The Extent Of The Problem
In its most basic form, natural selection is an elegant theory that effectively explains the obviously good fit of living things to their environments. As a mechanism, it is remarkably simple in principle yet incredibly powerful in application. However, the fact that it eluded description until 150 years ago suggests that grasping its workings and implications is far more challenging than is usually assumed.
Three decades of research have produced unambiguous data revealing a strikingly high prevalence of misconceptions about natural selection among members of the public and in students at all levels, from elementary school pupils to university science majors . A finding that less than 10% of those surveyed possess a functional understanding of natural selection is not atypical. It is particularly disconcerting and undoubtedly exacerbating that confusions about natural selection are common even among those responsible for teaching it. As Nehm and Schonfeld recently concluded, one cannot assume that biology teachers with extensive backgrounds in biology have an accurate working knowledge of evolution, natural selection, or the nature of science.
Table 2 Summary of studies showing the high degree of misunderstanding of natural selection and adaptation among various groups of subjects
How Can Overproduction Be Reduced
Avoid overproduction by making things only as quickly as the customer wants. Just-in-time inventory allows you to keep the minimum inventory required to keep your business running. You can order what you want to meet your immediate needs and reduce overproduction by producing only what is needed when needed.
Natural Selection: Peppered Moths Example
Before the industrial revolution in Britain, in the early 1800s, most peppered moths were of the pale variety. This meant that they were camouflaged against the pale birch trees that they rest on. Moths with a mutant black colouring were easily spotted and eaten by birds. This gave the white variety an advantage, and they were more likely to survive to reproduce.
During the last half of the 1800s, airborne pollution in industrial areas blackened the birch tree bark with soot. This meant that the mutant black moths were now camouflaged, while the white variety became more vulnerable to predators. This gave the black variety an advantage, and they were more likely to survive and reproduce. The dark moths passed on the alleles for black wing colour leading to offspring with the black wing colour phenotype. Over time, the black peppered moths became far more common in urban areas than the pale variety.
Note that this change in phenotype was not due to pollution making the moths darker. The dark variety had always existed, but was the best suited variant when the environment changed. It took many generations before the population of moths was mainly black in colour.
You May Like: New England Climate And Geography
Nature As A Selecting Agent
Thirty years ago, widely respected broadcaster Sir David Attenborough aptly described the challenge of avoiding anthropomorphic shorthand in descriptions of adaptation:
Darwin demonstrated that the driving force of evolution comes from the accumulation, over countless generations, of chance genetical changes sifted by the rigors of natural selection. In describing the consequences of this process it is only too easy to use a form of words that suggests that the animals themselves were striving to bring about change in a purposeful waythat fish wanted to climb onto dry land, and to modify their fins into legs, that reptiles wished to fly, strove to change their scales into feathers and so ultimately became birds.
Darwin himself could not resist slipping into the language of agency at times:
It may be said that natural selection is daily and hourly scrutinizing, throughout the world, every variation, even the slightest rejecting that which is bad, preserving and adding up all that is good silently and insensibly working, whenever and wherever opportunity offers, at the improvement of each organic being in relation to its organic and inorganic conditions of life. We see nothing of these slow changes in progress, until the hand of time has marked the long lapse of ages, and then so imperfect is our view into long past geological ages, that we only see that the forms of life are now different from what they formerly were.
What Does Overproduction Mean In Science
What does overproduction mean in science? Overproduction by definition, in biology, means that each generation has more offspring than the environment can support. For this reason, competition for limited resources occurs. Individuals have traits that are passed down to offspring.
What is an example of increased production? Overproduction is of particular concern as it tends to exacerbate transportation, inventory and movement waste. Examples include: producing components before the next stage of the process is ready to receive them. Print and save unnecessary documents.
How do you explain the increased production? Explanation. Overproduction is the accumulation of unsalable inventories in the hands of firms. Surplus production is a relative measure that indicates the excess of production over consumption. The tendency to overproduction of goods which leads to economic collapse is specific to the capitalist economy.
What is hypersecretion? Overproduction of offspring is the idea that a species produces far more offspring than the environment can support because most juveniles will not reach adulthood. This allows only the fittest to survive and reproduce.
