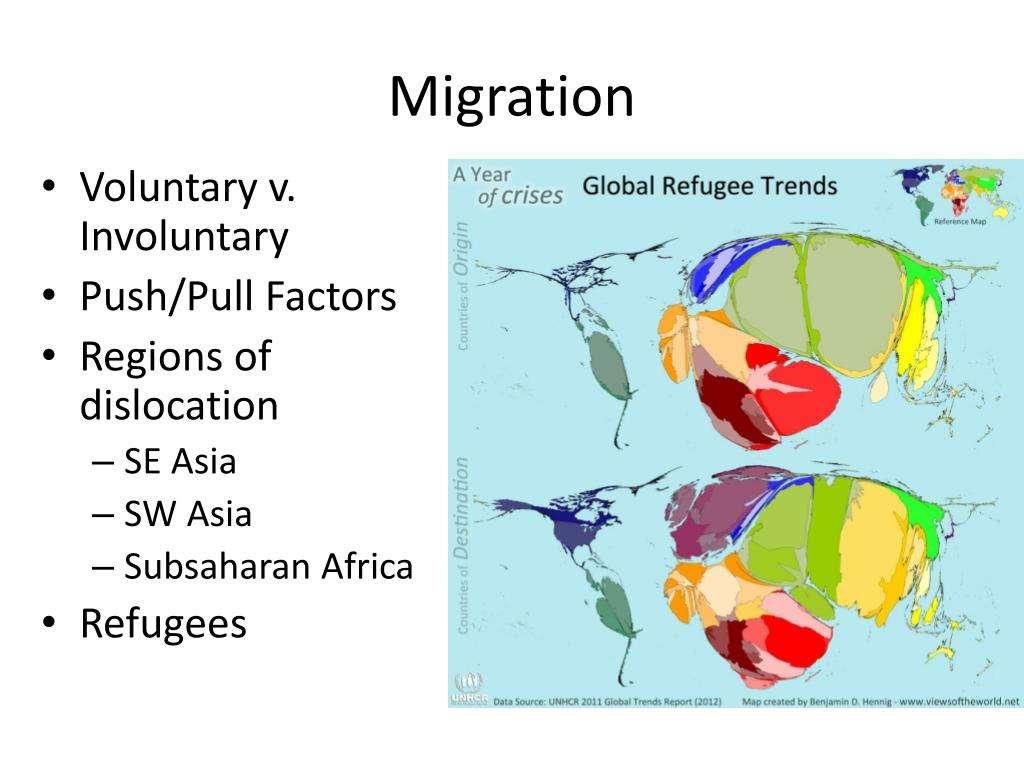
Questions For The Future
Global human populations are often controversial because there is no clear consensus on dealing with it. Demographers know that there are over 7.3 billion people on the planet, but they are not evenly distributed worldwide. One consistent global pattern is water nearly 80 percent of the worlds population lives near a large body of water.
- Why do you think populations converge on large bodies of water?
- What happens to populations when there is a shortage of water?
There are various ways that geographers and demographers study population dynamics and profiles, often representing this data in diagrams, graphs, and, most importantly, maps. Social scientists have tried to describe historical, current, and future population trends with the Demographic Transition Model. The model attempts to explain how more developed countries progressed with their demographics than less developed countries today. Some argue that though the model predicts demographic trends in North America and Europe, the model does not accurately represent population trends in other regions of the world. Others say the model is too simplistic because of environmental and cultural factors.
Previous/next navigation
What Is The Formula Of Cbr
The formula of the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation is C$ = C$ where C$ is the cost of goods sold, R is the number of stations, I is the number of programming hours, J is the number of journalists, K is the number of hours of programming a day, and R+I+J+K are the numbers of stations and programming hours.
Stage : Moderate Growth Rate
Today, Europe and North America have moved to Stage 3 of the demographic transition model. A nation moves from Stage 2 to Stage 3 when CBRs begin to drop while CDRs simultaneously remain low or even continue to fall. It should be noted that the natural rate of increase in nations within Stage 3 is moderate because CBRs are somewhat higher than CDRs. The United States, Canada, and countries in Europe entered this stage in the early 20th Century. Latin American nations entered this stage later in the century.
