Genetic Polymorphisms In Genes That Encode Xenobiotic Enzymes Involved In Haa Bioactivation
Genetic polymorphisms in genes that encode for enzymes that catalyze the activation and/or detoxification of HAAs could account for interindividual differences in susceptibility to this group of carcinogens . The constitutive P450 1A2 mRNA expression levels in human liver can vary by as much as 15-fold , and interindividual expression of P450 1A2 protein can vary by 60-fold . Environmental and dietary factors , varying extents of CpG methylation , and genetic polymorphisms in the upstream 5â²-regulatory region of the P450 1A2 gene , which affect the level of P450 1A2 mRNA expression, can all lead to variations in P450 1A2 protein levels. However, the genotype responsible for the > 60-fold range of interindividual differences in human hepatic P450 1A2 constitutive expression is still not well understood . In contrast to what is seen in humans, the amount of P450 1A2 protein in the liver of inbred rodent varies by only severalfold across different strains . The level of P450 1A2 protein expression in human liver, on average, is several- to 10-fold or greater than the level of P450 1A2 expression in liver of inbred rodents . The interspecies differences in the level of P450 1A2 expression, catalytic activity, and regioselectivity of P450 1A2-catalyzed oxidation influence the toxicological properties of HAAs and must be considered in any assessment of human risk.
Advantage And Disadvantage Of Polymorphism
Advantage:
Disadvantage:
Sse Model Selection And Parameter Estimation From Posterior Distribution Of Trees
SSE model selection using the empirical color polymorphism data performed on a posterior distribution of 1000 trees identified trait-dependent diversification models, HiSSE and BiSSE, as the best fit models 99.4% of the time , which largely supports a color polymorphism-dependent diversification scenario in the Lacertidae. The HiSSE and BiSSE models also had greater Akaike model weights than null or character-independent diversification models . The HiSSE model was identified as the best fit model most of the time . The BiSSE model, trait-dependent diversification with no hidden states was selected as the best fit model second-most often . Of the six times the HiSSE null model was selected as the best fit model, it achieved a |$\Delta $|AIC score |$> $| 1 only once. Out of 1000 potential evolutionary histories of the Lacertidae, the BiSSE null model and character-independent models of diversification were never selected as best fit models.
SSE model net diversification parameter estimates extracted from a subset of 50 phylogenetic trees overlapped with the estimates obtained from the maximum clade credibility tree .
Recommended Reading: What Is Pcc In Chemistry
Implementation Aspects Of Polymorphism
Static and dynamic polymorphism
Where the implementation is chosen, polymorphism can be defined by: constantly or dynamically. This is classified as static send and dynamic send, respectively, and static polymorphism and dynamic polymorphism are also considered the related modes of polymorphism. Static polymorphism is performed more easily when there is no dynamic overhead send, but extra accumulator brace is needed. In addition, static polymorphism allows accumulators, source program inspection instruments, and human editors to perform greater static analysis. For example, dynamic polymorphism facilitates duck typing, and a dynamically connected library will work on objects without understanding their complete form. Dynamic polymorphism is more stable, but slower.
Conclusion And Future Perspectives

Single nucleotide polymorphisms have become an important application in the development and research of genetic diseases or other phenotypic traits. Haplotypes are groups of SNPs that are generally inherited together. Haplotypes can have stronger correlations with diseases or other phenotypic effects compared with individual SNPs and may therefore provide increased diagnostic accuracy in some cases.
Polymorphic tandem repeated sequences have emerged as important genetic markers and initially, variable number tandem repeats were used in DNA fingerprinting in recent years, evidence has been accumulated for the involvement of VNTR repeats in a wide spectrum of pathological states.
