Examples Of Single Replacement Reactions
In chemistry, there are three basic types of reactions, which include addition reactions, decomposition reactions, and displacement reactions. Among them, this ScienceStruck article comes forward to discuss in length about a type of displacement reaction called single replacement reaction, accompanied by various examples.
Like it? Share it!
In chemistry, there are three basic types of reactions, which include addition reactions, decomposition reactions, and displacement reactions. Among them, this ScienceStruck article comes forward to discuss in length about a type of displacement reaction called single replacement reaction, accompanied by various examples.
| Did You Know?To protect structures made of iron from corroding, a more reactive metal like zinc is added to it. It reacts with the environment and corrodes itself, while the iron is protected. Such metals are aptly given the name sacrificial metal. |
In chemistry, the compounds that take part in a chemical reaction are called reactants, whereas the compounds that are formed after a chemical reaction are called products. Reactants are physically and chemically distinct from the products that they make. A chemical reaction can be given as:
A + B C + D
As a rule, the reactants A and B are written on the left-hand side, and their products are written on the right-hand side of the arrow .
Single Replacement ReactionsA + B-C B + A-CK > Na > Li > Sr > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Cr > Fe > Ni > Sn > Pb > H > Cu > Ag
Using The Reactivity Series To Predict Whether A Reaction Will Occur
Use the reactivity series to determine whether a single replacement reaction will occur.
For anion replacement, the reactivity series for the halogens is:
Most reactive F2> Cl2> Br2> I2 Least Reactive
This is the order of the halogens going down their group on the periodic table, so its easy to remember. The higher the halogen is on the periodic table, the more reactive it is. So, Cl2 replaces I2 in a single replacement reaction, but it wont react if the anion has fluoride ions.
The reactivity series for cations is longer and not as obvious. The least reactive metals wont react with the H+ ion, while the most reactive metals not only react with the ion, but can even pull the hydrogen ion off liquid water. Elements in-between can react with the H+ ion and sometimes pull the hydrogen off water vapor.
But, for a general chemistry class, you mainly need to know which metals can replace each other and which ones cant. For example, zinc can replace tin as the cation in a compound, but it cant replace potassium . In general, alkali metals are the most reactive, followed by alkaline earth metals. Noble metals, in contrast, are relatively unreactive.
How To Recognize A Substitution Reaction
You can recognize this type of reaction by looking for a trade between one cation or anion in a compound with a pure substance in the reactants side of the equation, forming a new compound in the products side of the reaction.
If, however, two compounds appear to “trade partners”, then you’re looking at a double displacement reaction rather than a single displacement.
You May Like: How To Find The Indicated Length
What Are The 6 Types Of Chemistry
Terms in this set
- organic chemistry. the study of of carbon-containing compounds.
- inorganic chemistry. the study of non-organic substances, many of which have organic fragments bonded to metals
- physical chemistry.
- Unit 6: General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Unit 7: p Block Elements
- Unit 8: d and f Block Elements
What Are Single Replacement Reactions
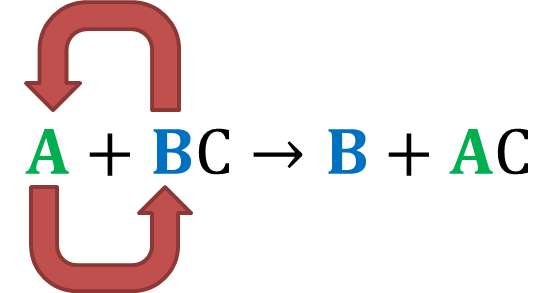
Now that you know what replacement reactions are, lets take a look at one of its subtypes. Consider the following reaction: A + BC B + AC
Here, A is an element, and BC is a compound, but A is more reactive than the compound BC. Therefore, when they undergo a chemical reaction, A will replace B, as it is more reactive, to form the compound AC. B is given out in either an elemental or ionic form. Only a single compound undergoes replacement in this reaction, thus the name single replacement.
A diagrammatic representation of Single Replacement Reaction
To understand this better, lets consider the following examples: Zn + CuCl2 ZnCl2 + Cu
This reaction easily fits in with the above explanation. Zinc is more reactive than Copper. Thus, when it is added in a solution of Copper Chloride, it replaces Copper and forms Zinc Chloride. Copper is given out in the ionic form. This reaction is also an excellent example of cationic replacement. We say this because the replacing ion has a positive charge, i.e., 2+. As such, it is a cation.