Advances in technology and medicine cause a decrease in IMR and overall CDR during Stage 2. Social and economic changes bring about a reduction in CBR during Stage 3. Nations that begin to acquire wealth tend to have fewer children as they move away from rural-based development structures toward urban-based structures because more children survive, and the need for large families for agricultural work decreases. Additionally, women gain more legal rights and chose to enter the workforce, own property, and have fewer children as nations move into Stage 3.
Recommended Reading: Practice And Homework Lesson 4.5
Stage : Low Growth Rate
We have lived in the first stage of the Demographic Transition Model for most of human existence. In this first stage, CBRs and CDRs fluctuated significantly over time because of living conditions, food output, environmental conditions, war, and disease. However, the worlds natural increase was pretty stable because the CBRs and CDRs were about equal. However, around 8,000 BC, the worlds population grew dramatically due to the first agricultural revolution. Humans learn to domesticate plants and animals for personal use during this time and became less reliant on hunting and gathering for sustenance. While this transition allowed for more stable food production and village populations to grow, War and disease prevented population growth from occurring globally.
Rate Of Natural Increase
- The rate of natural increase is also an annual statistic which estimates the percentage of population growth of a country for each year.
- To find the RNI, youll need the CBR and CDR and heres the formula: RNI = /10
- Additionally, it is also possible to have a negative RNI, as the rate of deaths can outnumber the rate of live births in a country, especially for the highly developed ones.
- For instance, Russia is undergoing a population decline, as seen with its own negative RNI, which is due to a large elderly population and fewer number of women wanting to have children in Russia.
- The RNI is also indicative of a countrys development and current population situation.
- However, it does NOT take into account immigration/emigration. Thus, the RNI doesn’t accurately predict population growth, so it is only an estimate.
Read Also: Ccl4 Structural Formula
Patterns Of Population Growth
Rates of population growth vary across the world.
Although the world’s total population is rising rapidly, not all countries are experiencing this growth.
In the UK, for example, population growth is slowing, while in Germany the population has started to decline.
More Economically Developed Countries have low population growth rates, with low death rates and low birth rates.
Less Economically Developed Countries have high population growth rates.
Both birth rates and death rates in LEDCs tend to be high.
However, improving healthcare leads to death rates falling – while birth rates remain high.
The table shows data in selected LEDC and MEDC countries. The figures are per 1,000 of the population per year.
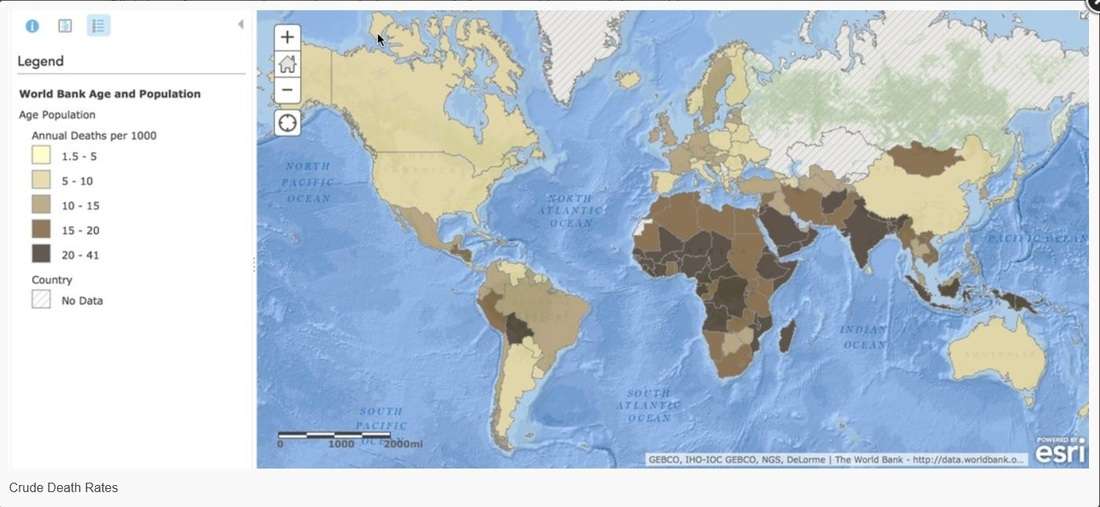
What Does Cdr Mean In Geography
There is no one definitive answer to this question since CDR can have a variety of meanings depending on the context. Generally speaking, CDR stands for country code region, which is a geographic term used to describe the areas within a country that are covered by a specific phone network. For example, in the United States, CDR would typically refer to the areas within the Northeast and Midwest.
