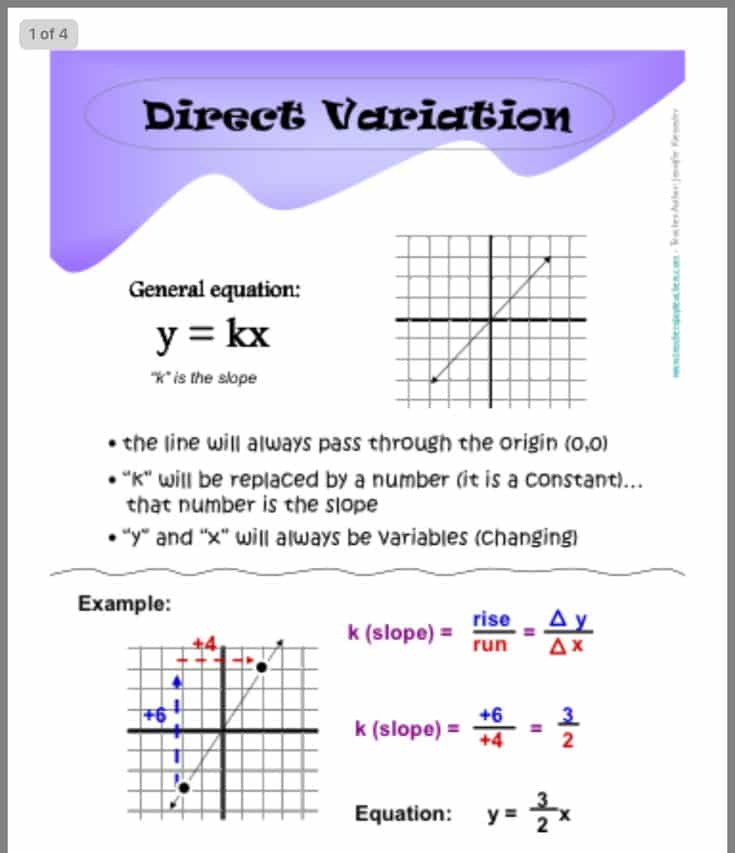
Solving A Direct Variation
The formula y = kx is used to solve a direct variation. If the proportionality constant needs to be determined, divide y by x to get the answer. If k is known and either x or y must be found, these values can be replaced into the equation above to discover the unknown value.
Example: Find constant of proportionality if x = 69 and y = 23 have a direct variation.
Solution:
How To Tell If An Equation Is A Direct Variation
To tell if an equation is a direct variation, look for the form y = kx. In particular, this means:
- There are only two variables .
- The only exponent of each variable in the equation is 1 .
- No variables are multiplied .
- The constant term in the equation is 0 .
Example 1: An Equation That Is A Direct Variation
Consider the equation:
This is a direct variation, since:
- There are only two variables: x and y.
- The exponent on each variable is equal to 1.
- No variables are multiplied .
- The constant term in the equation is 0 .
Example 2: An Equation That Is Not A Direct Variation
Consider the equation:
This is not a direct variation, since:
- There are three variables: x, y, and z.
Example 3: An Equation That Is Not A Direct Variation
Consider the equation:
This is not a direct variation, since:
- The variable x has an exponent of 3.
Example 4: An Equation That Is Not A Direct Variation
Consider the equation:
This is not a direct variation, since:
- There is an xy term .
Note: this is an example of inverse variation, since y = 2 / x.
Example 5: An Equation That Is Not A Direct Variation
Consider the equation:
This is not a direct variation, since:
- There is a nonzero constant term .
What Is Direct Variation
Direct variation exists between any two variables when one quantity is directly dependent on the other i.e. if one quantity increases with respect to the other quantity and vice versa. It is the relationship between two variables where one of the variables is a constant multiple of the other. Since the two variables are directly related to each other it is also termed as directly proportional.
Direct variation and inverse variation are two types of proportionalities. Proportionality refers to a relationship where two quantities are multiplicatively connected by a constant. In a direct variation, the ratio of the two quantities remains the same whereas in an inverse variation the product of the two quantities remains constant. Here we shall check in detail the definition and examples of direct variation.
Read Also: What Does Infrastructure Mean In Geography
How To: Given A Description Of A Direct Variation Problem Solve For An Unknown
Example 1: Solving A Direct Variation Problem
The volume of blood, B, in a person’s body varies directly as body weight, W. A person who weighs 160 pounds has approximately 5 quarts of blood. Estimate the number of quarts of blood in a person who weighs 200 pounds.
Solution
We know that y varies directly as x where y = kx. By changing letters, we can write an equation that describes the given mathematical statement.
B = kW
Use the given values to find k. A person who weighs 160 pounds has approximately 5 quarts of blood. Substitute 160 for W and 5 for B in the direct variation equation. Then solve for k. After obtaining the value of k, substitute the value of k into the general equation.
B = kW
Final Answer
Therefore, since the given set of ordered pairs are not the same for y/x, they do not represent a direct variation. Since the ordered pairs are the same for xy, then they represent an inverse variation.
