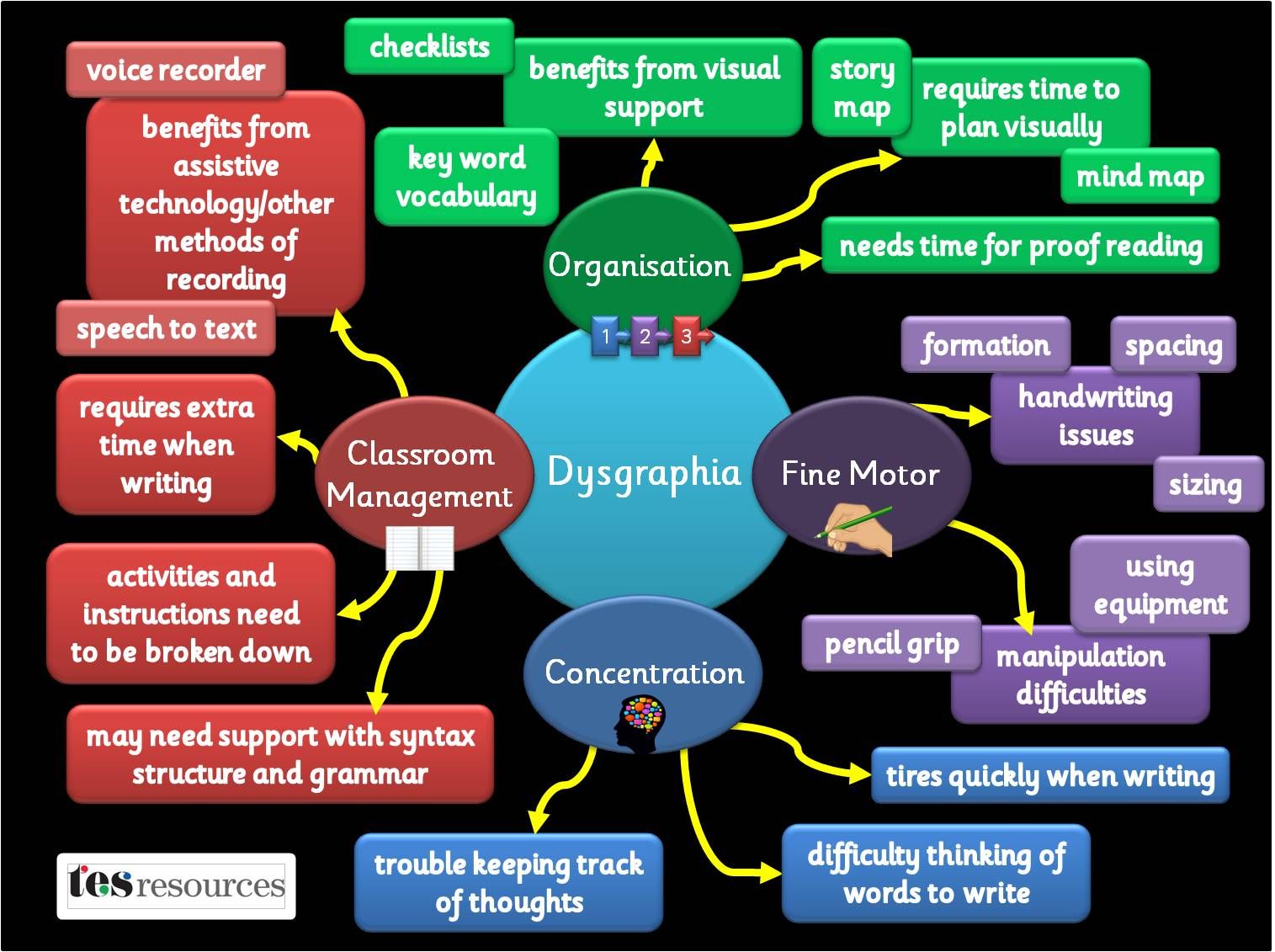
Some Ways To Support A Child With Dysgraphia
There are many ways to help someone with Dysgraphia in school/college and these generally strategies fall into three categories:
Accommodations: providing alternatives to written expression.
Modifications: changing expectations or tasks to minimise or avoid the area of weakness
Remediation: providing instruction for improving handwriting and writing skills.
Whatever the recommended strategies from the childs report, the person planning instruction and support should always play to the childs strengths. Examples of activities that may help:
Once Shes Got These Learning Systems In Place We Can Move On To Her Writing Skills
An occupational therapist can help here.
- To develop strength and control of her hands and fingers, she could start playing with clay. Then she could move on to joining-the-dots to improve her hand-eye coordination. And finally, she can work on tracing letters and pictures. To improve writing endurance, she can also experiment with holding her pen differently and writing more softly.
