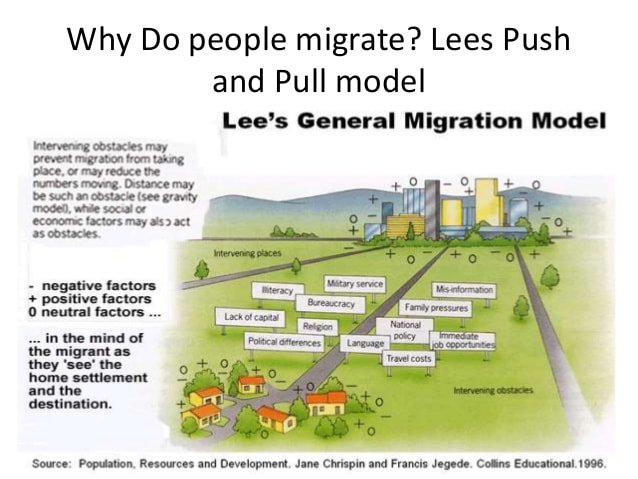
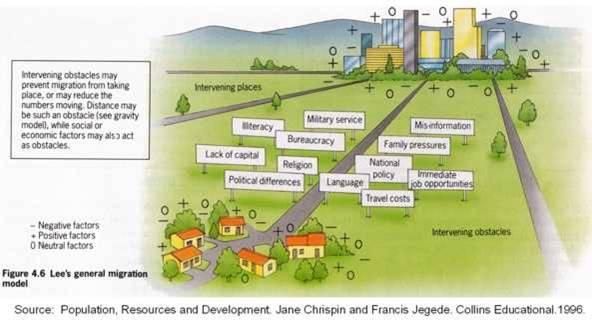
How Does Distance Decay Affect Migration
Distance decay can effect migration mainly through the push pull factors. Distance decay is the idea that the further away an idea gets from its source, the less is known about it. Also the many Intervening obstacles between the source and the destination would slow down push/ pull factors even more.
What Are 5 Pull Factors
Push and pull factors
- Economic migration to find work or follow a particular career path.
- Social migration for a better quality of life or to be closer to family or friends.
- Political migration to escape political persecution or war.
- Environmental to escape natural disasters such as flooding.
Intervening Obstacles In Migration
Intervening obstacle is an environmental or cultural feature that hinders migration Intervening opportunities Intervening opportunities are the nature and number of possible alternative migration destinations which may exist between place A and place B .
Intervening obstacles are factors that cause migrants challenges or prevent them from reaching their goal. Examples of intervening obstacles include mountains, forests, deserts, cities and bodies of water. Some of these barriers block the migration of some species, while they do not slow down other specie at all. For example, a large desert may prevent amphibians or insects from completing their migration, while birds fly right over it.
Humans may encounter intervening obstacles during migratory travels as well. Deserts and mountains are particularly difficult for humans to traverse, while forests and cities are easy for humans to cross. Over time, humans often constructed settlements near such challenging features, as a last stop in which travelers could resupply and rest before enduring difficult travels.
Don’t Miss: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet Answer Key
Activity : Cultural Identity Of The Lost Boys
Students watch excerpts from the film God Grew Tired of Us. They discuss the challenges the Lost Boys faced while adapting to life in the United States and trying to maintain their cultural identities.
DIRECTIONS
- What markers are representative of American culture?
- How do the values of the Lost Boys compare to your own?
- What questions and fears would you have if you were moving to a new place?
- What differences do you see between Dinka culture and American culture?
- How do you think you would adapt to life in a new country? Why?
- What can you do to make a difference in your community the way the Lost Boys have made a difference in their communities?
5. Have students brainstorm service-learning projects for your community.If possible, have students brainstorm possible service-learning projects for your community. Have a whole-class discussion about the needs of your community and what type of service would be most beneficial.
Activity : Mapping The Migration Of The Lost Boys
Students map the migration journey of the Lost Boys and Girls. They discuss the concept of a diaspora and the challenges of displacement.
