Diversity Of Approaches To Understand Drug Dependence
Even if such constructs that are related to a concept of a self are similar, there is no agreement about it: in the framework of PA it is a structure of the mental apparatus, whereas in context of CBT it is the persons recursive description of the person. Already some comparative discussion of the concept of the self occurs, however, an integrative process-oriented modeling is still missing . Integration of pathology of affective-motivational mechanisms discovered by PA and cognitive mechanisms cascades of dysfunctional thinking discovered by CBT, demands for our clinical example a comprehensive psychological model of addiction. Similar situations can be found in psychiatry of other mental disorders. Here we aim to constitute such a grounded framework.
A third important approach, mainly in context of neuropsychiatry, is brain-related . Brain research has discovered many neuronal mechanisms as correlates of addiction, from prefrontal cortex to limbic system from neurons to the genes. This approach is driven by the hope to obtain sufficient anti-addictive medications although it turns now from a brain center-oriented paradigm to a network view. At present, animal-based research also changes the terminology that are partially represented in RDoC . The neurobiological turn implicates a further gap in clinical psychology that is closely related to the brain mind problem .
Sponsored Online Social Work Programs
- Research-driven faculty dedicated to making an impact on social problems
- Prepares you to apply social work skills across practice settings
- Three certificates: Trauma Practice, Mental Health Practice or Practice with Groups and Families.
- Four program tracks: Advanced Standing, Accelerated, Full Time and Extended
- Join the #25 ranked Howard University School of Social Work1
- Four program tracks: Advanced Standing, Accelerated, Full Time and Extended
- Offered by USC Suzanne Dworak-Peck School of Social Work, top-ranked graduate school by U.S. News & World Report .1
- Features field education in or near students own communities.
- Traditional and Advanced Standing tracks
- Concentrate your degree in integrated practice or clinical practice
- CWRUs Mandel School is a top-10 ranked graduate school of social work .1
- Three paths of study are available to prepare social work leaders to work in clinical or community practice.
- Ethically integrates faith and social work practice
- Specialize in clinical practice or community practice
1U.S. News & World Report Best Schools for Social Work
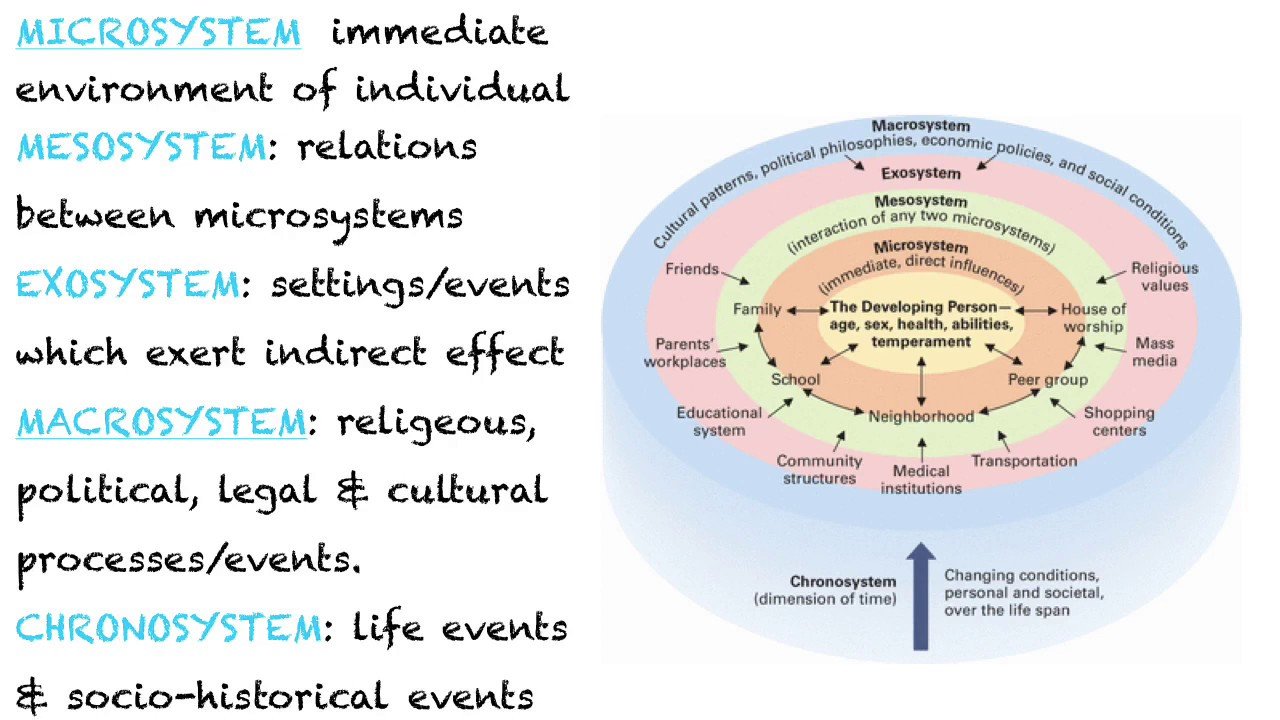
Open And Closed Systems
It is also important to differentiate between open and closed systems. In this, however, researchers dont agree on the criteria. If we follow Bertanlaffys conceptualization, a closed system is one that doesnt make any exchange with the medium. In contrast, an open system is in constant communication with the medium or other systems.