Also Check: What Is Associate Of Arts In Psychology
A General Note: Direct Variation
If x and y are related by an equation of the form
y=k^
then we say that the relationship is direct variation and y varies directly with the nth power of x. In direct variation relationships, there is a nonzero constant ratio k=\dfrac^}, where k is called the constant of variation, which help defines the relationship between the variables.
Example: Solving A Direct Variation Problem
The quantity y varies directly with the cube of x. If y=25 when x=2, find y when x is 6.
The general formula for direct variation with a cube is y=k^. The constant can be found by dividing y by the cube of x.
\begin k& =\dfrac^} \\ & =\dfrac^}\\ & =\dfrac\end
Now use the constant to write an equation that represents this relationship.
y=\dfrac^
Substitute x=6 and solve for y.
\beginy& =\dfrac^ \\ & =675\hfill \end
Analysis of the Solution
Also Check: What Is Activation Energy Biology
Example : Direct Variation Word Problem
The circumference of a circle varies directly with its diameter. If the diameter of 7 centimeters in diameter circle is 7, what is the circumference of the circle whose diameter is 10 centimeters? 15 centimeters 18 centimeters? 20 centimeters?
The circumference of a circle c varies directly as its diameter d can be expressed as the following equation.c/d = k
Substitute the given value of c and d in the equation.7/7 = k
Express c=kd in terms of in place of k.c = d
Substitute the value of d to solve for x when d = 10 centimeters, d = 15 centimeters, d = 18 centimeters, and d = 20 centimeters.c =
Therefore, the circumferences are 10, 15, 18, and 20.
Other Forms Of Direct Variation
The area A of a circle of radius r is given by the equation A = pr2, where p is a constant
In this situation, A is not directly proportional to r but A is directly proportional to r2. We say that A varies directly as the square of r or A r2.
Example:Given that y varies directly as the cube of x and that y = 21 when x = 3, calculate the value of y when x = 8.
Solution:y x3 that is y = kx3 where k is a constant
Substitute x = 3 and y = 21 into the equation: 21 = k k =
Read Also: What Is Synthesis In Chemistry
Example : Direct Variation Application
In a downtown office building, the monthly rent for an office is directly proportional to the size of the office. If a 450-square-foot office rents for $1350 per month, then what is the rent for an 800-square-foot office?
Solution
Given that the monthly rent is directly proportional to the office size, then the rent, R, varies directly with the area of the office, A. Since 450-square-foot office rents for $1350 per month, substitute to the direct variation formula and find k.
R = kA
1350 = k
k = 3
Now that we have the value of k, which is 3, then write the new equation incorporating the value of k. Then, to get the rent for an 800-square-foot office, insert 800 into the new formula.
R = 3A
Therefore, an 800-square-foot office rents for $ 2400 per month.
Can Direct Variation Be A Fraction
Direct variation can be a fraction. To be more precise, the constant of variation k can be a rational number .
In practical terms, if k is a fraction, we can interpret it as the slope . So, if k is the fraction a / b, then we can write:
Another interpretation is that every time x increases by b, y increases by a.
For example, if k = 2 / 3, then every time x increases by 3, y increases by 2. Every time x decreases by 3, y decreases by 2.
Note that k can be both negative and a fraction. For example, we could have k = -5 / 4.
Read Also: What Is Overproduction In Biology
Direct And Inverse Variations
Direct variation means when one quantity changes, the other quantity also changes in direct proportion. Inverse variation is exactly opposite to this. In this article, you will learn the definition of Direct and inverse variations along with some solved examples.
A few situations in life have either a direct or indirect relationship with each other:
- As the bill at the shopping centre increases, the amount to be paid also increases.
- As the speed of the car decreases, the time taken to reach the destination increases.
If the two values of the objects are related in such a way that an increase or decrease in the value of one object affects the value of the other, which is termed as a variation. The two types of variation are:
Can Direct Variation Have Exponents

Direct variation cannot have exponents other than 1 for the variables x and y. This is because direct variation is a linear relationship between x and y.
If the variables x and y have exponents other than 1, then we do not have a direct variation relationship. For example:
- y = 5×2 is not a direct variation, since we have an exponent of 2 for the x variable.
- y = 4×3 is not a direct variation, since we have an exponent of 3 for the x variable.
- y2 = 6x is not a direct variation, since we have an exponent of 2 for the y variable.
Also Check: What Does Both Mean In Math
Direct And Inverse Variation Problems
Example 1: A and B can do a particular work in 72 days. B and C in 120 days. A and C in 90 days. In how many days can A alone do the work?