- To strengthen visual memory for alphabets and words, the therapist can show her cue cards with letters on them and get her to visualise the letters before writing them. And slowly the therapist increases the delay between showing the letters and asking for them to be written.
What Are The Types Of Dysgraphia
Dysgraphia is commonly thought of in the following two ways:
Acquired dysgraphia is associated with brain injury, disease, or degenerative conditions that cause the individual to lose previously acquired skills in writing.
Developmental dysgraphia refers to difficulties in acquiring writing skills. This type of dysgraphia is most commonly considered in childhood. Researchers have identified several subtypes of developmental dysgraphia:
- Motor dysgraphia is due to deficient fine motor skills, poor dexterity, poor muscle tone, and/or unspecified motor clumsiness. Generally, written work is poor to illegible, even if copied by sight from another document. Letter formation may be acceptable in very short samples of writing, but this requires extreme effort, an unreasonable amount of time to accomplish, and cannot be sustained for a significant length of time. Writing is often slanted due to holding a pen or pencil incorrectly. Spelling skills are not impaired. Finger tapping speed results are below normal.
The writing of an eight-year-old German boy with spatial dysgraphia, before and after three months of Edublox training. Copyright: Edublox Online Tutor.
- Spatial dysgraphia is due to a defect in the understanding of space. This person has illegible spontaneously written work, illegible copied work, but normal spelling and normal finger tapping speed. Students with spatial dysgraphia often have trouble keeping their writing on the lines and difficulty with spacing between words.
Also Check: Geometry Dash Vault Of Secrets All Codes
How Is Dysgraphia Diagnosed
Diagnosing dysgraphia often requires a team of experts, including a physician and a licensed psychologist or other mental health professional trained in working with people who have learning disabilities. An occupational therapist, school psychologist, or a special education teacher may also help make the diagnosis.
For children, part of the diagnostic process may include an IQ test and an assessment of their academic work. Specific school assignments may also be examined.
For adults, examples of written work or written tests administered by a doctor may be evaluated. You will be observed as you write to look for fine motor skills problems. You may be asked to copy words from one source to another to help understand if there are language-processing problems.
Occupational therapy may be helpful in improving handwriting skills. Therapeutic activities may include:
- holding a pencil or pen in a new way to make writing easier
- working with modeling clay
Other Effects Of Dysgraphia

People with dysgraphia often have trouble concentrating on other things while writing. This can make it difficult to take notes during class or a meeting because so much attention is being paid to getting each word down on paper. Other things that are said may be missed.
Students with dysgraphia may also be accused of being sloppy or lazy because their handwriting isnt neat. This can affect self-esteem and lead to anxiety, a lack of confidence, and negative attitudes toward school.
Also Check: Chapter 7 Test Form A Geometry Answers
Is Trouble Typing A Symptom Of Dysgraphia
Because dysgraphia is related to problems with fine motor skills, it may manifest, in some cases, as trouble with typing in addition to writing. However, because writing and typing involve different motor skills, many individuals with dysgraphia find typing significantly easier than writing by hand, and allowing the use of a keyboard is a common accommodation for children and adults with dysgraphia.
Profiles Of Developmental Dysgraphia
However, the two-step cluster analysis went beyond this initial finding. It revealed structure within the group of dysgraphic children, separating them into two clusters. Two clearly distinguishable profiles of dysgraphic children appeared based on visual-magnocellular vs. auditory processing abilities. In comparison to normally spelling children, besides the already documented dysfunction in phonological working memory, Cluster 1 was characterized by deficits in visual magnocellular function, alongside a numerical but non-significant reduction also in visual attentional processing. In contrast, Cluster 2 was characterized by significantly worse auditory performance in comparison to normally spelling children, with significant deficits in both variables representing phonological processing abilities . The direct comparison of the two clusters revealed the differential impairment pattern in these profiles, with Cluster 1 demonstrating a visual impairment and Cluster 2 an auditory impairment.
Also Check: Segment Addition Postulate Answers
Dysgraphia Is A Learning Difference That Affects How A Child Writes
Sometimes its apparent right from when they pick up their first crayon. But for other children, it takes a bit longer. Youll probably first notice your childs handwriting is especially hard to read. Or that she writes really slowly. And as you pay more attention, you might notice that she mixes cursive and print. Or that her letter spacing is slightly off. Or maybe she says words out loud as she writes them? Whats happening is that her brain is developing slightly differently, which changes the way she processes words and letters.
Could Other Issues Be A Factor
While dysgraphia can occur on its own, other disorders can also contribute to writing troubles including autism spectrum disorders, visual or auditory processing disorders, Tourette Syndrome, ADHD, or dyslexia . Effectively supporting your child starts with receiving an accurate diagnosis. An evaluation from a diagnostician such as a Psychologistcan help you determine how to best support them.