For example, closed family systems do not maintain any type of communication with their environment. The final state depends on the initial conditions of the system. There is an impoverishment of progressive energy in the union and family system.
From this observation, authors such as Watzlawick, Beavin and Jackon from the school of Palo Alto give us The Theory of Human Communication, using the results of the study of other concepts taken from the General Theory of Systems.
Read Also: Law Of Figure And Ground
What Is Systems Theory In Therapy
Systems theory is a complex philosophy that focuses on the interdependence of individuals in a group to help understand and optimize the achievements of the system. When applied to psychology, it can help a group improve relationships and work more efficiently toward a common goal.
Dynamical Systems Theory Definition
Emotions go up and down over the course of days. But sometimes emotions are more constant. For instance, depression could be characterized with fairly constant negative emotions across days. When will hearing some negative information lead a person into a depressed pattern? When will the same negative information just lead to a bad day among the good days? Dynamical systems theory is a series of principles and tools for studying change. It is based on concepts from mathematics and is a general approach applicable to almost any phenomenon.
Recommended Reading: Holt Mcdougal Geometry Workbook Answers
Training In Systems Therapy: 4 Programs
There are many programs available to learn more about Systems Therapy. They often form part of a broader study of family science or therapy four popular ones include:
- Masters Degree in Family and Child Sciences Whether planning to head into therapy or further academic study, this masters from Florida State University explores advanced family studies and theories of family sciences. Use it as a springboard into a career in therapy or a path to PhD research.
- Masters Degree in Marriage and Family Therapy Oklahoma State University offers a masters degree focusing on marriage and family therapy as a branch of psychotherapy. Aimed at solving problems within human relationships, it provides an effective path to licensure or PhD study.
- Masters Degree in Couple and Family Counseling This masters from Northeastern Illinois University fulfills the educational requirements for licensure within the state and those considering employment in marriage and family counseling clinics. The course covers the development and theories of counseling, working with couples and families.
- Masters in Systemic Practice and Family Therapy Queens University in Northern Ireland offers a masters that focuses on systemic practice within family therapy. Students wishing to enhance their skills of working with families and couples can learn how to help them understand and support each other.
Systems Theory In Therapy
Since the development of systems theory, it has been successfully adapted for use in therapy. In systems psychology, therapists analyze human emotions and motivations as they relate to group dynamics. In most circumstances, this type of therapy is used to help groups of people overcome a problem, however, it can help individuals with mental health concerns related to system dynamics.
While it can be challenging to work closely with multiple people, effective systems psychology therapists can help improve relationships and emotional stability of the groups they work with. They also help individuals in the group achieve valuable insight into their own behavior and how that impacts others. Couples and family psychology are examples of areas in therapy where systems theory can be applied.
Recommended Reading: Segment And Angle Addition Worksheet
Introduction To The Eight Concepts
Bowen family systems theory is a theory of human behavior that views the family as an emotional unit and uses systems thinking to describe the units complex interactions. It is the nature of a family that its members are intensely connected emotionally. Often people feel distant or disconnected from their families, but this is more feeling than fact. Families so profoundly affect their members thoughts, feelings, and actions that it often seems as if people are living under the same emotional skin. People solicit each others attention, approval, and support, and they react to each others needs, expectations, and upsets. This connectedness and reactivity make the functioning of family members interdependent. A change in one persons functioning is predictably followed by reciprocal changes in the functioning of others. Families differ somewhat in their degree of interdependence, but it is always present to some degree.
Maintain A Clear Distinction Between Influences On The Variables From The Proposed Model And Other Influences
DST, by its nature, involves the study of processes that unfold over time in a deterministic manner , from an initial state, based solely on the functional relationships among the variables in the system. In the context of clinical psychology, it may be difficult to identify variables that operate in such a deterministic manner or to construct models that adequately characterize their interactions. Difficulties may arise from a number of sources, including the intentional actions of participants and the difficulties in isolating psychological variables from the myriad environmental influences that affect human beings. Unless DST researchers explicitly state otherwise, lay readers may assume that any influences mentioned by the researchers originate from the proposed model, and thus be unable to accurately assess the usefulness of the model. Therefore, when researchers discuss the influences on variables they examine, we believe that it is incumbent on them to be particularly careful in distinguishing between those influences arising from the proposed model and other influences.
