Learning A Language Requires Primitive Brain Areas To Be Rewired And Fine Tuned
Posted September 4, 2013
A new study released on September 3, 2013 found that infants up to 6 months old respond strongly to nonhuman primate vocalization as if it were coming from a human voice and sheds light on the developmental origin between speech and cognition.
The human process of unlearning innate reflexes and then relearning them through practice and the process of creating fine tuned motor skills is a fundamental part of healthy development and self-expression.
The biological connection between language acquisition and being able to use our hands to create things sets us apart from our primate cousins. Interestingly, another study also released on September 3, 2013 found that the same brain region used for language is also used when humans make complex tools, supporting the theory that language and tool making evolved in tandem.
The newest research suggests that the advancement of hand-held axe production may have coincided with the development of language, as these functions overlap in the same regions of the human brain. Language and tool making is another example of how the cerebrum and cerebellum work together.
Human Babies Respond to Calls from Primates
The Diving Reflex And Mental State
All of this happens as a reflex; theres no conscious thought required. The parasympathetic nervous system, and specifically the vagus nerve, take care of it for you. If your anxiety is spiking and youre approaching a panic attack or youre feeling totally dysregulated, this could be a quick way to settle things down in the body.
The diving reflex is also involved in the dialectical behaviour therapy TIPP acronym. The T is for temperature change, which involves sticking your face in a sink full of cold water, setting off the reflex.
Why Are Psychologists Interested In The Moro Reflex
The Moro reflex is certainly interesting, but why does it interest psychologists? When striving to understand human development, psychologists often start by examining what infants can and cannot do. Very young infants cannot turn over, feed themselves, or even hold up their own heads. When examining the mental capacities of infants, psychologists focus on examining what they are capable of doing and how they respond to different stimuli in the environment.
By looking at some of the adaptive infant reflexes such as the Moro reflex, the rooting reflex, the stepping reflex, and the grasping reflex, researchers can better understand how babies respond to the world around them.
Read Also: What Does Amu Mean In Chemistry
The Discovery Of The Conditioned Reflex
The Nobel laureate physiologist Ivan Petrovich Pavlov discovered the conditioned reflex in the first decade of the twentieth century. The initial work involved the autonomic nervous system with Pavlovs use of the salivating reflex in dogs. He discovered that presenting a neutral stimulus such as a bell that never normally elicited salivation could come to elicit salivation if presented repeatedly before giving the dog meat powder. The learned response was the dogs salivation to the bell. Presentation of the bell followed by presentation of the meat powder led to the formation of an association. Throughout the century following the discovery of classical conditioning, it has become one of the most widely employed paradigms for the investigation of associative learning and memory and its neurobiological substrates. Pavlov was the first scientist to observe that old dogs condition more slowly than young dogs. Thus, research on classical conditioning in normal aging has a long and illustrious history.
D.T. Cerutti, in, 2001
What Youll Learn To Do: Explain Learning And The Process Of Classical Conditioning

In this section, youll learn about learning. It might not be learning as you typically think of the word, because were not talking about going to school, or studying, or even effortfully trying to remember something. Instead, youll see that one of the main types of behavioral learning that we do is simply through an automatic process of association, known as classical conditioning. In classical conditioning, organisms learn to associate events that repeatedly happen together, and researchers study how a reflexive response to a stimulus can be mapped to a different stimulusby training an association between the two stimuli. Ivan Pavlovs experiments show how stimulus-response bonds are formed. Watson, the founder of behaviorism, was greatly influenced by Pavlovs work. He tested humans by conditioning fear in an infant known as Little Albert. His findings suggest that classical conditioning can explain how some fears develop.
Don’t Miss: What Is Activation Energy Biology
Not All Reflexes Are Simple
There are many different reflexes in the body. Some of them are complicated and involve multiple interneurons and many synapses. When there are many synapses, the reflex is called polysynaptic . These reflexes, just like the simple monosynaptic reflex, exist in living beings, especially humans, to keep us safe! Sometimes reflexes create more than one action. Imagine removing your foot from something sharplike a Lego piece that was left on the floor. If you removed your foot from the Lego because it hurt, but didnt place your other foot down, you would fall and that would hurt even more! So, the withdrawal reflex to remove your foot works with a reflex on the other side of the body telling you to put your other foot down. That reflex is called the crossed extensor reflex. These actions are all done without you thinking or planning, but your brain helps to assess the situation as an afterthought. It might think, That hurt! Who left the Lego there?