Br2 + 2KI 2KBr + I2
Similarly, when Bromine is added to a solution of Potassium Iodide, it replaces the position of Iodine in the compound. As a result, Potassium Bromide is formed, whereas a molecule of Iodine is given out. This reaction takes place because Bromine is more reactive than Iodine, which is why it replaces it. Because the replacement ions have a negative charge, this reaction is an example of anionic replacement.
Read Also: Geometry Dash Practice Music
Reactions At The Solid
Reaction can take place at the solid|gas interface, surfaces at very low pressure such as ultra-high vacuum. Via scanning tunneling microscopy, it is possible to observe reactions at the solid|gas interface in real space, if the time scale of the reaction is in the correct range. Reactions at the solid|gas interface are in some cases related to catalysis.
What Is Double Displacement Reaction
Double displacement reactions are those reactions where the cations and anions of reactants switch places with each other or replaces each other. Generally, it can be represented as follows
AB + CD CB + AD
Example of double displacement reaction Reaction between silver nitrate and sodium chloride is an example of double displacement reaction. The reaction given below
AgNO3 + NaCl AgCl + NaNO3
-
Examples of single displacement reaction
-
Reaction between zinc and copper sulphate
Zn + CuSO4 ZnSO4 + Cu
-
Reaction between copper and silver nitrate
Cu + 2AgNO3 CuNO3 + 2Ag
-
Reaction between iron and copper sulphate
Fe + CuSO4 FeSO4 + Cu
-
Reaction between lead and copper chloride
Pb + CuCl2 PbCl2 + Cu
-
Reaction between chlorine and sodium bromide
Cl2 + 2NaBr 2NaCl + Br2
-
Examples of double displacement reaction –
-
Reaction between potassium nitrate and aluminum chloride
KNO3 + AlCl3 Al3 + KCl
-
Reaction between lead nitrate and potassium iodide
Pb2 + 2KI 2KNO3 + PbI2
-
Reaction between iron chloride and barium hydroxide
FeCl3 + Ba2 Fe3 + BaCl2
-
Reaction between lead nitrate and sodium sulphate
Pb2 + Na2SO4 PbSO4 + 2NaNO3
-
Reaction between barium chloride and copper sulphate
BaCl2 + CuSO4 BaSO4 + CUCl2
Also Check: Geometry Of Ccl4
What Is A Displacement Reaction
A displacement reaction is the one wherein the atom or a set of atoms is displaced by another atom in a molecule. For instance, when iron is added to a copper sulphate solution, it displaces the copper metal.
A + B-C A-C + B
The above equation exists when A is more reactive than B.
A and B have to be either:
- Halogens where C indicates a cation.
- Different metals wherein C indicates an anion.
What Are The Three General Types Of Single Replacement Reactions
There are three main types of single replacement reactions determined by the reactivity series:
- Metal Replacement: where metal will displace another metal.
- Hydrogen Replacement: where hydrogen gas is produced through displacement by a metal.
- Halogen Replacement: when a halogen participates in displacement.
Read Also: Beth Thomas Psychopath
Reactions In Organic Chemistry
In organic chemistry, in addition to oxidation, reduction or acidâbase reactions, a number of other reactions can take place which involve covalent bonds between carbon atoms or carbon and heteroatoms . Many specific reactions in organic chemistry are name reactions designated after their discoverers.
Key Takeaways: Double Replacement Reaction
- A double replacement reaction is a type of chemical reaction that occurs when two reactants exchange cations or anions to yield two new products.
- Double replacement reactions are also called double replacement reactions, double displacement reactions, or metathesis reactions.
- Neutralization, precipitation, and gas formation are types of double replacement reactions.
Double replacement reactions take the form:
A+B-+ C+D- A+D-+ C+B-
In this type of reaction, the positive-charged cations and the negative-charged anions of the reactants both trade places , to form two new products.
Also Known As: Other names for a double displacement reaction are a metathesis reaction or a double replacement reaction.