You May Like: Paris Jackson Parents
Intervention With Systems Theory
According to Systems Theory and Social Work by Steven Walker, in 2019,, there are three broad schools of interventions that can be identified. They are:
Structural approaches: This type of intervention stems from the technique of observing the interactive patterns in a family or system, and then a structural approach would be taken to highlight problematic situations, find problem-solving solutions to interrupt them when they are happening, and then get the individual or family to try different ways of acting that lead to better outcomes.
Strategic approaches: The focus with strategic interventions is on the everyday problematic interactions and solving them with properly applied cognitive thinking. Often, perceptions people have about their problems influence how those issues are handled. This type of approach allows for a culturally relevant solution that focuses on a familys or individuals perceptions within a system, rather than trying to impose perceptions strictly from the outside.
Systemic approaches: This approach works with the whole family or system, rather than just the individual. The focus of this approach is to discover rules and ideologies that are sustaining dysfunctional patterns, then to encourage change in a way that avoids being perceived as blaming others within the system.
The Epistemic Cycle Between Empirics And Theory
In this paper, we suppose to establish a systemic framework of qualitative categories to describe the structure and dynamics of the mind. This project seems to be opposing to current empiricism in the psycho-sciences and therefore it should be seen in context of general developments in the sciences: history and philosophy of science show that many sciences over decades exert a dominance of experimental-empirical research that are followed by periods with emphasis on theoretical research, also switching from qualitative research to quantitative researchin theory and empirical fields . This cyclic epistemic long-term phenomenon can be captured by the term epistemic cycle . In case of empiricism of current behavioral neuroscience and psycho-sciences it is evident that already a huge amount of quantitative data already is available but there is a lack of a defined field of theoretical psychology that provides an appropriate integrative conceptual framework for quantitative and qualitative data and everyday observations and experiences. However, integrating quality and quantity of observations is important for understanding in practical clinical work.
Interplay in research between theory and empirics and from a qualitative level to a quantitative level of essential constructs, with focus on qualitative theory of the mental.
But first: what do we mean with mind?
Recommended Reading: What Is Figure Ground In Psychology
Systems Theory And Adult Sex Roles
Systems theory is a theory of interacting processes and the way they influence each other over time to permit the continuity of some larger whole. Systems act so as to continue. Systems change because their own balances are not optimal or because they are influenced by other systems. Some authors who provide excellent descriptions of these general ideas are van Bertalanffy and Miller. Miller’s discussion of living systems is especially useful to consider for a discussion of sex roles. Individuals, societies, and cells all appear to use similar processes to create boundaries, to take in stimulation, to process information, to act, and to change. For example, for cells, information may be chemical and may be filtered by cell walls for persons, information may be conceptual and may be filtered by perceptions for societies, information may be news and may be filtered by censors. Cells, persons, and societies all exist in relation to each other, which further complicates matters. Within systems theory, roles are structures of the social system which are equivalent to organs in the physical/person system they are organized ways of ensuring that some vital function is performed.
D. Chirot, in, 2001
A.C. Jordan, … B.J. Ellis, in, 2012
Summary And Resources For Further Learning
Systems theory plays a key role in the advancement of society. Only by looking at all the moving parts can we have a greater understanding of the whole and how it worksa principle that holds true in physical sciences and social sciences alike. By applying these broad truths across disciplines, we can further integrate our understanding of separate phenomena.
As it applies to social science, systems theory is crucial because it looks holistically at the individual to draw insights and use them to take steps forward.
Learn more about Ludwig von Bertalanffys research and its significance to systems theory in his work General System Theory: Foundations, Development, Applications.
For more information on social ecology and the socio-ecological model, see our article What is Social Ecology?
To learn more about Bowens family systems theory and its eight interlocking components, visit the Bowen Center.
Read Also: The Segment Addition Postulate Answers
What Is Systems Theory In Social Work
Systems theory in social work is based on the idea that behavior is influenced by a variety of factors that work together as a system. These factors include family, friends, social settings, economic class, and the environment at home. The theory posits that these and other factors influence how individuals think and act, and therefore examining these social structures to find ways to correct ineffective parts or adapt for missing elements of a given system can positively impact behavior. The fields of psychology, communication theory and psychiatry influence modern social work systems theory.
In this particular theoretical approach to social work, professionals observe and analyze the many systems that contribute to the subjects behavior and welfare. They then work to improve those systems according to the individuals unique situation.