Tonic Neck Or Fencing Reflex
The tonic neck or fencing reflex happens when you place your baby on their back and move their head to one side. The baby will assume the “fencing position,” extending the arm and leg on the side they’re facing. Their other arm and leg will be flexed, with that hand in a fist. This reflex is present until about 6 months of age.
You May Like: What Does Abiotic Mean In Biology
What Will Neurologist Do On First Visit
During your first appointment, a Neurologist will likely ask you to participate in a physical exam and neurological exam. Neurological exams are tests that measure muscle strength, sensation, reflexes, and coordination. Because of the complexity of the nervous system, you may be asked to undergo further testing.6 sep. 2016
Why Do Doctors Scrape The Bottom Of Your Foot
How is it tested? To test the Babinski sign, your doctor will use an object, such as a reflex hammer or a key, to stroke the bottom of your foot from your heel up to your big toe. Your doctor may scrape the object roughly across the bottom of your foot, so you might feel some minor discomfort or a tickle.
Don’t Miss: How To Calculate Half Life Chemistry
Reflexes Involving Cranial Nerves
| Name | |
| Corneal reflex, also known as the blink reflex | V |
Newborn babies have a number of other reflexes which are not seen in adults, referred to as primitive reflexes. These automatic reactions to stimuli enable infants to respond to the environment before any learning has taken place. They include:
What Causes Sluggish Reflexes
Peripheral neuropathy is today the most common causeof absent reflexes. The causes include diseases such as diabetes, alcoholism, amyloidosis, uremia; vitamin deficiencies such as pellagra, beriberi, pernicious anemia; remote cancer; toxins including lead, arsenic, isoniazid, vincristine, diphenylhydantoin.
Don’t Miss: How To Teach Sat Math
When To Contact A Medical Professional
The health care provider will often discover abnormal infant reflexes during an exam that is done for another reason. Reflexes that remain longer than they should may be a sign of a nervous system problem.
Parents should talk to their child’s provider if:
- They have worries about their child’s development.
- They notice that baby reflexes continue in their child after they should have stopped.
How Is The Rooting Reflex Different From The Sucking Reflex
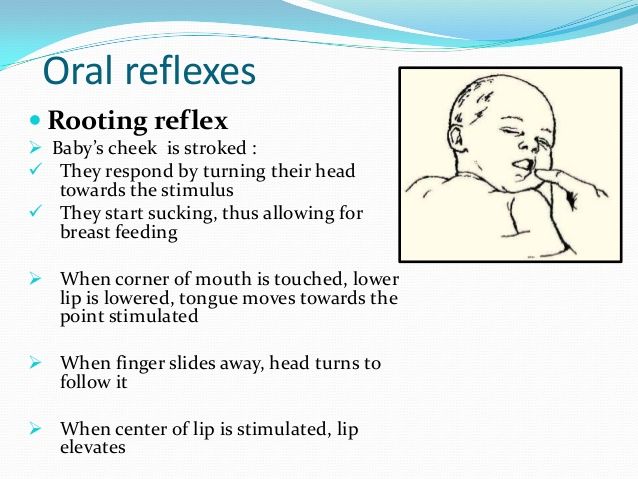
The sucking reflex is different from the rooting reflex. The two serve different purposes, but both are important for allowing your baby to eat.
The rooting reflex happens first, allowing your baby to reflexively find your breast or a bottle nipple. The sucking reflex kicks in when the roof of a newborns mouth is touched. When this area is stimulated, your baby will begin to suck or drink. For example, when you place your nipple or a bottle nipple in your babys mouth, they automatically start sucking because of the sucking reflex.
Don’t Miss: What Is Work Done In Physics
Unconditioned Response And Conditioned Response Differences
When trying to distinguish between the unconditioned response and the conditioned response, try to keep a few key things in mind:
- The unconditioned response is natural and automatic
- The unconditioned response is innate and requires no prior learning
- The conditioned response will occur only after an association has been made between the UCS and the CS
- The conditioned response is a learned response
For example, you naturally tend to tear up whenever you are cutting onions. As you are making dinner, you also enjoy listening to music and find yourself playing the same song quite often. Eventually, you find that when you hear the song you often play during your meal prep, you find yourself tearing up unexpectedly. In this example, the vapors from the onions represent the unconditioned stimulus. They automatically and naturally trigger the crying response, which is the unconditioned response.