The new global CNV map will transform medical research in four main areas: detection for genes underlying common diseases, study of familial genetic conditions, exclude variation found in unaffected individuals, helping researchers to target the region that might be involved and the data generated will also contribute to a more accurate and complete human genome reference sequence used by all biomedical scientists. Currently, approximately 2000 CNVs have been described there could be thousands more CNVs in the human population. About 100 CNVs were detected in each genome tested with the average size being 250,000 bases . With advanced molecular technologies more CNVs will be discovered and more DNA samples from worldwide populations are examined.
You May Like: What Does Pictorial Mean In Math
Trait Simulations On Empirical Mcc And Ml Phylogenies And Sse Model Adequacy
When we compared AIC values of six SSE models run on 1000 trait data sets simulated with no correlation to diversification rates on the empirical MCC and ML Lacertidae phylogenies, we found that trait-dependent diversification models were chosen as the best fit model less than 2% of the time. For uncorrelated trait simulations performed on the MCC species tree, the BiSSE null model was selected as the best fit model most often , followed by the HiSSE null model . Character-independent models, CID-2 and CID-4, were rarely the best fit models on simulated trait data and also had low Akaike model weights compared to other models . Character-dependent diversification models, BiSSE and HiSSE, were rarely the best fit models on simulated uncorrelated color trait data .
For 1000 uncorrelated trait simulations performed on the ML tree, we produce similar results. Here, the HiSSE null model was chosen as the best fit model most often . A trait-dependent diversification model was identified as the best fit model only 7 times . Ultimately, we recover a Type I error rate less than 1% of the time when we run a subset of six SSE models from our observed data on uncorrelated simulated trait data.
Why We Need Polymorphism
Polymorphism only gives you advantages if you need polymorphism. Its used anytime the specialization of another entity can be used as an individual in your intellectual idea. Specialization is the core term. The so-called taxonomy, which, for example, refers to living things, is a perfect example. People and dogs are also mammals. This suggests that all species that have such properties and behaviors in common are classified into the class of mammals.
A classification of a vehicle is both an ElectricCar and a DieselCar. So all you have is There Fuel so you expect to know if theres enough fuel to run it when you drive a car. Expectation is another wonderful term.
Drawing an ER diagram of the domain of your program before beginning it is always a fantastic idea. Thats because youre required to guess what sort of entities are going to be generated and you can save a lot of code to identify similar behaviors between entities if youre able enough. But code saving isnt the only advantage of a successful project.
You might be interested in finding out that so-called software engineering is a set of techniques and principles that enables you to write clean code .
Recommended Reading: How To Study Physics For Jee Advanced
Polymorphisms At Dna Level
Genomic variability at DNA level can be present in many forms including: single nucleotide polymorphisms, variable number of tandem repeats , transposable elements , structural alterations, and copy number variations. It can occur in the nucleus or mitochondria. Two major sources: mutations that may result as chance processes or have been induced by external agents such as radiation and recombination. Once formed, it can be inherited, allowing its inheritance to be tracked from parent to child .
Mapping Human Diseases And Risk Prediction
Genetic mapping and linkage: The mapping of the human genome has made possible to develop a haplotype map in order to better define human SNV variability. The haplotype map or HapMap will be a tool for the detection of human genetic variation that can affect health and diseases . The HapMap project is far more useful because it will reduce the number of SNVs required to examine the entire genome for association with a phenotype or diseases from the 10 million SNPs that are expected to exist to approximately tag 500,000 SNPs . The first large-scale effort to produce a human genetic map was performed mainly using RFLP other several projects are underway to identify more markers in humans and to make this data publicly available to scientists worldwide. Many groups that are involved in these massive efforts through DNA polymorphisms discovery resource include the SNP consortium . The reason for the current enormous interest in SNPs is the hope that they could be used as markers to identify genes that predispose individuals to common, multifactorial disorders by using linkage disequilibrium mapping.
The HapMap Project , and other approaches, such as genome wide association studies, have been widely reported for complex polygenic diseases, with some interesting novel genes affecting disease susceptibility now identified. Genome Wide Association the GWAS has now been used for a large range of traits and diseases e.g. baldness and eye color .