DIRECTIONS
1. Divide students into small groups and have them mark the migration journey of the Lost Boys.Make sure each group has one set of outline maps of Sudan, Africa, the world, and the United States. Ask groups to mark the routes the Lost Boys took. List each route on the board:
- Dinka homelands in southern Sudan to refugee camps in western Ethiopia
- refugee camps in western Ethiopia, across the border into Sudan, and to Kakuma refugee camp in northwestern Kenya
- Kakuma, Kenya to Nairobi, Kenya
- Nairobi, Kenya to Brussels, Belgium
- Brussels, Belgium to New York City
2. Introduce the vocabulary word diaspora and have students add routes to their maps.Explain to students that the vocabulary word diaspora refers to the migration of a people away from an established homeland, or the displacement of a people. Tell students that the Lost Boys have settled in eighteen states in the United States, including: Arizona, California, Colorado, Florida, Illinois, Kentucky, Massachusetts, Maine, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, North Carolina, New York, Pennsylvania, Texas, Utah, Virginia, and Washington. Have students add routes from New York City to those states.
4. Discuss the hazards and physical challenges of the routes.
Recommended Reading: Calculate Half Life From Rate Constant
Theory Of Intervening Opportunities
Theory of intervening opportunities attempts to describe the likelihood of migration. Its hypothesis is that this likelihood is influenced most by the opportunities to settle at the destination, less by distance or population pressure at the starting point.
Stouffer‘s law of intervening opportunities states, “The number of persons going a given distance is directly proportional to the number of opportunities at that distance and inversely proportional to the number of intervening opportunities.”
Stouffer theorises that the amount of migration over a given distance is directly proportional to the number of opportunities at the place of destination, and inversely proportional to the number of opportunities between the place of departure and the place of destination. These intervening opportunities may persuade a migrant to settle in a place in the route rather than proceeding to the originally planned destination. Stouffer argued that the volume of migration had less to do with distance and population totals than with the opportunities in each location. This is in contrast to Zipf’s Inverse distance law.
What Is Physiological Density Quizlet
4.5/5densityPhysiological Densityphysiological densityexplained here
Physiological Density. Definition: the number of people supported by a unit area of arable land. Agricultural Density. Definition: the ratio of the number of farmers to the amount of arable land. Crude Birth Rate/Crude Death Rate.
how do you calculate physiological density? Arithmetic density, also known as real density, is very simply the total number of people divided by the total land area. Physiological density is the number of people per unit area of arable land. Arable describes land that is suitable for growing crops.
In this regard, what is physiological density example?
The physiological density or real population density is the number of people per unit area of arable land. Egypt is a notable example, with physiological density reaching that of Bangladesh, despite much desert.
What is the difference between arithmetic density and physiological density?
Arithmetic density is also known as real density while physiological density is the number of people per unit of arable land. The key difference between the two is that arithmetic is total population divided by total land while physiological is total population divided by arable land.
Read Also: How To Intimidate Someone Psychologically
What Is An Example Of Intervening Opportunity
Specifically in geography, intervening opportunities occur when a competing community can begin transporting a product to that products customer base at a lower cost than the previous area of production could because of favorable geographic conditions (Austria is closer and most often, the
What is the theory of migration?
Neoclassical economic theory This theory of migration states that the main reason for labor migration is wage difference between two geographic locations. These wage differences are usually linked to geographic labor demand and supply. Labor tends to flow from low-wage areas to high-wage areas.
What Is An Example Of An Intervening Opportunity That Influenced Migration
The Pacific states have a higher cost of living than the states further inland. Which of the following is the best example of an intervening opportunity that influenced migration? Many African American citizens were heading to Chicago after the Civil War, but settled in border cities just north of the Deep South.