Recommended Reading: Edgenuity Economics Unit Test Answers
Why Is Natural Selection So Difficult To Understand
Two obvious hypotheses present themselves for why misunderstandings of natural selection are so widespread. The first is that understanding the mechanism of natural selection requires an acceptance of the historical fact of evolution, the latter being rejected by a large fraction of the population. While an improved understanding of the process probably would help to increase overall acceptance of evolution, surveys indicate that rates of acceptance already are much higher than levels of understanding. And, whereas levels of understanding and acceptance may be positively correlated among teachers , the two parameters seem to be at most only very weakly related in students . Teachers notwithstanding, it appears that a majority on both sides of the evolution-creation debate do not understand the process of natural selection or its role in evolution .
Notable Examples Of Overproduction
All species may be considered to overproduce if all couples have offspring and they all survive, but there are some notable examples of overproduction in a species, even if those conditions are not met. For example, many species of fish lay millions of eggs at one time, though only a fraction of those survive. Sea turtles can lay anywhere from 70 to 190 eggs at a time, though only about one out of 100 typically survive. Oysters can also lay 60 to 80 million eggs at a time, but again, only a few survive to reproduce themselves.
Don’t Miss: Books Never Written Math Worksheet Answers Algebra
What Role Does Overproduction Play In Natural Selection
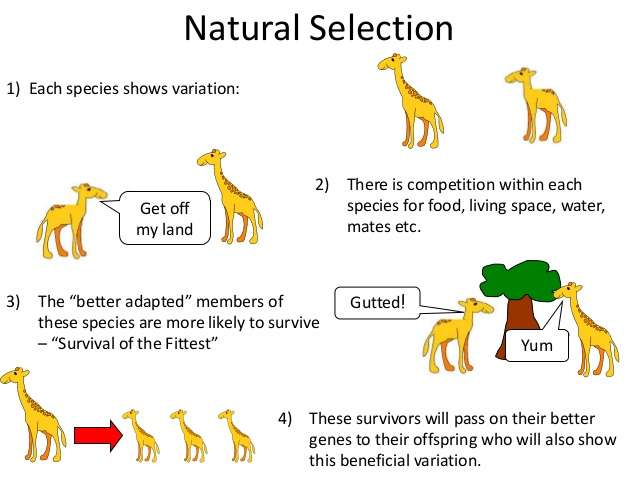
What role does overproduction of organisms play in natural selection? Overproduction of organisms plays a role in natural selection by making it so that there is not enough food for all species, which will lead to competition, in which only organisms with preferred traits will remain.
Natural Selection And The Evolution Of Populations
Though each has been tested and shown to be accurate, none of the observations and inferences that underlies natural selection is sufficient individually to provide a mechanism for evolutionary change. Overproduction alone will have no evolutionary consequences if all individuals are identical. Differences among organisms are not relevant unless they can be inherited. Genetic variation by itself will not result in natural selection unless it exerts some impact on organism survival and reproduction. However, any time all of Darwin’s postulates hold simultaneouslyas they do in most populationsnatural selection will occur. The net result in this case is that certain traits will, on average, be passed on from one generation to the next at a higher rate than existing alternatives in the population. Put another way, when one considers who the parents of the current generation were, it will be seen that a disproportionate number of them possessed traits beneficial for survival and reproduction in the particular environment in which they lived.
Also Check: Cpm Algebra 1 Chapter 9 Answers Pdf
Evidence Of Natural Selection
Let’s look at an example to help make natural selection clear.
Industrial melanism is a phenomenon that affected over 70 species of moths in England. It has been best studied in the peppered moth, Biston betularia. Prior to 1800, the typical moth of the species had a light pattern . Dark colored or melanic moths were rare and were therefore collectors’ items.
Figure 2. Image of Peppered Moth
During the Industrial Revolution, soot and other industrial wastes darkened tree trunks and killed off lichens. The light-colored morph of the moth became rare and the dark morph became abundant. In 1819, the first melanic morph was seen by 1886, it was far more common — illustrating rapid evolutionary change.
Eventually light morphs were common in only a few locales, far from industrial areas. The cause of this change was thought to be selective predation by birds, which favored camouflage coloration in the moth.
In the 1950’s, the biologist Kettlewell did release-recapture experiments using both morphs. A brief summary of his results are shown below. By observing bird predation from blinds, he could confirm that conspicuousness of moth greatly influenced the chance it would be eaten.