You May Like: What Is Uneven Development In Geography
Quantitative Trait Loci Mapping Candidate Genes And Complex Traits
The identification of genes affecting complex trait is a very difficult task. For many complex traits, the observable variation is quantitative, and loci affecting such traits are generally termed quantitative trait loci . can be used as genetic markers for constructing high-density genetic maps and to carry out association studies related to complex traits and diseases .
The Evolutionary History Of Color Polymorphism And Diversification In The Lacertidae
Color polymorphism data
Ancestral state reconstruction of color polymorphism in the Lacertidae
To understand the evolutionary history of color polymorphism in lacertids, we used ancestral state reconstructions jointly estimated with character transitions and diversification rates in the HiSSE package with the MarginRecon function . We present ancestral state reconstructions for both our MCC species tree and a recently published lacertid tree inferred in a maximum likelihood framework by that differed somewhat in taxon representation and topology to test if our results were robust to phylogenetic uncertainty .
State-dependent diversification models
Trait simulations and SSE model adequacy
Phylogenetic uncertainty and SSE model comparison
You May Like: What Is Cbr In Human Geography
Overloading And Overriding In Polymorphism
Polymorphism refers to the tendency of multiple shapes to exist. In other words, the power of a reference variable to modify behavior depending on what instance of an entity it is.
Overloading:
- Two or more methods within the same class that share a separate parameter list with the same name.
- Methods that are overloaded could vary in the form and/or number of their parameters.
- Different return forms can be crowded.
- It is also possible to overpower constructors.
Overriding:
- Inside an inherited or subclass, override methods are redefined.
- In sub groups of distinct process bodies, they have the same process signature.
Method Overloading
Concept Overloading has no relation with polymorphism. This applies to specifying various ways of a system . It can be used as a polymorphism that is unchanged. At coding time, the option to call an application or another is made. In this case, note that the signature of the system must alter.
Operator Overloading
Operator overloading is a separate polymorphism-related term that applies to a certain language-dependent operator s tendency to function differently depending on the form of its operands .
Method Overriding
How Do Polymorphisms Arise And Persist
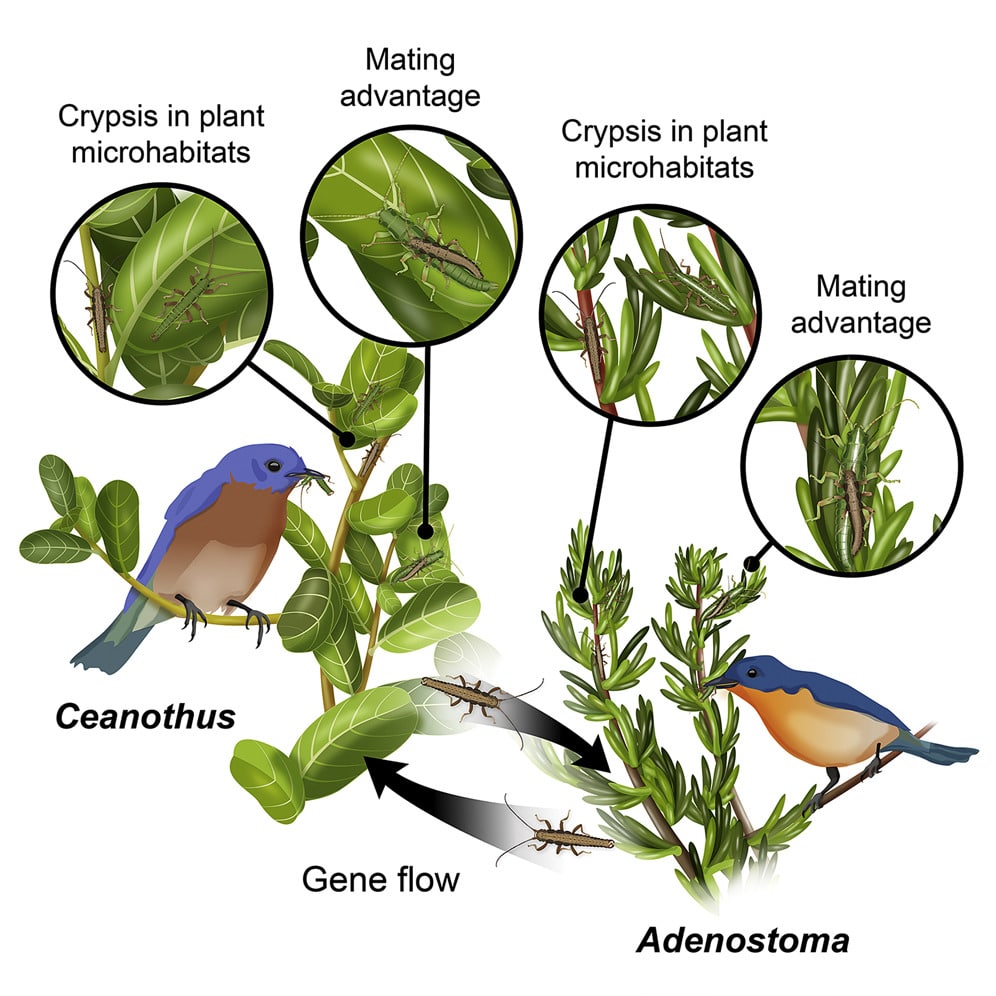
They arise by mutation. But what keeps them in the population? Several factors may maintain polymorphism in a population.