Also Check: Mega Hack V5
Why Might A Country Have A High Cbr And A High Cdr
A country with a high CBR and a high CDR may have a high level of economic development and stability. Countries with a high CBR may have more efficient transportation systems, which allows them to export more goods and services, and they may also have more efficient economic institutions, which allows them to generate more economic growth. Countries with a high CDR may have a higher level of development, as they may have better access to resources and have better infrastructure.
Why Does Mexico Have A Lower Cdr Than The United States
There are a few reasons Mexico has a lower CDR than the United States. One reason is that Mexicos economy is more developed than the United States. The United States has a more developed banking system and a more developed economy. Mexico also has a lower rate of population growth, which affects the countrys ability to generate new money.
Don’t Miss: Beth Thomas Brother Jonathan
What Is Cbr In Human Geography
Crude birth rate total number of live births per every 1000 people per year. Crude death rate- total number of deaths per every 1000 people per year. Natural increase rate- % by which a population grows in a year .Crude birth rate total number of live births per every 1000 people per year. Crude death rate- total number of deaths per every 1000 people per year. Natural increase rate
statistic calculated by subtracting the crude death rate from the crude birth rate of a given region
S And Equipment Used In Geography
Although human geography does not need equipment as you need physical geography, but they do not dispense with the use of some of the ways to facilitate geographers work, including maps, which has been used for a long time as a major tool in geography, as it helps explain some of the sites and determine the advantages standards multiple, and with the technological development has become computers and laboratories that use images remotely sensed systems determine the easiest geographical locations geographers to provide their material illustrations and provide basic data for field studies on which to evaluate images for different tasks in their field.
You May Like: Four Main Areas Of Biological Contamination
What Are 5 Stages Of Demographic Transition
Demographic Transition Model Stages
- Stage 1: High Population Growth Potential.
- Stage 2: Population Explosion.
- Stage 3: Population Growth Starts to Level Off.
- Stage 4: Stationary Population.
- Stage 5: Further Changes in Birth Rates.
- Summarizing the Stages.
- Graph of the Demographic Transition Model.
- Limited Predictive Capacity.
Distinguish Between: Distinguish Between Birth Rate And Death Rate:
| Birth Rate | Death Rate |
| It is the number of live births per thousand of population during a year for a particular region | It is the number of deaths per thousand of population during a year for a particular region |
| It is calculated using the following formula:CBR = Bi/P xlOOO | Here, CDR = crude death rate,D = Number of deaths in a year,P = the estimated midyear population of that year |
| If birth rate is more than death rate, it results in positive growth of population. | If death rate is more than birth rate it results in negative growth of population. |
Read Also: Geometry Mcdougall Littell Answers
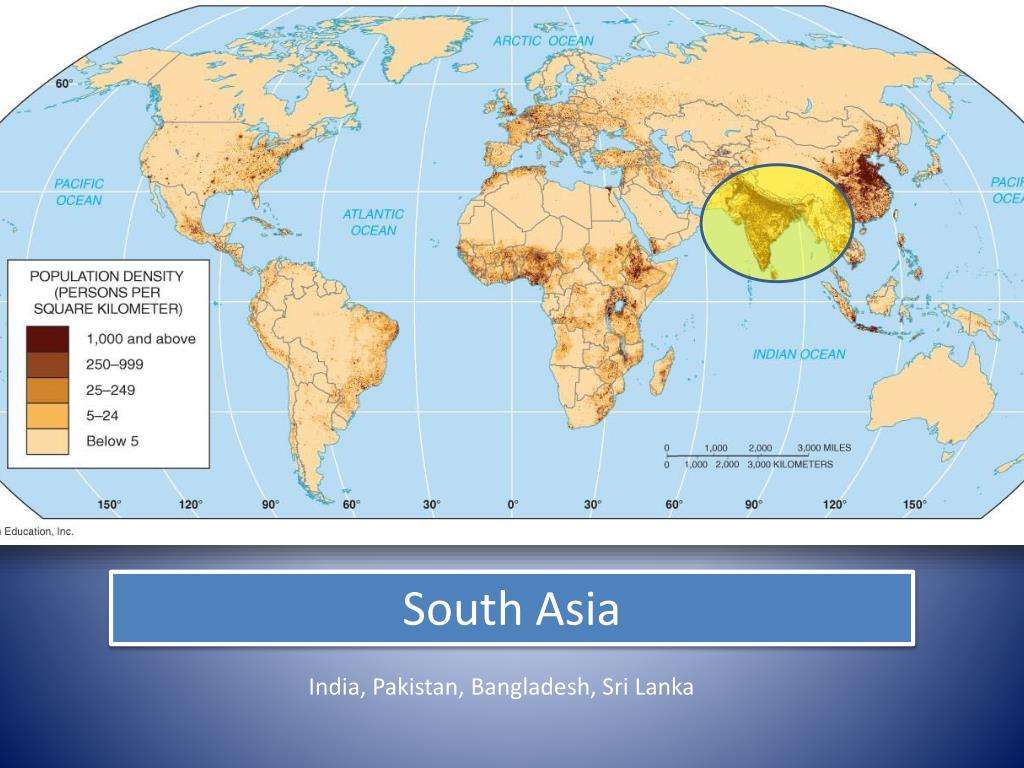
Distribution Of The Worlds Population
Economist Jeffrey Sachs, director of the Earth Institute at Columbia University, believes that there are two reasons why the global population and extreme poverty occur where they do:
- Capitalism distributes wealth to nations better than socialism or communism
- Geography is a significant factor in population distribution in relationship to wealth
