What Is The Meaning Of Enclosure Movement
The Enclosure Movement was a push in the 18th and 19th centuries to take land that had formerly been owned in common by all members of a village, or at least available to the public for grazing animals and growing food, and change it to privately owned land, usually with walls, fences or hedges around it.
Examples Of Relative Location
The relative location of a place changes based on how its location is being described in terms of its relative position to another location.
- The White House is approximately nine miles from Ronald Reagan National Airport in the District of Columbia.
- The White House is approximately 30 miles from Dulles International Airport in Chantilly, Virginia.
- Washington, D.C. is around 40 miles from Baltimore, Maryland.
- The Port of Baltimore in Maryland is 197 nautical miles away from the Port of Norfolk in Virginia.
- AIM Mail Center is in the shopping center located at the intersections of Grelot and Hillcrest roads in Mobile, Alabama.
- The fourth grade classroom is in the second building past the gymnasium.
- Interests along the eastern coast of the Gulf of Mexico should closely monitor the storm’s progress.
What Is The Impact Of Migration
Positive Impact
Migration helps in improving the quality of life of people. It helps to improve social life of people as they learn about new culture, customs, and languages which helps to improve brotherhood among people. Migration of skilled workers leads to a greater economic growth of the region.
You May Like: Define Abiotic Biology
What Was The Impact Of Enclosures On The Poor Farmers
The following are the impact of Enclosure on Poor:
The poor could no longer collect the firewood or graze their animals on common land. Now they could not hunt small animals for the meal. Poor farmers lost their livelihood and those who earlier bought threshing machines found it difficult to pay the remaining amount.
Geography’s Ways Of Looking At The World
A central tenet of geography is that “location matters” for understanding a wide variety of processes and phenomena. Indeed, geography’s focus on location provides a cross-cutting way of looking at processes and phenomena that other disciplines tend to treat in isolation. Geographers focus on “real world” relationships and dependencies among the phenomena and processes that give character to any location or place. Geographers also seek to understand relationships among places: for example, flows of peoples, goods, and ideas that reinforce differentiation or enhance similarities. Geographers study the “vertical” integration of characteristics that define place as well as the “horizontal” connections between places. Geographers also focus on the importance of scale in these relationships. The study of these relationships has enabled geographers to pay attention to complexities of places and processes that are frequently treated in the abstract by other disciplines.
Integration in Place
Places are natural laboratories for the study of complex relationships among processes and phenomena. Geography has a long tradition of attempting to understand how different processes and phenomena interact in regions and localities, including an understanding of how these interactions give places their distinctive character.
Interdependencies Between Places
Suggested Citation:Rediscovering Geography: New Relevance for Science and Society
Interdependencies Among Scales
Also Check: Unit 1 Test Geometry Basics Answer Key
What Role Did The Enclosure Movement Play In The 16th And 17th Century England
What role did the enclosure movement play in sixteenth- and seventeenth-century England? It created a crisis where many people had no way to make a living. In the battles between Parliament and the Stuart kings, English freedom: remained an important and much-debated concept even after Charles I was beheaded.
Place: Human And Environmental Differences
Place refers to a description rather than a location. Place is divided into two categories: human differences and physical differences. The concept of human differences refers to the ways in which people change and develop a place. These changes may be concrete, as in building construction or cultural. The concept of physical differences describe the ways in which a part of the world is characteristically different from others. For example, some places have mountains, while others have desert terrain.
Also Check: Define Y Intercept In Math
What Does Cage And Enclose Mean
1 : a box or enclosure having some openwork for confining or carrying animals 2a : a barred cell for confining prisoners. b : a fenced area for prisoners of war. 3 : a framework serving as support the steel cage of a skyscraper. 4a : an enclosure resembling a cage in form or purpose a cashiers cage.
Examples Of The Five Themes Of Geography
The five themes of geography include location, human-environment interaction, place, region, and movement. These five concepts help educators explain how and why humans map the Earth, as well as the ways in which people affect and are affected by the Earth. The five themes of geography help students comprehend the concepts of geography and apply them to their daily lives.
TL DR
Geography has five themes that help humans comprehend different aspects of the field and how they relate to human life. The concepts of location, human-environment interaction, place, region, and movement make up this list.
You May Like: Gina Wilson Geometry Answer Key Unit 1
Factors Triggering Mass Wasting
Previously, the word mass wasting indicated a variety of processes by which large masses of crustal substances are moved by gravity from one place to another. Latterly, the word mass movement has been substituted to involve mass wasting processes and the sinking of restrained areas of the Earths ground surface. That said, Mass movements on slopes and sinking are often sustained by water and the importance of both types is the part each plays in the alteration of landforms.