- Founder Effect: If a population began with a few individuals â one or more of whom carried a particular allele â that allele may come to be represented in many of the descendants. In the 1680s Ariaantje and Gerrit Jansz emigrated from Holland to South Africa, one of them bringing along an allele for the mild metabolic disease porphyria. Today more than 30000 South Africans carry this allele and, in every case examined, can trace it back to this couple â a remarkable example of the founder effect.
- Genetic Drift: An allele may increase – or decrease – in frequency simply through chance. Not every member of the population will become a parent and not every set of parents will produce the same number of offspring. The effect, called random genetic drift, is particularly strong in small populations and when the allele is neutral that is, is neither helpful nor deleterious
Eventually the entire population may become homozygous for the allele or – equally likely – the allele may disappear. Before either of these fates occurs, the allele represents a polymorphism.
Two examples of reduced polymorphism because of genetic drift:
Don’t Miss: Punchline Algebra Book B 13.16 Answers
Sumo Logic Guards Against Polymorphic Threats
Cyber attackers are using polymorphism to create malicious code and scripts that change the form, including changing their filename, encryption and compression characteristics. These programs are increasingly difficult to detect with anti-malware programs. Researchers at Webroot recently discovered that 97% of malware infections leverage polymorphism to circumvent security measures.
Sumo Logic helps enterprise organizations detect malware and other unwanted intrusions with behavior-based threat detection techniques that are more well-suited to detecting polymorphic malware than traditional signature-based detection methods.
Dopamine And Other Receptor Polymorphisms
Genetic polymorphisms in dopamine receptors have been associated with drug abuse liability and the reinforcing effects of alcohol, cocaine, and nicotine. Genetically variant dopamine receptors are also associated with increased incidence of tardive dyskinesias following long-term treatment of schizophrenia with dopamine receptor antagonists. Schizophrenia is itself a complex set of diseases that is not adequately managed in many patients. Accordingly, both typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs have been found to be effective in some but not all patients with schizophrenia. Genetic polymorphisms in antipsychotic medication receptor targets have been associated with different clinical responses. Combinations of drug target polymorphisms and drug metabolism variants may eventually form the basis for targeting genetic subgroups of patients with schizophrenia for effective treatment with both typical antipsychotics and newer atypical antipsychotic drugs.