For example, the population tends to be lower in extreme environments such as arid climates, rainforests, polar or mountainous regions. Another example is a nation with a large body of water within its boundaries or has extensive mineral deposits or resources likely to have more wealth and a larger population.
Humans only occupy five percent of the Earths surface because oceans, deserts, rainforests, and glaciers cover much of the planet . The term for areas where humans permanently settle is ecumene. Population growth and technology dramatically increase the ecumene of humans, which affects the worlds ecosystems.
Additionally, regions that are too cold pose problems for large population clusters and food production. The cold Polar Regions have a short growing season, and many of the Polar Regions have limited amounts of moisture because they are covered by high- pressure systems . Thus, cold polar regions are defined by temperature and lack of moisture, despite access to snow, ice, and glaciers. Mountainous and highland regions lack population clusters due to steep slopes, snow and ice cover, and short growing seasons.
Stage 1 Of The Demographic Transition Model
October 14, 2014
This is post 2 of 6 in a series about the Demographic Transition Model a fundamental concept in population education, which is covered in Social Studies courses, most notably AP Human Geography.
Stage 1 of the Demographic Transition Model is characterized by a low population growth rate due to a high birth rate and a high death rate . In this first stage, total population is in flux as a result of these variables dynamic patterns, neither being consistent from year to year. Because the birth rate and death rate are relatively equal to one another there is little change in total population. But why are both rates high?
There are a number of factors that can influence a country towards a high birth rate and high death rate. Historically, high birth rates are attributed to societies that relied heavily on agricultural productivity or unskilled manual labor, because larger families meant a larger workforce.
Stage 1 of the Demographic Transition Model is considered the pre-industrial stage, or pre-transition, and today no countries are classified within Stage 1 of the DTM. This is quite a feat given that for all of human history up until the 18th Century, all countries were considered within Stage 1.
You May Like: Unit 1 Test Study Guide Geometry Basics Gina Wilson
Key Factors Influencing Population Change
When trying to predict or analyze population change, three key factors to understand are the total fertility rate, infant mortality rate, and life expectancy at birth. Total fertility rate is the average number of children a woman would be expected to have during childbearing years . The global average for TFRs is about 2.5, but in less developed countries, it is as high as 5.0 or higher, and in more developed countries, it is as low as 2.0 or less. Fertility patterns can vary widely within countries. Racial and ethnic minorities may have higher fertility rates than the majority, and families with low incomes or low education levels typically have more children than those who are affluent or well-educated. Women who work outside the home typically have fewer children than those who stay home, and rural families tend to have more children than city dwellers. In 2016, the number of births per 1,000 people worldwide was 20, with extremes ranging from a low of 8 or 9 , to 60 or more in a few West African nations .
2.2 Demographic Transition Model
What Does Imr Stand For In Human Geography
4.6/5infant mortality rateabout it here
IMR. The annual number of deaths of infants under one year of age, compared with total live births. Its is expressed as the annual number of deaths among infants among infants per 1000 births rather than a percentage.