Recommended Reading: Ct Algebra 1 Curriculum Version 3.0
Strategies For Treatment Of Dysgraphia
Dysgraphia cannot be cured but can be treated. There are many effective ways to manage the symptoms of this condition and reduce its impact on your life. The coping strategies below are helpful for many individuals with dysgraphia:
- Occupational therapy to improve fine motor skills, muscle memory, and visual-spatial skills.
- Physical exercises or special hobbies to increase the strength of hand muscles
- Speech or language therapy to address problems with grammar, word usage, and sentence composition.
- Using graphic organizers to structure ideas.
- Breaking written work down into small, manageable steps.
- Creating an editing checklist to refer to when proofreading .
- Utilizing supportive technology. Many people with dysgraphia can improve their writing ability by working on their keyboarding skills and using spell checkers, speech-to-text tools, etc.
Which Assessments Do We Use For Dysgraphia
The specific assessments used will be chosen based on the child or young person. The main assessments we use are:
- DASH 17 – Detailed assessment of speed of handwriting measures precision skills, fine motor skills, speed alteration and symbol production
- Beery VMI – Beery-Buktenica developmental test of visual-motor integration measures the integration of motor and visual skills, motor co-ordination and visual perception
- WAIS – Wechsler adult intelligence scale can measure reasoning, retention of information, processing information, organisation of information, verbal comprehension
- WISC-V – Wechsler intelligence scale for children is a cognitive assessment
- BAS 3 – British ability scales can be used to assess childrens current intellectual functioning and measures verbal ability, non-verbal reasoning, spatial ability, general conceptual ability, special non-verbal composite
- WIAT – Wechsler individual achievement test measures reading, comprehension and fluency, written expression, mathematics, total achievement
There are other assessments which may be used during a Dysgraphia assessment, if these are predicted beforehand then they will be discussed during the Initial Discussion. If it is thought during the Initial Discussion that it would be more appropriate for one of our in house occupational therapists to carry out the DASH 17 and the Beery VMI then this would be discussed beforehand.
Recommended Reading: What Does Movement Mean In Geography
Lesser Known Symptoms Of Dysgraphia
Pain while writing
Many people who are dysgraphic will experience pain while writing. The pain usually starts in the center of the forearm and then spreads along the nervous system to the entire body. This pain can get worse or even appear when a dysgraphic is stressed. Few people who do not have dysgraphia know about this, because many with dysgraphia will not mention it to anyone. There are a few reasons why pain while writing is rarely mentioned:
- Sufferers do not know that it is unusual to experience this type of pain with writing.
- If they know that it is different from how others experience writing, they know that few will believe them.
- Those that do believe that the pain while writing is real will often not understand it. It will usually be attributed to muscle ache or cramping, and it will often be considered only a minor inconvenience.
Cognitive Profiles Of Dysgraphia And Their Relationship To Dyslexia
The distributions of dysgraphic participants with vs. without accompanying reading difficulties across the clusters did not differ significantly in the present sample. These data can be taken to reflect either that the type of cognitive profile of a dysgraphic child is not influenced by his/her reading ability or that the observed cognitive profiles have rather comparable impact on reading ability, at least in the sample studied here.
In order to reflect the communalities of developmental dysgraphia and dyslexia, the new evidence about dysgraphic children will now be compared to the existing knowledge about dyslexia. In a first step, the underlying skills of the spelling and reading deficit are compared and in a second step, the clusters obtained in the present study are compared to those previously found by Heim et al. .
In summary, the present study revealed communalities with respect to deficits in underlying cognitive abilities of developmental dyslexia and dysgraphia, i.e., in phonological, auditory and visual magnocellular processing. The whole group of dysgraphic children in our study and dyslexics alike differ from normally spelling/reading children with respect to worse performance in phonological processing , dyslexics additionally differ in worse performance in visual attention tasks .
Read Also: Hawkes Learning College Algebra Answers
What Is Graphomotor Processing
Graphomotor processing is the ability to transfer components of writing from the brain to the page a disorder in graphomotor processing therefore precludes a person from recording information on the page, even if they conceptually understand what they are trying to record. Orthographic processing is the ability to identify the correct components of writing, such as spelling and punctuation, prior to executing them on the page. Children with dysgraphia may struggle with one or both types of processing.
How Parents Can Help
There are plenty of ways in which you can help your child. Being organised is one way, and you do need to be organised, I talk about why and how here.
Also Check: Chapter 4 Test Form 2c
Introduction: Definitions And Disagreement
At its broadest definition, dysgraphia is a disorder of writing ability at any stage, including problems with letter formation/legibility, letter spacing, spelling, fine motor coordination, rate of writing, grammar, and composition. Acquired dysgraphia occurs when existing brain pathways are disrupted by an event , resulting in the loss of previously acquired skills. In contrast, this review will concentrate on developmental dysgraphia, i.e., the difficulty in acquiring writing skills despite sufficient learning opportunity and cognitive potential. This article will use the terms dysgraphia and specific learning disorder with impairment of written expression in their broadest terms, to encompass any difficulty an individual may have in written communication.