Sara Mahdiabadi, Nima Rezaei, in, 2022
Read Also: What Is The Definition Of Algae In Biology
Structural And Copy Number Variations
Structural and copy number variations are another frequent source of genome variability . The term CNVs therefore encompasses previously introduced terms such as large-scale copy number variants , copy number polymorphisms , and intermediate-sized variants . Some currently used terms are structural variations a genomic alteration that involves segments of DNA > 1 kb, copy number polymorphisms a duplication or deletion event involving > 1 kb of DNA , intermediate-sized structural variant and a structural variant that is 840 kb in size, this can refer to a CNVs or a balanced structural rearrangement .
What Is Transient Polymorphism
When a rare gene starts gaining and preserving an over-all advantage, it will keep spreading and will reduce its normal allele as much as it reaches the status of a mutant. While this process is occurring, it generates a transient polymorphism. It happens because of intense environmental selective pressure. It causes the directional selection to eliminate one allele.
An example is a peppered moth. During the industrialization era of Britain, the soot from industries landed on the trees and turned them dark. During this time, the population of light-winged and dark-winged moths was equal, and their predators consumed them both. However, the population of white-winged moths began to decline as their light coloration made them an easy prey over the dark-winged moths. They are consumed more than the dark-winged moths. Eventually, the dark-winged moths became more predominant than the light-winged moths.
You May Like: Algebra 1 Chapter 9 Answers
Natural Vs Sexual Selection
Balanced polymorphism in Soay sheep.
Hirta is a tiny island in the North Atlantic 100 miles off the northwest coast of Scotland. In 1932 a small population of domestic sheep was introduced onto the island from the neighboring island of Soay. Since then these sheep have been allowed to run wild and, since 1985, have been intensively studied.
RXFP2Ho+HoP
You can read about these findings in Johnston, Susan. E., et al., Nature502, 9395, 3 October 2013.
What Polymorphism Is Not
Although polymorphism is potentially quite a broad term, in biology it has been given a specific meaning. This section indicates its proper use.
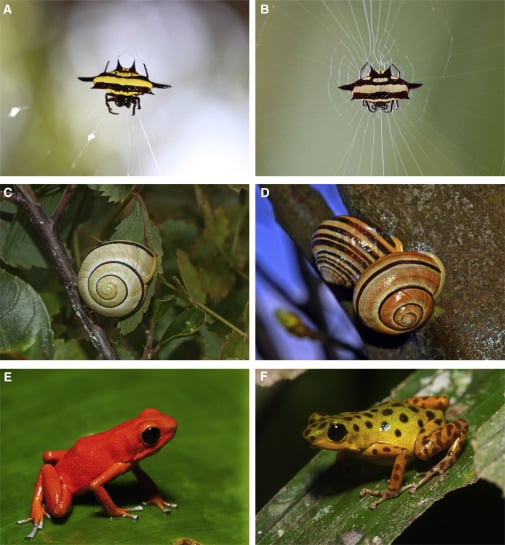
- The term omits continuous variation even though this has a heritable component. Polymorphism deals with forms in which the variation is discrete or strongly bimodal or polymodal.
- Morphs must occupy the same habitat at the same time: this excludes geographical races and seasonal forms. The use of the words morph or polymorphism for what is a visibly different geographical race or variant is common, but incorrect. The significance of geographical variation is that interbreeding between different locations is reduced or eliminated, a possible prelude to species splitting. True polymorphism takes place in panmictic populations, and has to do with the adaptation of a species to its environment.
- Rare variations are not classified as polymorphisms and mutations by themselves do not constitute polymorphisms. To qualify as a polymorphism there has to be some kind of balance between morphs underpinned by inheritance. The criterion is that the frequency of the least common morph is too high simply to be the result of new mutations or, as a rough guide, that it is greater than 1 percent .
Don’t Miss: What Makes Something Living Biology