Subsequently, question is, what is total fertility rate ap human geography? The total fertility rate is the average number of children born to each woman in a given region during the course of her lifetime. Anything higher than four is a very high total fertility rate and anything lower than two is a very low total fertility rate.
Besides, what does Nic mean in human geography?
newly industrialized country
What is exponential growth in human geography?
The process of moving out of a particular country, usually the individual person’s country of origin. Exponential growth. Growth that occurs when a fixed percentage of new people is added to a population each year. Exponential growth is compound because the fixed growth rate applies to an ever-inrceasing population.
Read Also: How Many Physics Questions Are On The Mcat
G The Demographic Transition Model
Limitations Of The Demographic Transition Model
Like any model, there will be outliers and exceptions to the rule and the Demographic Transition Model is no different. Additionally, there are things the DTM cannot reveal: the impact of other demographic variables such as migration, are not considered, nor does the model predict how long a country will be in each stage. But even so, the relationship between birth rate and death rate is an important concept when discussing population and any patterns, such as those provided by the DTM, that aid in understanding are helpful.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Find The Displacement
Stage : High Growth Rate
Around the mid-1700s, global populations began to grow ten times faster than in the past for two reasons: The industrial revolution and increased wealth. The Industrial Revolution brought with it a variety of technological improvements in agricultural production and food supply. Increased wealth in Europe and later North America because of the Industrial Revolution meant that more money and resources could be devoted to medicine, medical technology, water sanitation, and personal hygiene. Sewer systems installed in cities led to public health improvements. All of this dramatically caused CDRs to drop around the world. At first, CBRs stayed high as CDRs decreased this caused populations to increase in Europe and North America. Over time, this would change.
Africa, Asia, and Latin America moved into Stage 2 of the demographic transition model 200 years later for different reasons than their European and North American counterparts. The medicine created in Europe and North America was brought into these emerging nations, creating what is now called the medical revolution. This diffusion of medicine in this region caused death rates to drop quickly. While the medical revolution reduced death rates, it did not bring wealth and improved living conditions and development that the Industrial Revolution created. Global population growth is highest in the regions that are still in Stage 2.
What Are The Stages Of The Demographic Transition Model
In Stage 1, which applied to most of the world before the Industrial Revolution, both birth rates and death rates are high. As a result, population size remains fairly constant but can have major swings with events such as wars or pandemics.In Stage 2, the introduction of modern medicine lowers death rates, especially among children, while birth rates remain high the result is rapid population growth. Many of the least developed countries today are in Stage 2.In Stage 3, birth rates gradually decrease, usually as a result of improved economic conditions, an increase in womens status, and access to contraception. Population growth continues, but at a lower rate. Most developing countries are in Stage 3.In Stage 4, birth and death rates are both low, stabilizing the population. These countries tend to have stronger economies, higher levels of education, better healthcare, a higher proportion of working women, and a fertility rate hovering around two children per woman. Most developed countries are in Stage 4.A possible Stage 5 would include countries in which fertility rates have fallen significantly below replacement level and the elderly population is greater than the youthful population.
Recommended Reading: Definition Of Similar In Geometry
Topic : Human Populations Dynamics
Significant Ideas:
- A variety of models and indicators are employed to quantify human population dynamics
- Human population growth rates are impacted by a complex range of changing factors.
Big questions:
- What strengths and weaknesses of the systems approach and the use of models have been revealed through this topic?
- To what extent have the solutions emerging from this topic been directed at preventing environmental impacts, limiting the extent of the environmental impacts, or restoring systems in which environmental impacts have already occurred?
- What value systems can you identify at play in the causes and approaches to resolving the issues addressed in this topic?
- How does your own value system compare with others you have encountered in the context of issues raised in this topic?
- How are the issues addressed in this topic of relevance to sustainability or sustainable development?
- In what ways might the solutions explored in this topic alter your predictions for the state of human societies and the biosphere some decades from now?
- How do models help our understanding of human dynamics?
- To what extent have population policies been effective in their aims?
- How do environmental value systems affect population dynamics? Give examples to support your answer.
- What are your views on these?
- Examine the relationship between population dynamics related to sustainable development.
Knowledge and understanding: