What Is The Difference Between Population Geography And Demography
When we consider about both terms, it is clear that there are some similarities as well as differences in both. When we think of similarities, the main thing is that both these subject fields can be considered as subfields of Sociology, but they have developed to be separate fields in modern world context. Both subject areas are interested in human population growth and distribution. Also, both these subject fields incorporate similar criteria in their analyses.
When we think of the differences, we see that demography is more concerned with population growth, whereas population geography is more concerned in the distribution of the human population.
Demography mainly focuses on birth, aging and death rates of the human population and even though population geography studies those as well, its primary concern falls to migration.
However, both demography and population geography are important subject fields in the modern world because they focus on population growth and its distribution.
Using The Geographic Perspective To Enrich History
Geography and history are complementary subjects best taught together within the social studies curriculum. It is part of the collected wisdom of teachers that one cannot teach history without geography or geography without history. But what exactly is the nature of the relationship? What are the key concepts in geography that contribute to the teaching of history? And, what strategies can teachers use most effectively to link them together?
This article uses two standards from Geography for Life:National Geography Standards 19941 to examine the relationship between geography and history. It presents a framework of four questions that focus on using geography to interpret the past. And it explores one strategy for developing history lessons that are well-grounded in geography in order to create memorable learning experiences.
The geographic perspective is not strongly represented in the modern social studies curriculum. This is because most social studies teachers receive their training in history, and have little or no background in geography. Geography is typically defined as the physical environment and viewed as the backdrop before which history unfolds. Yet, more often than not, geography intrudes into the drama of historical change, rather than merely providing an arena for history.3
Linking Geography and HistoryWhat are the links between geography and history? The answer involves three assumptions:
Some interesting questions to examine further are:
History And Present Social Life
The segregation which kills the vitality of history is divorce from present modes and concerns of social life. The past just as past is no longer our affair. If it were wholly gone and done with, there would be only one reasonable attitude toward it. Let the dead bury their dead. But knowledge of the past is the key to understanding the present. History deals with the past, but this past is the history of the present. An intelligent study of the discovery, explorations, colonization of America, of the pioneer movement westward, of immigration, etc., should be a study of the United States as it is to-day: of the country we now live in. Studying it in process of formation makes much that is too complex to be directly grasped open to comprehension. Genetic method was perhaps the chief scientific achievement of the latter half of the nineteenth century. Its principle is that the way to get insight into any complex product is to trace the process of its making, – to follow it through the successive stages of its growth. To apply this method to history as if it meant only the truism that the present social state cannot be separated from its past, is one-sided. It means equally that past events cannot be separated from the living present and retain meaning. The true starting point of history is always some present situation with its problems.
You May Like: Fsa Warm Ups Grade 5 Answer Key
Main Differences Between Geography And Geology
Key Differences Between Geography And Geology
Upcoming points will discuss the differences between geography and geology:
Conversely, Geology is a multi-disciplinary science which studies about the Earth, its origin, present scenario and future implications.
Read Also: Holt Geometry Workbook Answer Key
Business Education Finance Geography Health History Ict Jobs Latest Updates Sports Watcing The World
Product costs are often treated as inventory and are referred to asinventoriable costs because these costs are used to value the inventory. When products are sold, the product costs become adjusting entries part of costs of goods sold as shown in the income statement. Part 16The raw material purchased is debited to raw materials inventory account under the perpetual inventory system.
- Product costs are further classified into direct material, direct labor and factory overhead.
- Product costs are those that the firms accounting system associates directly with output and that are used to value inventory.
- This is because some costs are fixed and have to be paid whether you produce one unit or one thousand.
- Sure, you can look at your cost of goods sold to see how much it costs to produce a good.
When a company accepts government funds, the funding agency may also have several strict mandates in place regarding the maximum indirect cost rate and what expenses qualify as indirect costs. For example, if an employee is hired to work on a project, either exclusively or for an assigned number of hours, their labor on that project is a direct cost. If your company develops software and needs specific assets, such as purchased frameworks or development applications, those are direct costs.
The Scientific Process Of Geography
- Observe a particular feature, phenomenon, or event in the world that stimulates a series of questions and thought process.
- Develop an educated thought that tries to answer the questions posed, called a hypothesis.
- Design an experiment or way to “test” your hypothesis.
- Implement the experiment and observe the results using unbiased data and measurement techniques.
- Propose a solution, answer, or rule that explains the hypothesis and experiment.
hypothesis theory
Recommended Reading: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
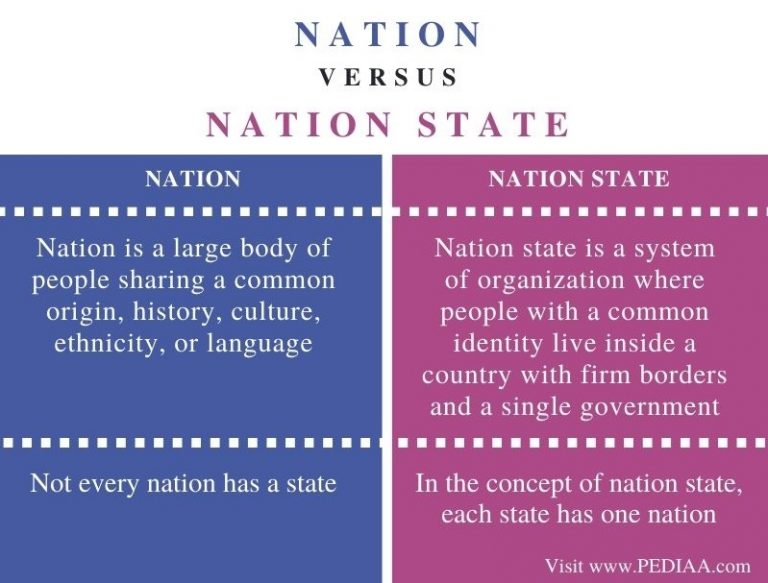
Difference Between Geography And Demography
There are two sciences that are in charge, one to describe the planet we live in and the other to study human populations. These are Geography and Demography respectively. While it is true that both can help each s t it is also important to understand cu to be their characteristics that differentiate them.
Geography
The word Geography comes from the Greek word geo < terra> and graphing < draw> . It is the science in charge of the graphic representation of this planet: Earth. It studies the territories, places and the terrestrial surface, that is to say, the whole territorial structure. Geography began to develop from ancient Greece, where Erat or stenes one of the first Ge or graphs or at least one of the m to s recognized whose work was lost when the Library of Alexandria í to was burned.
Today, Geography is divided into many branches and is also complemented with other sciences since now it is not only limited to studying the structure or representation of terrestrial space but also studies various phenomena, establishing relations between them and the locations in which they occur. C studies or how climate change, natural phenomena and various historical events that cut across human societies contribute to geographical changes.
Demography
History Vs Social Studies
History and social studies fall under the field of the academy. Both are considered as matters of inquiry and are included as compulsory subjects in the majority of schools and curricula. The human element is prevalent in both studies. History focuses on the people involved in history as well as human contributions that lead to historical events. Meanwhile, social studies focus on society as a collective human entity and on its members as individual human beings. Although both social science and history are similar in nature as a study, they have differences in terms of scope and nature.
For instance, history is the study of an entity with respect to its past, events, people, and other important variables that contributed to what is present in a particular context. As a study, it aims to discover, collect, and interpret data or information from the past. This may be people or artifacts that serve as proof of the human record. History often creates constructions and contributions of the past that are linked to the present.
On the other hand, social studies involve various fields and an entity called society. It deals with society, how it works, and other people-related issues like social behavior or compliance, traditions, and cultures. Social science integrates the social studies and humanities fields under this umbrella term dealing with human behavior, interactions, as well as the human societies of both the past and the present.
Also Check: Geometry Dash Ericvanwilderman
Critical Review: Historical Geographies Of Imperialisms
Historical geographies of imperialism emphasize the complexity of imperialism in space. By exploring colonial encounters, recent research reveals imperialism as a complex lived event and colonial authority as ambiguous. Diverse views about difference, superiority, belonging, and identity complicated encounters and relations among people. By increasing mobility and migration, and thus throwing peoples together in new ways, imperialisms developed hybrid identities, contested spaces, and network connectivity. Imperial projects generated new locales inscribed as expressions of power and domination but often these formed within localities where imperial authorities competed with other forms of governance so that their power was negotiated and challenged. Even the racist and sexist representations that imagined and sustained empires were themselves resisted and reworked, whether in the metropolitan centers or the imperial peripheries. By researching the contact zones, networks, traces, and surveys of imperial encounters historical geographers are remapping the bounds of empire and challenging synoptic views of empires as homogenous territories.