Recommended Reading: Automatic Processes Definition Psychology
Quantitative Relationships Based On Chemical Equations
A balanced chemical equation not only describes some of the chemical properties of substancesby showing us what substances react with what other substances to make what productsbut also shows numerical relationships between the reactants and the products. The study of these numerical relationships is called stoichiometry. The stoichiometry of chemical equations revolves around the coefficients in the balanced chemical equation because these coefficients determine the molecular ratio in which reactants react and products are made. It is very similar to cooking. For example, to make a hamburger, for each hamburger patti, you need to have two slices of bread for the bun. Thus, the ratio of bread to hamburger is 2 to 1.
Consider the following balanced chemical equation:
2C2H2 + 5O2 4CO2 + 2H2O
The coefficients on the chemical formulas give the ratios in which the reactants combine and the products form. Thus, we can make the following statements and construct the following ratios:
STATEMENT:
This statement can then be represented mathematically into ratios that represent these written relationship statements.
As usual with a conversion problem, we start with the amount we are given 26 C2H2 and multiply it by a conversion factor that cancels out our original unit and introduces the unit we are converting toin this case, CO2.
Thus, we have two choices for our conversion factor
Single Replacement Reaction Definition
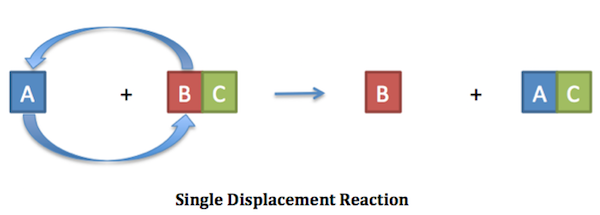
A single replacement reaction is a chemical reaction where one element replaces another in a compound. It is also known as a single displacement reaction. The general form of a single replacement reaction chemical equation is:A + BC B + ACSingle replacement reactions occur when A is more reactive than B or product AC is more stable than BC. A and B can be either two metals or else two halogens . If BC and AC are in aqueous solutions, C acts as a spectator ion.
Read Also: Algebra 1 Warm Ups
What Is Single Replacement In Chemistry
singledisplacement reactionsinglereplacementchemical
. Similarly, it is asked, what is an example of a single replacement reaction?
Single Replacement Reactions. A single replacement reaction occurs when one element replaces another in a single compound. An example of a single replacement reaction occurs when potassium reacts with water . A colorless solid compound named potassium hydroxide forms, and hydrogen gas is set free.
how do you know if a reaction is single replacement? Recognizing a Single–Displacement ReactionYou can predict whether a single–displacement reaction will occur by comparing the reactivity of an element using an activity series table. In general, a metal can displace any metal lower in the activity series . The same rule applies to halogens .
In respect to this, what is the difference between single and double replacement?
A single–replacement reaction replaces one element for another in a compound. A double–replacement reaction exchanges the cations of two ionic compounds.
How are single replacement reactions used in our daily lives?
One everyday item that we use that is the result of a single displacement is table salt. When calcium chloride reacts with sodium, the result is sodium chloride and calcium. Sodium chloride is table salt. Any time a simple metal reacts with an acid, it is a single displacement reaction.
example
Hugues Serrahima
What Is A Replacement Reaction
Before diving into the subtypes, lets explore the basics of this chemistry principle. Have you ever seen a rusted iron rod? This type of object is a prime example of a chemical reaction. A process in which one or more substances are converted into one or more different substances is called a chemical reaction. The substances that undergo a change are referred to as reactants, while those being formed are called products. In the case of rusting, our reactants are represented by iron and water vapor in the air. When these two react, they form rust, which is referred to as our product.
The Chemistry of Rusting
However, to classify reactions and make things a bit easier, we have broken this down into specific categories. In replacement reactions, more reactive elements replace the less reactive elements of a compound to form a stable product. These replacement reactions are also known as displacement reactions.
Read Also: Geometry Dash 2.1 Hack Tool
Types Of Chemical Reactions
Learning Objectives
- Recognize chemical reactions as single-replacement reactions and double-replacement reactions.
- Use the periodic table, an activity series, or solubility rules to predict whether single-replacement reactions or double-replacement reactions will occur.
Up until now, we have presented chemical reactions as a topic, but we have not discussed how the products of a chemical reaction can be predicted. Here we will begin our study of certain types of chemical reactions that allow us to predict what the products of the reaction will be.
A single-replacement reaction is a chemical reaction in which one element is substituted for another element in a compound, generating a new element and a new compound as products. Presented below:
is an example of a single-replacement reaction. The hydrogen atoms in \ are replaced by \ atoms, and in the process a new elementhydrogenis formed. Another example of a single-replacement reaction is
Here the negatively charged ion changes from chloride to fluoride. A typical characteristic of a single-replacement reaction is that there is one element as a reactant and another element as a product.