Recapture Success
Conceptual Frameworks Versus Spontaneous Constructions
It has been suggested by some authors that young students simply are incapable of understanding natural selection because they have not yet developed the formal reasoning abilities necessary to grasp it . This could be taken to imply that natural selection should not be taught until later grades however, those who have studied student understanding directly tend to disagree with any such suggestion . Overall, the issue does not seem to be a lack of logic , but a combination of incorrect underlying premises about mechanisms and deep-seated cognitive biases that influence interpretations.
Read Also: Chapter 10 Test Form 2c
The Evolution Of Theory
The theory of evolution is one of the great intellectual revolutions of human history, drastically changing our perception of the world and of our place in it. Charles Darwin put forth a coherent theory of evolution and amassed a great body of evidence in support of this theory. In Darwin’s time, most scientists fully believed that each organism and each adaptation was the work of the creator. Linneaus established the system of biological classification that we use today, and did so in the spirit of cataloguing God’s creations.
In other words, all of the similarities and dissimilarities among groups of organisms that are the result of the branching process creating the great tree of life , were viewed by early 19th century philosophers and scientists as a consequence of omnipotent design.
Figure 1: A phylogenetic “tree of life” constructed by computer analysis of cyochrome c molecules in the organisms shown there are as many different trees of life as there are methods of analysis for constructing them.
However, by the 19th Century, a number of natural historians were beginning to think of evolutionary change as an explanation for patterns observed in nature. The following ideas were part of the intellectual climate of Darwin’s time.
Darwin’s Theory
The primary mechanism of change over time is natural selection, elaborated below. This mechanism causes changes in the properties of organisms within lineages from generation to generation.
The Process of Natural Selection
Topic 52 Natural Selection
Essential idea:
- The diversity of life has evolved and continues to evolve by natural selection.
Nature of science:
- Use theories to explain natural phenomenathe theory of evolution by natural selection can explain the development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
- List three trends that have been observed in the development of antibiotic resistance.
- Use a graph to illustrate antibiotic resistance over time.
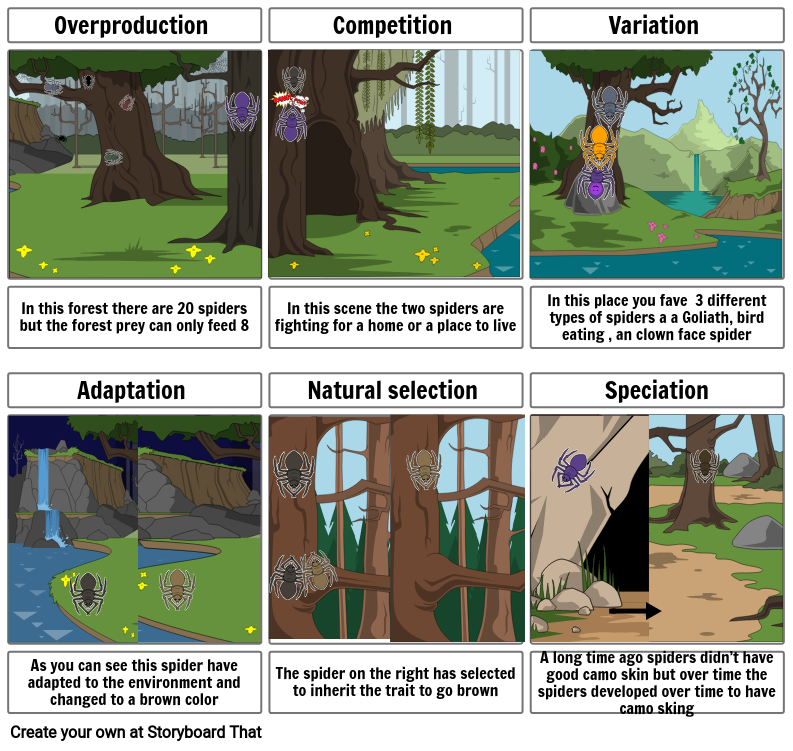
Understandings:5.2.U1 Natural selection can only occur if there is variation among members of the same species.
- Define variation.
- Explain why natural selection can only function if there is variation in a species.