Secondly, Deuel proposed a second subtype of dysgraphia termed spatial dysgraphia. The primary impairment in this sub-type of dysgraphia was thought to be related to problems of spatial perception, which impaired spacing of letters and greatly impacted drawing ability. In such cases, oral spelling and finger tapping were preserved but drawing, spontaneous writing, and copying text were impaired.
What Are The Symptoms
Illegible handwriting is a common sign of dysgraphia, but not everyone with messy penmanship has the disorder. Its also possible to have neat handwriting if you have dysgraphia, though it may take you a long time and a lot of effort to write neatly.
Some common characteristics of dysgraphia include:
- incorrect spelling and capitalization
- difficulty visualizing words before writing them
- unusual body or hand position when writing
- tight hold on pen or pencil resulting in hand cramps
- watching your hand while you write
- saying words aloud while writing
- omitting letters and words from sentences
Also Check: Ultimate Review Packet Ap Human Geography
Dysgraphia: Symptoms Causes Treatments
In terms of dysgraphia, it is used as a child or as a problem in both calligraphy and spelling .
The learning of reading will involve a wide variety of knowledge, skills and abilities that in many cases will be really complicated to master by many children who may have a .
Disorders of written expression are part of specific learning disorders and refer to the presence of writing skills below what was expected for the childs age, intellectual level and school year .
Dysgraphia Vs Dyslexia And Dyscalculia
We are often asked whether dysgraphia is a form of dyslexia. Generally, the answer is no. Yet, the symptoms of dysgraphia, dyslexia, and dyscalculia sometimes overlap, making it hard to differentiate between these conditions. Dysgraphic and dyslexic individuals often have similar issues with spelling, for example, and both dysgraphic and dyscalculic people typically struggle to read charts and maps. Complicating matters further, a person can have both dysgraphia and dyslexia its a special type of dysgraphia called dyslexic dysgraphia. There are, however, several key traits that make these learning disabilities distinct from one another.
Dyslexia primarily affects a persons ability to read and speak. Some dyslexic individuals also have poor handwriting, but handwriting issues alone dont signify dyslexia. For a diagnosis of dyslexia to be made, an individual must have pronounced difficulty sounding out words, reading , memorizing sight words, and organizing his or her thoughts when speaking. Dyslexic children and adults experience these challenges because their brains dont process graphic symbols or certain sounds properly. Dysgraphia, by contrast, arises from fine motor skill deficits and problems with orthographic coding .
Also Check: Are Elton John’s Kids His
More About Variations Psychology
Variations Psychology is a group practice specializing in diagnostic testing to identify psychological disorders and conditions that affect learning.
Our comprehensive evaluations test for conditions that impact mental health and development such as ADHD, autism spectrum disorders, depression, anxiety, learning disorders, and developmental delays.
In addition to diagnostic services, we offer Independent Educational Evaluations of K-12 students to assess needs for accommodations in school. IEEs provide an objective second opinion on existing IEP and 504 Plans.
For K-12 and post-secondary students, we offer evaluations to assess needs for accommodations on standardized tests, college entrance exams , and graduate and professional licensing exams .Click below to schedule your free 15-minute consultation to learn how our diagnostic services can support you and your family.
Variations Psychology is located in Newport Beach, CA and provides psychological testing to residents throughout Orange County and its surrounding areas including Newport Beach, Newport Coast, Irvine, Shady Canyon, Laguna Beach, Laguna Hills, Coto de Caza, Corona del Mar, Costa Mesa, Yorba Linda, Dana Point, Laguna Niguel, Aliso Viejo, Mission Viejo, Pelican Hill, Crystal Cove, Rancho Santa Margarita, San Clemente, Lake Forest, Huntington Beach, Sunset Beach, Seal Beach, and more.
How Common Is Dysgraphia
Due to a lack of a clear-cut definition for dysgraphia and the dearth of research focused specifically on it, there are few statistics regarding prevalence. However, written language disabilities are very common in students with learning disabilities, including in children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder , and they tend to be persistent. According to Kushki et al. , between 10% and 30% of children experience difficulty writing, although the exact prevalence depends on the definition of dysgraphia.
There is an overlap between the signs and symptoms of dysgraphia and dyslexia. From the first studies of dyslexia, there has been continuing evidence that mild clumsiness a possible symptom of dysgraphia is associated with dyslexia. In a review of Ortons research, Geschwind noted: He pointed out the frequency of clumsiness in dyslexics. Although others have commented on this, it still remains a mysterious and not adequately studied problem.
Don’t Miss: Structural Formula Of Ccl4