M. Tanskanen, in, 2009
What Is Geography And History
Although there was a much earlier teaching of what is now called geography, the academic discipline is largely a 20th-century creation, forming a bridge between the natural and social sciences. The history of geography is the history of thinking about the concepts of environments, places, and spaces.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
Content: Geography Vs Geology
| A science which deals with the description of areal differentiation of the surface of Earth. | A scientific discipline which studies the Earth and its past and anticipates future implications. | |
| Discusses | How human culture influences the natural environment? How different regions have an impact on the people living there? | How the Earth is made? What it is composed of? How did it transform over the years? |
| Subject Matter | It records the area of land forms, length of mountain ranges and coastal lines, forms of water sources and its location, human activities, etc. | It researches about the surface of land, rocks and its types, energy sources and its sustainability, climatic changes, the impact of development on the environment, etc. |
Differences Between Direct And Indirect Costs And Why Its Important

A manufacturers product costs are the direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead used in making its products. Period costs are not a necessary part of the manufacturing process. As a result, period costs cannot be assigned to the products or to the cost of inventory. Period costs are the costs that cannot be directly linked to the production of end-products.
Part 14The predetermined manufacturing overhead rate per machine hour is closest to $12.50. In case the applied manufacturing overhead is less than the actual manufacturing overhead, then the overhead is said to be under applied. In case the applied manufacturing overhead is more than the actual manufacturing overhead, then the overhead is said to be over-applied. Companies that manufacture products using job order costing system usually receive orders for products with customized specifications.
You May Like: Algebra 2 Eoc Fsa Practice Test
Similarities And Differences Between History Geography
Never confuse history and story again difference between history and the seaside paring holidays never confuse history and story again scientific diagram
Education sciences full text parison as a method for geography html what are the differences and similarities between year 2 geography the seaside paring holidays what are the similarities and differences between geography history quora this cross curricular unit links geographical and historical study to enable s research understand develop an a
Integrating History And Geography
Renewing the Social Studies Curriculum
The California History-Social Science Framework places great emphasis on integrating history and geography in social studies. As a member of the committee that helped create this dynamic curriculum document, I urged, along with geographer Christopher Salter, a strong integrated geography component. Many of us on the committee worried that geography would be relegated to one or two grade levels and that students would study geographic concepts and vocabulary apart from history and other social science disciplines. Although the framework recommends the infusion of geography at all grade levels, formal integration is placed within the sequential study of history in grades 4 through 11.
Integrating the Five Themes of GeographyAn effective approach to designing integrated history and geography curricula and teaching strategies is to place a history unit in the context of the five themes of geography. The themes are all related-if you use one, you use them all. You might emphasize aspects of a theme at one point, but you must keep in mind their strong interrelationships. According to the Guidelines for Geographic Education , the five themes of geography are location, place, relationships within places , relationships between places , and regions .
1. Location. Where did the Oregon Trail begin and end? Name three rivers that pioneers followed on the Oregon Trail.
National Geographic Society
Don’t Miss: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet
Difference Between Sociology And History
Sociology and History are closely related to each other. It is said that History without Sociology has no fruit, while Sociology without History has no root.
Yet for all their closeness, both the branches of social science are distinct from one another.
History is the study of past events. It also includes a survey of conditions and developments in economic, religious and social affairs.
Sociology is the study of the pattern of human interaction, culture, and social relationships that surround everyday life.
*Sociology and History are Optional Subjects in the UPSC Mains Exam
This article will attempt to highlight the differences between the two within the context of the IAS Exam
The difference between Sociology and History is given in the table below:
Differences between Sociology and History
Aspirants can find study materials for UPSC History and Sociology optional subjects through the links given below:
The Relationship Between History And Geography Education Essay
Info: 2379 words Essay 1st Jan 2015 inEducation
Whilst geography and history are two discrete subjects within the National Curriculum , Martin believes that it is possible to identify areas of similarity between them from looking at the importance of history and geography statements. Moreover, she points out that there are links between history and geography through the knowledge and understanding, skills, concepts and values and attitudes and therefore it is possible to incorporate cross-curricular links when teaching the subjects. However, before these links are explored it is important to provide an overview of both subjects in their own right.
If you need assistance with writing your essay, our professional essay writing service is here to help!
Cooper et al state that geography is fundamental to childrens understanding of the world they live in. They highlight that geography allows children to study people and develop a sense of place. Furthermore, they point out that geography fosters childrens appreciation of the environment and helps them to understand why sustainability is important. Similarly, Catling and Willy suggest that primary geography allows children to develop a curiosity about the world through exploring people and the environment.
You May Like: Eoc Fsa Warm Ups Algebra 1 Answers