during this period were similar to those in Europe.:74 In spite of these high fertility rates, global population growth was still very slow, about 0.04% per year, mostly due to high mortality rates and the equally slow growth in the production of food.
1800 to 1950
1950 to the present and projections
| World historical TFR |
| Years |
Is The Population Growth Going To Slow Down
Most geographers and demographers agree that over the course of the twenty-first century, the population growth will slow considerably. This is based on the belief that the current rapid population growth is an anomaly in Earths history and that the planet cannot sustain such rapid growth for another century.
Also Check: Figure And Ground Psychology
What Is Nir In Ap Human Geography
4.8/5NIRNIRread here
In 2018, rate of natural increase for WORLD was 10.82 persons per thousand population. Rate of natural increase of WORLD fell gradually from 20.38 persons per thousand population in 1969 to 10.82 persons per thousand population in 2018.
Similarly, how is Nir computed? In demography, the rate of natural increase is a statistic calculated by subtracting the crude death rate from the crude birth rate of a given region. This rate gives demographers an idea of how a certain country’s population is growing. A country’s RNI can help determine which stage of the DTM they are in.
Similarly one may ask, what is Ecumene in AP Human Geography?
The geographic term ecumene is used to describe land that is permanently populated by human society. It can also refer to industrial and agricultural land that is permanently used to sustain the human population.
What are the 2 big breaks in the demographic transition and what were their causes?
Identify the two big breaks and their causes. The first break: the sudden drop in the birth rate that comes from technological innovation. The second break: the sudden drop in the birth rate that comes from changing social customs. Low CBR and an increase in CDR thus a negative NIR.