After multiple associations between a certain song and the unconditioned stimulus, the song itself eventually starts to evoke tears.
So what happens when an unconditioned stimulus is no longer paired with a conditioned stimulus? When the conditioned stimulus is presented alone without the unconditioned stimulus, the conditioned response will eventually diminish or disappear, a phenomenon known as extinction.
You should read more about how this process as well as some of the key differences between how classical and operant conditioning work.
Origin Of The Term Classical Conditioning
Before the 1940s, the process of classical conditioning was referred to most often as the conditioned reflex, Pavlovian conditioning, or simply as conditioning. However, in the 1930s, scientists began to understand that the laws governing learning, in paradigms where reinforcement was contingent upon the organisms behavior appeared to be fundamentally different from the laws governing the conditioned reflex. The latter type of learning would come be known as instrumental or operant conditioning. This created a need to distinguish different forms of conditioning. It appears that the term classical conditioning developed as a contraction of the descriptive phase classical Pavlovian conditioning which was used to denote the well-known type of conditioning used by Pavlov .
Ken Nakayama, in, 1998
Don’t Miss: Practice 2 4 Reasoning In Algebra Answer Key
The Unconditioned Response And Classical Conditioning
The concept of the unconditioned response was first discovered by a Russian physiologist named Ivan Pavlov. During his research on the digestive systems of dogs, the animals in his experiment would begin to salivate whenever they were fed. Pavlov noted that when a buzzer was rung every time the dogs were fed, the animals eventually began to salivate in response to the buzzer alone.
In Pavlov’s classic experiment, the food represents what is known as the unconditioned stimulus . The UCS naturally and automatically triggers a response. Pavlov’s dogs salivating in response to the food is an example of the unconditioned response.
By repeatedly pairing a conditioned stimulus with the unconditioned stimulus , the animals eventually came to associate the sound of the buzzer with the presentation of food. At this point, salivating in response to the sound of the buzzer became the conditioned response.
Examples Of Unconditioned Responses
Have you ever accidentally touched a hot pan and jerked your hand back in response? That immediate, unlearned reaction is a great example of an unconditioned response. It occurs without any type of learning or training.
Some more examples of unconditioned responses include:
- Gasping in pain after being stung by a bee
- Jerking your hand back after touching a hot plate on the oven
- Jumping at the sound of a loud noise
- Twitching your leg in response to a doctor tapping on your knee
- Salivating in response to a sour taste
- Jumping back from a growling dog
In each of the above examples, the unconditioned response occurs naturally and automatically.
Read Also: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet
When To Seek Help
Some babies are able to naturally start breastfeeding right away. Others may need a bit of help with their latch, or their rooting or sucking reflexes.
You can test your babys rooting reflex by gently stroking their cheek or mouth. They should turn their head in response to the touch, or look like theyre rooting from side to side.
If youre concerned your baby isnt rooting properly, talk to their pediatrician. The pediatrician may recommend a lactation consultant to help address any issues that arise with breastfeeding.
If youre concerned your baby isnt getting enough to eat, remember that in the first few days of life, newborns dont need a lot of breastmilk or formula per feeding because their stomachs are very small. Youll want to feed them frequently, though, especially if youre breastfeeding. Frequent nursing can help your milk to come in.
Your babys diapers are your best way to confirm that theyre getting enough milk. After day 3, breastfed babies typically have about three wet diapers per day, and by day 5, about 5 or more wet diapers per day. The wet diapers will get heavier and may be more frequent as your baby grows.
Talk to your babys pediatrician if youre concerned about the number of wet or dirty diapers, or if your baby isnt gaining weight. The pediatrician may recommend a lactation consultant to address any issues with breastfeeding.
