What Is The Future Of Gis Technology
Beacon Dodsworth have spent more than 25 years working with GIS technology and in this time we have seen major improvements in interface, processing power and functionality.
GIS use was initially limited to a dedicated environment, ideally on a powerful, or preferably a network of powerful computers and operated by trained specialists. Nowadays GIS are more manageable, so that anyone with a desktop PC can run a robust form of GIS, such as our own Prospex software. Recently the internet has developed the data bandwidth to support online GIS tools, as such we have developed our online MapVision product. MapVision offers accessible, resource-light GIS functions without the need to host any software locally. This opens up geographical analysis and location intelligence to smaller businesses who wouldn’t previously have had the resources or expertise to benefit from such valuable insight.
GIS technology is still in its infancy and is a rapidly developing field. With data collection increasing, and an increasingly global outlook in all fields, a tool to help to make this data understandable, and put it in context, is more valuable than ever. A GIS is a great way to avoid data overload and make the most informed decisions from large datasets, so its place in business and beyond is assured.
What Do Gis Maps Mean
GIS digital maps can be easily shaped for the purpose or analysis needed according to geographic or non-geographic data.
Different types of maps can be produced with various data layers in GIS. GIS maps are especially used for visualizing and displaying the analyzes and studies on the screen or printing. With smart mapping, updating the data on the map, adding and removing new data can be done easier.
- GIS maps are used to compare the effects of human activity on nature.
- GIS maps are used to predict settlements that will be damaged in natural disasters or to identify and visualize risky areas.
- Information such as the average income of a particular region, book sales or voting numbers can be associated. Even presentations and analyzes can be made by creating thematic maps based on this data.
- GIS maps can be used to show information about numbers and density. For instance, it can show how many doctors are in a particular region compared to the population.
- Changes of many events over time can be revealed with GIS technology. Comparative maps can be created to examine issues such as advancement or retraction of ice cover in polar regions and how this event has changed over time.
- Spatial information of the area of study can be displayed with GIS maps.
- GIS maps are used in determining the value, boundaries, ownership and characteristics of the cadastral land in a certain region, keeping and managing the legal status records.
Gis Is A Computer System That Captures Stores Checks And Displays Information Related To Positions On Earths Surface
The ability to link maps digitally to information enables us to visualize and understand patterns and relationships around us. Geographic information systems, or GIS, provides this link. GIS is a computer system that captures, stores, checks, and displays information related to positions on Earthâs surface. It helps analysts and scientists study climate change, sea level rise, land use planning, business, and even our nationâs defense.
You may be surprised to learn how much geography matters in our everyday lives. The ability to link maps digitally to information enables us to visualize and understand patterns and relationships around us. Geographic information systems, or GIS, provides this link.
Did you know?
Each year, we celebrate GIS Day in November as part of Geography Awareness Week. GIS Day started in 1999 as an educational event for GIS users to showcase their projects that have real-world applications. Opening their doors to schools, businesses, and the public, GIS users and vendors demonstrate the benefits of GIS and how it makes a difference in our society. Today, GIS Day is recognized globally with events occurring in dozens of countries.
More Information
Also Check: How To Get Demon Keys In Geometry Dash
Data Output And Cartography
Cartography is the design and production of maps, or visual representations of spatial data. The vast majority of modern cartography is done with the help of computers, usually using GIS but production of quality cartography is also achieved by importing layers into a design program to refine it. Most GIS software gives the user substantial control over the appearance of the data.
Cartographic work serves two major functions:
First, it produces graphics on the screen or on paper that convey the results of analysis to the people who make decisions about resources. Wall maps and other graphics can be generated, allowing the viewer to visualize and thereby understand the results of analyses or simulations of potential events. Web Map Servers facilitate distribution of generated maps through web browsers using various implementations of web-based application programming interfaces .
Second, other database information can be generated for further analysis or use. An example would be a list of all addresses within one mile of a toxic spill.
An archeochrome is a new way of displaying spatial data. It is a thematic on a 3D map that is applied to a specific building or a part of a building. It is suited to the visual display of heat-loss data.