How Does Systems Theory Apply To Social Work
A holistic approach to an individuals personality, choices and hardships is important when it comes to successful social work. Like the other fields mentioned, a social worker must look at all factors that come together in a unique way to shape their experiences and who they are.
Social workers may employ systems theory to understand problems like child abuse, family issues and community dysfunction as they relate to individuals personal issues, such as anxiety, low self-esteem, self-harm or relationship issues. Based on systems theory, multiple practices have been created that are specific to social work. Below are several prominent examples.
Recommended Reading: What Does K Stand For In Math
Five Core Theories Systems Theory Organisation Development
There are five core theories that provide a solid foundation for the work that OD practitioners do. Good grounding in theory is essential for every OD practitioner. The better you understand the theory, the better you will understand the complex and intricate nature of the OD process and OD tool kit.
Systems Theory in Brief
Systems Theory was first introduced by Van Bertalanffy and was introduced into the organisational setting by Kataz and Khan . Systems theory is an approach to organisations which likens the enterprise to an organism with interdependent parts, each with its own specific function and interrelated responsibilities. The system may be the whole organisation, a division, department or team but whether the whole or a part, it is important for the OD practitioner to understand how the system operates, and the relationship the parts of the organisation have.
The emphasis in OD is that that real systems are open to, and interact with, their environments, and it is possible to acquire new properties through emergence, resulting in continual evolution. Rather than reducing an organisation to the properties of its parts or elements, systems theory focuses on the arrangement of and relations between the parts which connect them into a whole.
Key Points
Social Work Approaches Informed By Social Systems Theories
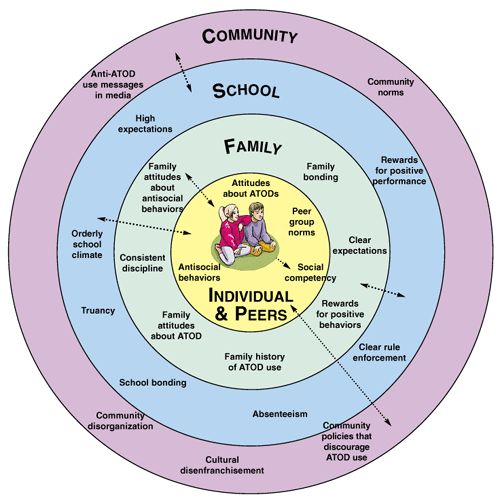
The socio-ecological model can be used to understand challenges faced by individuals at multiple levels of their social ecosystem and to develop therapeutic interventions and programs that address these problems. Consider the problem of child abuse and neglect for example child outcomes will be greatly influenced by risk and protective factors at each level of the social ecosystem. Understanding the risk and protective factors at each level of a familys social ecosystem is critical to treating the child and working with the family.
The social-ecological model of development can also be used to understand why parents abuse or neglect their children. Socio-ecological theories of why child maltreatment is perpetrated acknowledge the complexity of the social problem in a way that cognitive behavior theories may not. To address a parents abusive or neglectful behaviors, a social worker might provide individual and/or family counseling or parenting classes . He might also advocate for increasing government spending on afterschool programs, daycare, or mental health clinics as a preventive measure.
Multisystemic Therapy is another treatment approach informed by social systems theory which has been used to address child and youth mental health problems, juvenile delinquency, and substance abuse. MST requires therapists to treat the whole family system and to treat the child at multiple levels of his and his familys social system in the home and other community locations.
You May Like: Exponent Rules Worksheet Algebra 2
Aim And Structure Of The Paper
In this paper we focus on correspondence of cognition and emotion to terms like structure, and dynamics, but also function, process, equilibrium etc. We dont intend a new conceptual taxonomy of the mental, especially of emotions and motives but a systemic version of some established concepts.
In this first part of our paper, we start now with the meta-theoretical – and in this way: philosophical basis of explicit systems thinking, stressing the necessity of qualitative systemic modeling instead of usual data-driven reasoning. Several basic categories of psychology are mentioned and defined as systems thinking demands clear definitions of the elements of the respective structured whole. In line with this, we briefly mention some methodological and theoretical issues of systems science in the next section. In a second part of the paper we aim a higher precision of the use of the terms structure in the psycho-sciences, especially regarding concepts like life space or representations of object relations. In a next section, we explore the respective meaning of dynamics. In addition, we discuss fruitful applications of the control loop paradigm briefly, that enables a better integrative understanding of emotions and motivations and their interaction dynamics. Finally, we sketch an integrative conceptual systems model of the mind that allows for an integrative but differential and detailed description of mental structures, processes and their dynamics.