If youre having trouble breastfeeding, the following tips may help:
| Reflex |
Aattention As Selection Operation
Imagine you have closed your eyes in a room with a mechanical clock in it. At first you do not hear the clock, but then you start attending to it. Attending to the sound looks like turning on the loudness of the loudspeaker: the ticking is getting louder. Attending to another source of sound such as a whisper of your friend sitting in a corner turns off the sound of the clock in your mind. This is how our attention works! As this example shows, attention is associated with enhancement of relevant sensory information and suppression of irrelevant sensory information. These enhancement/inhibition operations can be named by a single term selection operations. In the same way, attention as a psychological process can be determined as selection operations in sensory modalities with a goal to process relevant sensory information more accurately.
Robert E. Clark, in, 2002
Recommended Reading: How To Calculate Frequency Physics
When Someone Is Brain Dead Where Is Their Soul
Death is only declared with death of the heart , So the brain dead patient is not dead body but he is still alive that’ why we still call him a patient . Regarding the soul of the brain dead patient , it is still in his body and it leaves his body only with the death of his heart …26-Jul-2019
Read also
What Is A Reflex Psychology
reflexreflexreflex
Also, what are examples of reflexes?
A few examples of reflex action are:
- When light acts as a stimulus, the pupil of the eye changes in size.
- Sudden jerky withdrawal of hand or leg when pricked by a pin.
- Coughing or sneezing, because of irritants in the nasal passages.
- Knees jerk in response to a blow or someone stamping the leg.
Subsequently, question is, what is a reflex biology? noun, plural: reflexes. An innate, immediate involuntary action to a stimulus without prior conscious thought. Supplement. In physiology, a reflex is a response or a reaction to a stimulus. The response is innate and need not to be learned.
Likewise, what are the 4 types of reflexes?
Terms in this set
- Receptor. Site of stimulus action.
- Sensory Neuron. Transmits afferent impulses to CNS.
- Integration Center. Either monosynaptic or polysynaptic region within CNS.
- Motor Neuron.
- Stretch Reflex.
What is the difference between a reflex and a reaction?
The key difference between a reaction and a reflex is that a reaction is voluntary and requires the brain to process the information from the stimulus while a reflex is involuntary and takes place without involving the brain.
Recommended Reading: What Does F Mean In Physics
Module 1: The Nervous System
- List the components of a reflex arc
- Compare and contrast somatic and visceral reflexes
- Identify the components of the reflex arc for the stretch and withdrawal reflexes
- Define monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflexes
So far we have discussed the CNS and PNS. Now lets consider what the central nervous system might do with the information it is receiving from the afferent division of the PNS.; One option is to make conscious decisions about how to react to the information, such as deciding how to change our behavior if we are cold or hungry.; The other option is to use this sensory information to initiate a pre-programmed reflex.; A reflex is an unlearned, rapid, involuntary and predictable response.; A reflex arc is a neural pathway involved in a reflex. The reflex arc consists of 5 components:
1. sensory receptor
4. motor neuron
5. effector target
In a reflex, sensory information activates a receptor that sends information to the CNS via a sensory neuron, some level of processing occurs in the integration center, and then the response is communicated to the effector target via the motor neurons. You might recognize this as the same model used to maintain homeostasis. Reflexes are a unique category of responses because they do not require the higher centers used for conscious or voluntary responses. Instead reflexes are involuntary, stereotyped responses that occur quickly.
The Revolution In Defining Pain: From Reflexes To Subjective Experience
The focus on reflexes in twentieth-century physiology and psychology led to definitions of pain in terms of innate and conditioned reflex responses to noxious stimulation: escape, avoidance, and other aversive behaviours. Subjective experience was deemed to be unscientific. In the 1940s, however, WK Livingston argued that nothing can properly be called pain unless it is consciously perceived as such. In short, pain is not a form of behaviour; it is what we feel. The definition of pain as a subjective experienceand only thatwas finally established by Harold Merskey and his colleagues. Merskey presided over a Committee of the International Association for the Study of Pain that provided a definition now widely accepted: Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Merskey’s report goes on to say:
Pain is always subjective. Each individual learns the application of the word through experience related to injury in early life. It is unquestionably a sensation in a part of the body but it is also always unpleasant and therefore also an emotional experience. Many people report pain in the absence of tissue damage or any likely pathophysiological cause If they regard their experience as pain and if they report it in the same ways as pain caused by tissue damage, it should be accepted as pain. This definition avoids tying pain to the stimulus.
Don’t Miss: What Is Z In Chemistry