Drive Decisions With Spatial Analysis
Never before have we had more pressing issues in need of a geospatial perspective. For example, climate change, natural disasters and population are all geographic in nature. These global issues need location-based knowledge that can only come from a GIS.
Most people think GIS is only about making maps. But we harness the power of GIS because of the insights of spatial analysis. We use spatial analysis through math in maps. Spatial analysis is difficult with paper maps so thats why we need GIS. Here are examples of spatial analysis:
BUFFER:
The buffer tool generates a polygon around features at a set distance. By creating buffers, you can find the surrounding features that are within buffers.
HOT SPOT:
Hot spots highlight areas that have clusters of points. Whereas cold spots have a small density of points.
Read Also: Definition For Movement In Geography
Examples Of Google Earth Gis Lessons And Activities
The Warm-up Passports lessons in Google Earth require teachers to use the “Iâm Feeling Lucky” and Street View in Google Earth âto randomly select a location in the world and then relate that location to a disciplinary concept.â The Warm-up Passports can be used for different subjects and grade levels in making cross-curricular connections. Examples include:
- Math Grade 5: Double the area of this location. Write the new area in square feet. If the area of this location was divided in half, what would the size of each part be in square feet?
- Math Grade 7: Research the average annual temperature in this location for last year. Scientists predict that temperatures will increase by 6% globally this year. Write two equivalent expressions to represent this change.
- Social Studies Grade 6: Research the biggest industry of this location. What does that tell you about how people make a living there?
- Social Studies Grade 8: What transportation services are available in this location?
- ELA Grades 6-8: Identify or research one example of how humans have changed the physical environment of this location. Overall, was this change positive or negative? Use specific details to support your answer. Write a poem about the physical characteristics of this location that includes the following elements: rhyme scheme, alliteration, and stanzas.
What Can A Gis Be Used For
The potential applications of analysing trends or features in an area are very broad. Globally, people use GIS to look at climate, migration, and economic trends. Nationally people look at population changes, social trends, and crime patterns, whilst locally the scope for detailed analysis of any feature is possible. Here are a few examples of the uses you could put a GIS to, taken from our own experience in the commercial and private sector
You May Like: Homework 4 Angle Addition Postulate Answers
Disease Surveillance Outbreak Investigation And Syndromic Surveillance
GIS has a long history of providing support to traditional disease surveillance. Most electronic disease surveillance systems now include a mapping module so that analysts and public health leaders can visualize disease outbreaks on the map. When an outbreak is detected and public health personnel go into the field for additional investigation, GIS strengthens local data collection, management, and analysis. From the beginning, GIS provides a baseline for monitoring and evaluating outbreak investigation activities. Mobile GIS allows field personnel to leverage GPS
devices to navigate more efficiently and quickly to locations for data collection. This is critical when time is of the essence. Surveillance of case locations is maintained more effectively, so the geographic progression of the disease is continually monitored. High-transmission areas or areas with environmental conditions ideal for disease vectors are more easily identified when field staff have maps, imagery, and descriptive metadata at their fingertips.
With accurate location information, GIS can provide spatial visualization of complex relationships between cases, contacts, and objects in the environment in both time and space. Spatial visualization helps in identifying disease sources and the best implementation of countermeasure and response strategies.
Gis For Education Policy
GIS helps students think critically about authentic problems by using real-time data, but there are other educational applications. A GIS can support large and small school districts in decision and policy making. For example, a GIS can provide district administrators and community safety experts the information about school buildings and surrounding areas to design and manage safety programs. In other examples, GIS data analysis of the community’s transportation infrastructure can help streamline bus routes. When communities experience population shifts, a GIS can help districts in making decisions about building new schools or when to close old ones. The GIS can also provide school district administrators with tools to visualize patterns in student needs in attendance, academic achievement, or after-school support.
Read Also: Does Michael Jackson Have Biological Children
What Is Gis Mapping
GIS mapping produces visualizations of geospatial information. The 4 main ideas of Geographic Information Systems are:
- Create geographic data.
- Manage it in a database.
- Analyze and find patterns.
- Visualize it on a map.