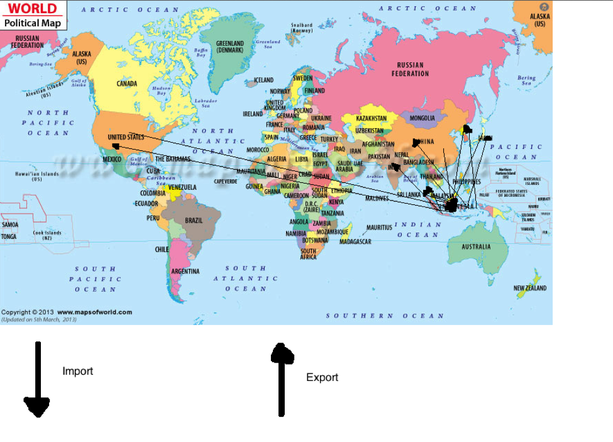
What Does The Theme Of Movement Mean In Geography
Movement As humans, we move people, goods, and ideas across the planet at will. The theme of movement examines this and is one of the most essential parts of geographical exploration. It deals with the examination of immigration, emigration, populations, and distribution in the regions and countries of the world.
Recommended Reading: Answer Key Algebra Nation Section 1 Test Yourself Answers
What Is The Purpose Of Enclosure
An enclosure, according to the National Electrical Manufacturers Association , is a surrounding case constructed to provide a degree of protection to personnel against incidental contact with the enclosed equipment and to provide a degree of protection to the enclosed equipment against specified environmental
How Do You Explain Migration

migration, n.
a. The movement of a person or people from one country, locality, place of residence, etc., to settle in another an instance of this. Migration is, first and foremost, a normal human activity. Human beings have always moved from one country, locality, place of residence to settle in another.
Also Check: How To Do Percent Error Chemistry
How Do We Interact With The Environment
There are 3 types of human environment interaction:
Examples Of Absolute Location
The absolute location of a place does not change. The broadest example of a place’s absolute location is its combined latitude and longitude. The place’s position on a map and its address are also examples of absolute location.
- The White House’s latitude is 38.8977° N and its longitude is 77.0365° W.
- The White House’s address is 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington, D.C.
These examples hold true for any place, from your home to your school to your favorite places to visit and beyond.
Don’t Miss: My Hrw Answers Algebra 1
What Is The Human Environment Interaction In Italy
People in Italy interact with the environment in many ways. For example, because of the many hills, people have to adapt and build different houses to fit on those hills. Some negative interactions are air pollution from sulfur dioxide emissions and water pollution from agricultural fertilizers and pesticides.
Examples Of Physical Place Characteristics
Physical place is represented by the physical features of a location.
- Islands are above water and surrounded by it.
- Mountainous terrains can be steep, jagged or gently sloping.
- Terrain can be flat, rocky, even, or uneven.
- An area can be heavily forested or free of vegetation.
- Arctic climates are extremely cold.
- Tropical climates are extremely hot.
- Soil can have varying levels of acidity.
Recommended Reading: Homework Practice Workbook Geometry Answers
Features Of Mass Movements
-
Mass movement is also known as Mass Wasting, bulk movements of rock and soil
-
Debris down slopes in response to the pull of gravity, or the rapid or steady sinking of the Earths surface in a principally vertical direction is influenced with many factors.
-
It is the movement of masses of bodies of mud, soil, rock, bedrock residue, which commonly occurs along steep-sided hills and mountains due to the gravitational pull.
-
Gravity imposes its force on all matter, both bedrock and the elements of weathering. Therefore, weathering is not crucial for mass movement though it aids mass movements.
-
Mass movements that are sliding of massive amounts of rock and soil are observed in landslides, mudslides, and avalanches.
-
These are very active over weathered slopes rather than over unweathered materials.
-
The ice, water or air does not carry debris with them from place to place but conversely, the residue may transport with it ice, water, or air.
-
Mass movements do not appear under erosion though there is a shift of substances from one place to another.
-
Heave, slide and flow are the three forms of movements.
What Is Physical Geography Crash Course Geography #4
Related Searches
what is human environment interaction in geographywhat is human environment interaction examplesinteraction geography exampleswhat does region mean in geographyhuman environment interaction definitionwhat does relative location mean in geographywhat does human-environment interaction mean in the 5 themes of geography
Read Also: Holt Geometry Book Answers
What Is Human Activity In Geography
The study of the patterns and dynamics of human activity on the landscape. Broadly conceived, human geography includes both those areas of geographic study that are more narrowly focused on human activity, and those that are particularly concerned with human-environment dynamics, or the naturesociety tradition (W.
What Is Slumping In Geography
4.4/5slumpSlumps
Accordingly, what is slumping and sliding?
Slumps and slides are downslope movements of sediments above a basal shear surface where there is, respectively, significant and insignificant internal distortion of the bedding . In slumps, the bedding should be recognizable, otherwise they classify as debris flows.
Secondly, what is sliding in geography? Slides. A slide happens when a section of soil or rock suddenly gives way and moves down a slope. The material moves as a single mass along a slippery zone. The slippery zone is often made up of wet sediment . Translational slides move along a flat slippery zone.
Considering this, what is slumping GCSE?
Slumping: involves a whole segment of the cliff moving down-slope along a saturated shear-plane.
What is a rockfall in geography?
Rockfall is a form of mass movement or mass wasting in which pieces of rock travel downward through some combination of falling, bouncing, and rolling after they are initially separated from the slope.