A double-replacementreaction occurs when parts of two ionic compounds are exchanged, making two new compounds. A characteristic of a double-replacement equation is that there are two compounds as reactants and two different compounds as products. An example is
Example \
What Is Single Displacement Reaction
Those reactions in which one element replaces another element from its salt or compound are called single displacement reactions. These are also called single replacement reactions. General representation can be written as well
A + B-C A-C + B
It will occur if A is more reactive than B. Generally, metals and its salts give single displacement reactions. In these reactions more reactive metal displaces less reactive metal from its salt. For example, potassium is more reactive than magnesium, so potassium replaces magnesium from magnesium chloride. The reaction between potassium and magnesium chloride occurs as follows
2K + MgCl2 2KCl + Mg
You May Like: What Effect Did Geography Have On The Way Greece Developed
What Is Reactivity Series
Reactivity series is the series of metals based on their reactivity from highest to lowest. So, reactivity series of metals can be defined as a series of metals, in order of reactivity from highest to lowest. It is also known as activity series. The reactivity of metals is because of their incomplete outer orbitals or due to their electronic configuration. Metals form positively charged ions as they tend to lose electrons. Metals with high atomic numbers tend to be more reactive as their electrons are far from the positively charged nucleus. So, they can be removed easily.
What Is A Reactant
The substance to the left of the arrow in a chemical equation are called reactants. A reactant is a substance that is present at the start of a chemical reaction. The substance to the right of the arrow are called products . A product is a substance that is present at the end of a chemical reaction.
Don’t Miss: How To Find Halflife
Single Replacement Reaction Examples
There are two different scenarios for single replacement reactions. In one form of the reaction, one cation replaces the other. In the other form of the reaction, one anion replaces the other.
Cation Replacement Examples
Usually the cation is a metal, but it doesnt have to be. Here are examples of single replacement reactions involving the cations:
- Zn + 2 HCl ZnCl2 + H2
- 2 K + 2H2O 2 KOH + H2
- Cu + 2 AgNO3 2 Ag + Cu2
- Ca + 2 H2O Ca2 + H2
But, if the reactant in element form is not more reactive than the other cation, no reaction occurs. In some cases, the reverse reaction is favored, but the forward reaction is not.
Anion Replacement Examples
Instead of cation replacement, a single replacement reaction may involve the anion. In practice, the only anions participating in single replacement reactions are the halogens . The general form of the reaction is:A + BC BA + C
In addition to being a single replacement reaction, this is also an oxidation-reduction or redox reaction. Examples of anion replacement reactions include:
- Cl2 + 2 NaBr 2 NaCl + Br2
- Br2 + 2 KI 2 KBr + I2
Again, if the elemental reactant is not more reactive than the other anion, no reaction will occur. For example, the following reaction does not occur:
I2 + 2 KBr no reaction
Writing And Balancing Chemical Equations
Water is composed of hydrogen and oxygen. Suppose we imagine a process in which we take some elemental hydrogen and elemental oxygen and let them react to make water. The chemical equation below is used to express this reaction:
In this chemical reaction, the chemical formulas of the reactants are written on the left side of the equation, and the chemical formulas of the products are written on the right side. A plus sign connects the initial substances , and an arrow represents the chemical change . In reactions, it is also common to include a phase label with each formula for solid, for liquid, for gas, and for a substance dissolved in water, also known as an aqueous solution.
Figure 5.2 shows a rather dramatic example of this very reaction.
Figure 5.2 Chemical reactions can be violent in nature. When exposed to a spark or a flame, hydrogen and oxygen react violently to form water. Here the hydrogen gas in the zeppelin, SS Hindenburg, reacts with the oxygen in the air to make water.
The Hindenburg Photo is made available from theUS Navy.
Practice Writing and Balancing Equations
CH4 + Cl2 CCl4 + HCl
CH4 + Cl2 CCl4 + 4HCl
CH4 + 4Cl2 CCl4 + 4HCl
Now we double check: each side has one carbon atom, four hydrogen atoms, and eight chlorine atoms. Yes, the chemical equation is balanced.
Recommended Reading: How Did Geography Spur Industrialization In The Northeast