Because viewing and analyzing data on maps impacts our understanding of data, we can make better decisions using GIS.
It helps us understand what is where. The analysis becomes simple. Answers become clear.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Gis
Below are the advantages and disadvantages :
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| It can process multiple data formats and data sets. For example, Satellite images, vector data points like coordinates, latitude, and longitude drive files from drones and high sensors cameras. | GIS often requires trained candidates from the field of Geology, bioinformatics or Information technology. Non GIS person will end up ruining the setup completely. |
| GIS can be integrated with various hardware and software to create a robust environment. | It is incomplete without the available meaningful spatial datasets and databases. |
| This system can analyze past data sets and analytics on future predictions based on the trends. | People and organizations complain about GIS being very expensive for implementing and integrating. |
| It is used for natural resource management by analyzing, managing, and monitoring natural hazards. | It requires a large amount of data to be inputted into the system, and hence, there are more chances of errors. |
| It is highly efficient when it comes to data collection, processing, and visualization. | Most of the time organizations fail to implement fully functioning GIS. |
| It allows easy record keeping of geographical changes for further analysis. | Data privacy and integrity is an important asset of GIS. It has more risks when it comes to privacy violation. |
You May Like: Is Michael Jackson Paris Biological Father
Health / Medical Resource Management
GIS is vital to the proper planning and analysis of the provision of cancer services for the UK socialised healthcare system, the NHS . The package is used to plan and examine a number of issues including catchment areas for GP surgeries. A study recently found that there was greater provision for cancer treatment in the midlands than the actual population. Such maps are used to better manage resources of the NHS.
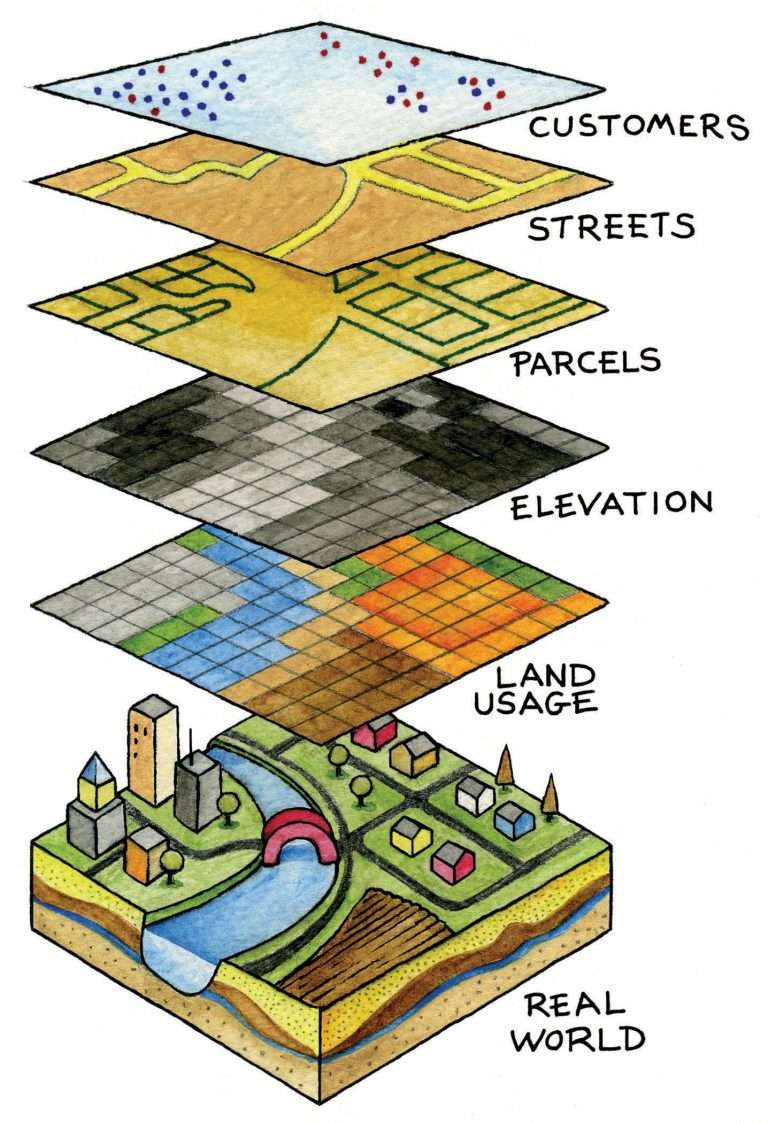
What Kind Of Data Will I Find In A Gis
You will always find a minimum of two types of data in GIS software. The first is raster data which is, in simple terms, the large images or maps upon which to overlay your data. Because our own specialism is UK business data, our raster data tends to come from or , as their road network and infrastructure maps give the perfect amount of data for business, network, or customer analysis. Another GIS, focussed on geology for example, might use topographical maps, aerial photographs, three dimensional imagery, or even Lidar images as its rasters.
The second type of data is vector data. Vectors map geographical locations in a geometric way that means they can be processed accurately by computer. They can be used to analyse details on maps such as road and rail networks, postcode or administrative boundaries, and coastlines. This vector data, allows a GIS to map a users own unique data into a geographical context, whilst the rasters allow it to be displayed in an attractive and user-friendly way.
On top of the two core data building blocks of rasters and vectors, you will of course put your own data for analysis, often called attribute data. In the context of our area of expertise, this could be store locations, sales territories, competitor, customer, or resident data. Once you add in an understanding of the impact of location and context to any aspect of your organisation it takes your decision making abilities to a whole new level.
Also Check: Pre Algebra With Pizzazz Page 163 Answers
Summary: What Is Geographic Information Systems
You might ask yourself: Havent geographers been answering these questions for centuries? Yes, they have. But geographers can answer these questions much better with Geographic Information Systems.
When we first started recording inventories on paper maps, it was quite a tedious process. But what did we really need? We needed a GIS to record and store observations. Also, we needed a table to store attributes about the data.
Whats the bottom line? Geographic information systems let us interpret data understanding relationships, patterns, and trends. Then, viewing and analyzing data geographically impacts our understanding of the world we live in.
Public Health Emergency Preparedness And Response
GIS has been used for decades in response to natural disasters such as floods, earthquakes, wildfires, and hurricanes. Following events such as 9/11, the anthrax attacks, and hurricane Katrina, the debate ensued regarding exactly what public health emergency preparedness was and how it should be measured . Regardless of ones definition of public health emergency preparedness, it is clear preparedness and response depend on location-based information, such as the location of incidents, where responders are, and where emergency services and health facilities are located. GIS supports emergency preparedness through
- Needs assessments and planning.
In 2003, WHO and the Hong Kong Department of Health launched an interactive web mapping application to provide up-to-date, accurate information ont eh distribution of SARS in Hong Kong, China, and other parts of the world
Read Also: Segment And Angle Addition Worksheet Answers
What Is Gis And How Is It Used
Hundreds of thousands of organizations are using GIS to solve problems. But what is GIS, and how is it being used?
GIS, or Geographic Information Systems, is a technological field that incorporates geographical features with tabular data for one to map, analyze, and assess real-world problems. According to Esri, the company that builds and manages ArcGIS, a geographic information system is a computer-based tool for mapping and analyzing things that exist and events that happen on earth. However, GIS is more than just a generated computer system and, in many ways, GIS can change the way we view the world.
Geographic information systems operate on various levels. On the most basic level, geographic information systems technology is used as computer cartography or straightforward mapping. The real power of GIS is through using spatial and statistical methods to analyze attribute and geographic information giving one a deeper understanding of the layers of collective data.
GIS Integration
EEC Environmentals technology professionals assist in all phases of new application development and adoption of GIS design and asset management software implementation. We match the appropriate technology to our clients business needs and deploy these solutions to ensure that they remain sustainably effective.
Contact EEC for more information.
Uses For Gis Data In Everyday Life
It comes as no surprise that GIS has real-world applications far beyond mere scientific curiosity, but some of the applications of GIS data might surprise you. Here are a few specific uses of using GIS in everyday life for location intelligence:
Don’t Miss: Debbie Rowe Michael Not Biological Father