Read Also: Geometry Of Ccl4
What Is Intervening Opportunity Model
4.1/5intervening opportunitiesopportunitiesrelated to it here
Specifically in geography, intervening opportunities occur when a competing community can begin transporting a product to that product’s customer base at a lower cost than the previous area of production could because of favorable geographic conditions (Austria is closer – and most often, the
Beside above, who proposed intervening opportunity model of human migration? S.A. Stouffer, an American sociologist, introduced one such modification in the gravity model. Stouffer formulated his intervening opportunity model in 1940, and claimed that there is no necessary relationship between mobility and distance .
Keeping this in consideration, what is intervening opportunity in human geography?
Intervening Opportunity. an environmental or cultural feature of the landscape that helps migration. Migratory Movement. human relocation movement from a source to a destination without a return journey, as opposed to cyclical movement.
What is an example of intervening obstacle?
Intervening obstacle. Definition: An environmental or cultural feature of the landscape that hinders migration. Example: As the Hernandez family makes their way to the US, they find themselves in Mexico City with a good job and economic status and, thus, decide to stay.
Why Are Intervening Opportunities Important
Intervening opportunity is an important factor in spatial interaction, and has very important impacts on tourist destination development in a region. There are few literatures on this topic in tourist researches, and especially in China fewer tourist researchers pay attention to intervening opportunity theory.
You May Like: Who Is Paris Jackson Mother
Activity : The Lost Boys Of Sudan
Students learn where the Lost Boys are from and how they got their name. Then they watch an excerpt from the film, God Grew Tired of Us, and write about it.
DIRECTIONS
- why the Lost Boys had to flee Sudan
- reasons they could not stay in Ethiopia
- what life was like in the refugee camp
- what new things the Lost Boys experienced on the journey from Kenya to the U.S.
Ravensteins Laws Of Migration
Watch: AP HUG –
Also Check: Child Of Rage Documentary Beth Thomas
What Are Examples Of Intervening Obstacles
Intervening obstacles are factors that cause migrants challenges or prevent them from reaching their goal. Examples of intervening obstacles include mountains, forests, deserts, cities and bodies of water. Some of these barriers block the migration of some species, while they do not slow down other specie at all.
What Is Periodic Movement In Human Geography
movementperiodic movementsmovementperiodic movement
. Thereof, what is cyclic movement in human geography?
Cyclic Movement. movement that has a closed route repeated annually or seasonally. Distance Decay. the various degenerative effects of distance on human spatial structures and interactions.
Likewise, what is an example of cyclic movement? Cyclic movement. Or circulation – for example, nomadic migration – that has closed route and is repeated annually or seasonally e.g., activity space – space within which daily activity occurs commuting, seasonal, nomadism.
In this manner, what are the three types of movement in AP Human Geography?
Commuting, seasonal movement, and nomadism is what type of movement? International migration and internal migration is what type of movement?
What is transhumance in human geography?
transhumance. A pattern of regular seasonal movement by human groups. It can be seen as a form of pastoralism or nomadism.livestock is moved seasonally between one area of pasture and another. international refugee. fleeing from one country to another.
Also Check: Beth Thomas Father
Human Barriers To Migration
Documentation is required to allow migration. Within the European Union migrants only need a passport. However, to migrate into other countries long application processes for visas or work permits are necessary.
Each country will have a specific set of rules about how many visas they give out each year or the type of skills and qualifications that someone might need to have.
Physical Barriers To Migration
Economic migrants will often arrive by aeroplane, but refugees, asylum seekers and illegal immigrants might all try to find the easiest way to cross a border.
From 2015 to the present, a huge number of illegal migrants have journeyed across the Mediterranean Sea to get to Greece, Turkey, Italy or Spain.
Many of these people might already have made their way across deserts or mountain ranges to escape persecution, conflict or war.
These physical barriers can be difficult to cross and many people are intercepted and returned to their place of origin.