- Inherited Variation There is genetic variation within a population which can be inherited
- Competition There is a struggle for survival
- Selection Environmental pressures lead to differential reproduction within a population
- Adaptations Individuals with beneficial traits will be more likely to survive and pass these traits on to their offspring
- Evolution Over time, there is a change in allele frequency within the population gene pool
5.2.U2 Mutation, meiosis and sexual reproduction cause variation between individuals in a species.
- List sources of genetic variation.
- New alleles arise from the mutation of existing alleles, usually by changing one or a few base pairs
- Genetic mutations are the original source of variation within a species.
Meiosis:Sexual reproduction:
- Define adaptation.
- List examples of adaptations.
Malthusian DilemmaApplicationTOK
Don’t Miss: Glencoe Geometry Concepts And Applications Practice Workbook Answers
What Is The Main Purpose Behind Overproduction In Natural Selection
In 1859 Charles Darwin introduced the idea that organisms evolve through a process called natural selection. He observed that organisms of every species exhibit variation in their traits, and some of those variations can help an individual survive longer than other individuals. That individual then breeds more successfully, making it more likely that the genes the successful organism carries will be more prevalent in the overall population. That is natural selection, and it depends upon the fact that more organisms are born than are likely to survive.
How Overproduction Is A Waste
Overproduction leads to wastage up front by overusing resources before the customer purchases the product. Overproduction in manufacturing often leads to wasted resources and time. Any amount of time or resources used to produce a product that exceeds the customers requirements is considered a waste.
Read Also: My.hrw.com Algebra 2
Darwin’s Theory Of Evolution By Natural Selection
“Variation is a feature of natural populations and every population produces more progeny than its environment can manage. The consequences of this overproduction is that those individuals with the best genetic fitness for the environment will produce offspring that can more successfully compete in that environment. Thus the subsequent generation will have a higher representation of these offspring and the population will have evolved.”
What Is Overproduction Lethality And What Seems To Cause It
What is overproduction lethality and what seems to cause it? And so why would new reporter proteins Show more What is overproduction lethality and what seems to cause it? And so why would new reporter proteins be useful in studying protein export? So what advantages would GFP have in that regard? Show less
Read Also: Negative Work Physics
The Meaning Of Fitness In Evolutionary Biology
In order to study the operation and effects of natural selection, it is important to have a means of describing and quantifying the relationships between genotype , phenotype , survival, and reproduction in particular environments. The concept used by evolutionary biologists in this regard is known as Darwinian fitness, which is defined most simply as a measure of the total reproductive output of an organism with a particular genotype . In the most basic terms, one can state that the more offspring an individual produces, the higher is its fitness. It must be emphasized that the term fitness, as used in evolutionary biology, does not refer to physical condition, strength, or stamina and therefore differs markedly from its usage in common language.
What You Need To Know
- You need to know the conditions required for natural selection to occur. These include: overproduction of offspring, inherited variation, and the struggle to survive, which result in differential reproductive success.
- You need to understand genetic drift and gene flow.
- You need to know how mutation and genetic recombination increase genetic variation.
Read Also: How Did Geography Affect Greece Development
What Is The Importance Of The Offspring
Benefits of overproduction
In all species, overproduction helps improve the genetic line by supporting the survival of the fittest. Since resources are limited, those offspring that are stronger or more adaptable to environmental challenges are able to survive.
Which Traits Are The Most Fit

Directional natural selection can be understood as a process by which fitter traits increase in proportion within populations over the course of many generations. It must be understood that the relative fitness of different traits depends on the current environment. Thus, traits that are fit now may become unfit later if the environment changes. Conversely, traits that have now become fit may have been present long before the current environment arose, without having conferred any advantage under previous conditions. Finally, it must be noted that fitness refers to reproductive success relative to alternatives here and nownatural selection cannot increase the proportion of traits solely because they may someday become advantageous. Careful reflection on how natural selection actually works should make it clear why this is so.
Read Also: What Influence Did Geography Have On The Development Of Greek Society
Examples Of Overproduction In A Species
Survival of the fittest takes rather a morbid turn when you consider the idea of overproduction of offspring. Overproduction of offspring is the idea that species produce far more offspring than an environment can support because most of the juveniles will not make it to adulthood. This allows only the fittest to survive and reproduce.
Humans also overproduce and, in recent centuries, advances in medicine, public safety, and food production has allowed most babies to survive and reproduce, creating a problem nature hasn’t provided a solution for.