Solution:
Let us say A, B, C can respectively do work alone in x, y, z days
Therefore, In 1 day A, B, C alone can work in 1 / x, 1 / y, 1 / z days
in 1 day can do 1 / x + 1 / y work
can do full work in 1 / day
1 / = 72 i.e.,
1 / x + 1 / y = 1 / 72
similarly, 1 / y + 1 / z =1 / 120 –
1 / z + 1 / x = 1 / 90
From , 1 / x 1 / z = 1 / 72 1 / 120
1 / x + 1 / z = 1 / 92
Adding IV & V, 2 / x = 1 / 72 1 / 120 + 1 / 90
= / = 6 / 360 = 1 / 60
x = 120
Example 2: A and B undertake to do a piece of work for Rs. 600. A alone can do it in 6 days, while B alone can do it in 8 days but with the help of C, they finish it in 3 days. Find the share of C.
Solution:
A, B, C can do work in 6 days, 8 days, & x days respectively.
Together, they will do it in 1 / days.
Now, 1 / = 3
+ + = 1 / 3
1 / x = 1 / 3 1 / 6 1 / 8 = 1 / 24
x = 24 days
Efficiency ratio of A : B : C = : : = 4 : 3 : 1
Example 3: 45 men can complete a work in 16 days. Six days after they started working, 30 more men joined them. How many days will they now take to complete the remaining work?
Solution:
45 men, 16 days 1 work.
1 man, 1 day 1 / work
For the first 6 days: 45 men, 6 days / work = 3/8 work
Work left = 1 =
Now, 45 + 30 = 75 men, 1 man, 1 day = 1 / = work 75 men,
1 day = 75 / work 75 men, x days = 75x / work
Solution:
= min
Example 2 Function Table
Look at the function tables below. Can you see the pattern? Remember, when you have a table giving you the x and y values, you simply divide y by x to see if you get a constant . If you do not get the same value, then the function table does not represent direct variation.
| y = kx |
|---|
| 10 | 11 |
Tables can be used to write direct variation equations. You divide y by x and get the same value, which will become k. For example, in the direct variation table above, each time you divide y by x, you should get 8. This means that 8 is the constant and that each time x increases by 1, y increases by 8. Once you have this information, you can write an equation. The equation for this table would be: y = 8x
You May Like: How Does Math Impact Our Lives
Example : Finding The Constant Of Proportionality
Suppose a variable q is directly proportional to a variable z.
Solution
Since q is directly proportional to a variable z., q=kz where k is a constant of proportionality. Substituting q = 12 and z = 5 gives us the following computation.
12 = 5k
Since k = 12/5, the formula q = kz has the specific form.
q=12z/5
Thus when z=7, the value of q will be as shown below.
q = 12 / 5
q = 16.8
Final Answer
The value of k is equal to 12/5 and q is equal to 16.8 when z = 7.
Example : Direct Variation As An Nth Power
The distance a ball rolls down an inclined plane is directly proportional to the square of the time it rolls. During the first second, the ball rolls 10 feet. See the figure below.
Solution
Let d be the distance in feet the ball rolls and I the time in seconds. Since this is an example of a direct variation as an nth power, write the general formula in the format A = kB2.
d = ki2
Now, since the value of d is equal to 10 when times is equal to 1 second, solve the value of constant of variation k.
d = ki2
10 = k2
k = 10
So, the equation relating distance to time is given by the equation below putting the value of k = 10. When t = 3 seconds, find the distance traveled.
d = 102
Direct Variation as an Nth Power
Final Answer
The ball will roll 90 feet during the first three seconds.
Recommended Reading: What Is Frictional Force In Physics
How To Solve Direct Variation
To solve direct variation, plug in matching values of variables to find k. Then, if necessary, use the value of k with a value of x or y to find the other variables value.
Example 1: Solving A Direct Variation For k
Lets say that there is a direct variation between x and y. That means:
for some constant k.
Lets assume we know that y = 15 when x = 3. Plugging in these values of x and y, we get:
So, y = 42 when x = 7.
The Constant Of Variation
The values are related by K, ……or the constant of variation. Now we can plug our known values into the Direct Variation formula. It doesn’t matter which value is X and which is Y, but you do have to be consistent. Lets assign two to X, and three thousand for Y. We divide both sides by 2 and get….
… K is equal to one thousand five hundred. Look what happens …… when we double 3000 lbs to 6000 lbs. Notice thex value is also doubled. When variables have a direct variation, as one variable increases, so does the other. What do you think happens as one variable decreases? That’s right, when we divide one value by four, the other decreases by a factor of four as well! Since k is our constant, it never changes.
Also Check: Intermediate Algebra Custom New York City College Of Technology Custom
Guidelines For Solving A Direct Variation Equation
Example 1: Application Involving Direct Variation
The speed of a racing canoe in still water varies directly as the square root of the length of the canoe.
Solution
Let s be the speed of the canoe and L be its length. Translate the given mathematical statement to come up with the general variation model.
s = kL
Then, solve the value of variation constant k, given that s = 4 mph and L = 20 feet.
s = kL
4 = k20
k = 0.894
Create a general formula incorporating the value of constant of variation k = 0.894. Then, substitute the length of the 24-feet canoe in finding the new speed.
s = 0.894L
s = 4.38 mph
Final Answer
Therefore, given the variation model s = 0.894L, the value of the 24-feet canoe is 4.38 mph.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Basic Principles Of Chemistry