Don’t Miss: Chapter 4 Test Form 2c
Who Proposed Intervening Opportunity Model Of Human Migration
modelintervening opportunity model
What is intervening population?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Theory of intervening opportunities attempts to describe the likelihood of migration. Its hypothesis is that this likelihood is influenced most by the opportunities to settle at the destination, less by distance or population pressure at the starting point.
what is intervening opportunity in human geography?Intervening Opportunityhuman
Contents
What Are Some Examples Of Intervening Obstacles
Intervening obstacles are factors that cause migrants challenges or prevent them from reaching their goal. Examples of intervening obstacles include mountains, forests, deserts, cities and bodies of water. Some of these barriers block the migration of some species, while they do not slow down other specie at all.
Also Check: Mcgraw Hill Geometry Answers
What Are Intervening Obstacles In Migration
Intervening obstacles are factors that cause migrating animals challenges or prevent them from reaching their goal. Examples of intervening obstacles include mountains, forests, deserts, cities and bodies of water. Some of these barriers block the migration of some species, while they do not slow down other specie at all. For example, a large desert may prevent amphibians or insects from completing their migration, while birds fly right over it.
Birds are some of the most well known migrants, and they are especially skilled at the practice. Because most birds fly so well, they can simply go over most intervening obstacles. However, not all birds can cross large oceans, and many are limited to places which are accessible via land. Mountains can also provide significant barriers to birds that cannot fly over them. Deserts, cities and rivers are important barriers to mammalian migrations, and often mammals must travel much further to go around such obstacles.
Humans may encounter intervening obstacles during migratory travels as well. Deserts and mountains are particularly difficult for humans to traverse, while forests and cities are easy for humans to cross. Over time, humans often constructed settlements near such challenging features, as a last stop in which travelers could resupply and rest before enduring difficult travels.
How Does Illegal Immigrant Get Green Card

The process involves submitting USCIS Form I-589, together with detailed documentation of your membership in the group that you claim and the persecution that you faced or fear. If you are granted asylum, you can apply for a green card one year after your approval, and for U.S. citizenship four years after that.
Recommended Reading: Linear Algebra What Is A Span
What Does It Mean To Deport Someone
Deportation is the act of throwing a foreigner out of a country, whether they are a resident or an intruder. If you’ve ever heard that someone was deported expelled from a country then you can probably guess that deportation is the act of that happening. … Deportation means something close to exile.
Presentation On Theme: Intervening Obstacles Hinders Migration Historical
1 Intervening Obstacles Hinders migration Historical- mountains deserts oceans Modern Day- passports, visas
2 U.S. Quota Laws 1924: 1965 1978 1990 Preferences Family reunificaton Skilled workers diversity Brain Drain
3 Unauthorized immigration Characteristics of unauthorized immigrants Source country Children Years in the United States Labor Force Distribution
4 Undocumented Immigration to the United States Undocumented immigrants ½ enter legally but remain after they are supposed to leave ½ illegally cross the border without passport or visa Become documented with forged documents The minority caught are deported
6 Americans divided on issue of immigration 1986 Immigration Reform and Control Act Could become permanent residents if they could prove continuous residence & apply for citizenship after 5 years Few applied Discouraged immigration it made it harder for recent immigrants to get jobs because of employer fines
7 U.S. States as Immigrant Destinations Fig. 3-8: California is the destination of about 25% of all U.S. immigrants another 25% go to New York and New Jersey. Other important destinations include Florida, Texas, and Illinois.
12 Undocumented Immigration: Mexico to Arizona Fig. 3-7: The complex route of one group of undocumented migrants from a small village north of Mexico City to Phoenix, Arizona.
13 United States/Mexico Border
14 Characteristics of Migrants Gender- Age and Education
23 Turkish Kebab Stand in Germany
Recommended Reading: All 2.1 Vault Codes
What Crimes Make You Deportable
For example, crimes that can get a green card holder or nonimmigrant deported include alien smuggling, document fraud, domestic violence, crimes of “moral turpitude,” drug or controlled substance offenses firearms trafficking, money laundering, fraud, espionage, sabotage, terrorism, and of course the classic serious …