Also Check: Why Was The Pail Pale Math Worksheet
Examples Of Movement In A Sentence
movementmovementsmovementmovementsmovementsmovementmovementmovementmovement Washington PostmovementRolling Stonemovement Fortunemovement The Atlanticmovement Forbesmovement New York Timesmovement The Enquirermovement PEOPLE.com
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘movement.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
What Does Contiguous Mean
If the world was like how it used to be, with all the tectonic plates fused when the world’s continents were bordering each other the world would be contiguous because there would be no physical separation between the continental plates. Now, it is non-contiguous because the tectonic plates have moved which has made landmasses disperse, divided by vast stretches of oceans. The biodiversity of the world was also not as varied in the contiguous landscape as it is today. The absence of isolation did not favor the independent evolution of the species of the world. The contiguous land masses also encouraged the migrations of early humans across the landscape. The word contiguous in Geography might also mean undivided political or geographical land. For example, the 48 contiguous states of the United States are called so because, though each state has defined local borders, they are part of one single political entity.
Also Check: What Does Ml Stand For In Chemistry
Location: Coordinates And Relative Distance
Two distinct but related parts the specific and the general make up the idea of location. Specific location refers an actual address, like “123 Main Street,” or a set of geographical coordinates like “40.7128° N, 74.0060° W.” General location describes where a place is in relation to another place. It does not give a direct address but indicates a place’s relative location and its relative distance. For example, the general location of a certain store could be “20 minutes away by car, next to the bank.”
Teaching The Five Themes Of Geography
As many of my long-time readers know, I spent time as a K-12social studies teacher and as a professor of social studies education. Duringthis time, one of my favorite things to teach was thefive themes of geography. The five themes of geography are location, place,human-environment interaction, movement, and region.
These themes were developed in 1984 by the National Councilfor Geographic Education and the Association of American Geographers to organizeand facilitate the instruction of geography in K-12. While they have been replacedby the NationalGeography Standards, I still think they provide an excellent way to promotethe teaching of geography. If I were still teaching social studies, I would useboth. Since come of you may not be familiar with the five themes of geography,lets discuss them.
A brief discussion of each the five themes of geography
Location Location pertains to a place or position.The instruction of geography usually begins with location. Location can be twokinds: absolute location and relative location. Absolute location is defined usingits exact address . Relative location describes where aplace is in relation to other locations.
Place Place pertains to the physical and human attributesor characteristics of a location. This concept allows us to compare andcontrast two places on Earth. The place theme of geography illustrates clear imageof a place in the minds of the learners.
Why do students need to learn the five themes ofgeography?
Don’t Miss: Compass Rose For Kids
What Is A Mass Movement
Mass Movement, also known as mass wasting, represents the downhill movement of cliff material under the persuasion of gravity. It depicts the bulk movements occurring in soil and rock residue down slopes in response to rapid or steady sinking of the Earths surface in a vertical direction or the pull of gravity. Previously, the word mass wasting was used to reflect different processes by which huge masses of crustal substances are moved by gravity from one place to another.
What Is The Connection Of The Study Of Geography To Social Science
Geography encompasses both natural science and social science as it examines people and their environment and serves as a bridge between the physical and cultural worlds. Others concentrate on the spatial associations of the human environment that result from the political, social and economic activities of people.
Read Also: What Is Vo In Physics
What Does Human Environment Interaction Mean In Geography
Human Environmental Interactionsinteractionshumanenvironment
. Similarly one may ask, what is human environment in geography?
Integrated geography is the branch of geography that describes and explains the spatial aspects of interactions between human individuals or societies and their natural environment, called coupled humanenvironment systems.
Additionally, what are the 3 types of human environment interaction? There are 3 types of human environment interaction:
- The way people depend on the environment for food, water, timber, natural gas etc.
- The way people adpat the environment to fulfill their own needs.
- The way people modify the environment positively or negatively like drilling holes, building dams.
Likewise, people ask, what is an example of human environment interaction in geography?
HumanEnvironment interaction: Altering the EnvironmentHumans alter the environment by, for example, building roads through wildlife areas.
What is interaction in geography?
The definition to geographical interaction is how humans change the Earth. It is part of The Five Themes of Geography, which are location, place, human-environment interaction, movement and region.
Why Did Landowners Enclose Their Land
landowners enclosed their land with fences or hedges. The increase in their landholdings enabled them to cultivate larger fields, using new seeding and harvesting methods. Within these larger fields, called enclosures, landowners experimented to discover more produc- tive farming methods to boost crop yields.
Recommended Reading: Beth The Psychopathic Child Now
What Are The Types Of Human Activities Class 9
1. Economic activities: Activities undertaken with the object of earning money or something and include production, exchange and distribution of goods and services. 2. Non- Economic activities: Activities undertaken with the object of getting only psychological satisfaction and not money or anything else in return.
What Does Migration Mean In Human Geography
Migration is the physical movement of people from one place to another it may be over long distances, such as moving from one country to another, and can occur as individuals, family units, or large groups. When referring to international movement, migration is called immigration.
Read Also: Paris Jackson’s Father