X Assessing Fertilization And Egg Activation In Egg
The oocyte enters the spermatheca in metaphase I of the first meiotic division and meiotic resumption and fertilization occur concurrently . As the oocyte enters the spermatheca, the meiosis I spindle assembles into in a pentagonal array of chromosomes. Next the DNA is translocated to the cortex, the spindle then rotates perpendicular to the cortex, and the chromosomes begin to separate . If fertilization occurs, the cell will proceed through anaphase I and half of the chromosomes will be deposited into the first polar body . The oocyte chromosomes subsequently undergo the second meiotic division and a second polar body is extruded. Finally, pronuclei form around both the maternal and paternal chromatin .
In addition to triggering meiotic resumption, the newly fertilized egg undergoes a number of changes that are necessary for proper egg activation and embryo development. These include the activation and/or degradation of selected maternal mRNAs and proteins, release of cortical granules , secretion of a chitinous eggshell, and the mounting a membrane block to polyspermy to prevent fertilization by a second sperm . If all of these processes are coordinated and completed properly, the embryo will develop as it passes through the uterus and is eventually laid at approximately the 30-cell stage .
Can You Feel When An Egg Gets Fertilized
You wont feel when an egg gets fertilized. You also wont feel pregnant after two or three days. But some women can feel implantation, the process in which the fertilized egg travels down the fallopian tube and buries itself deep within the wall of the uterus.
This happens about eight to nine days after fertilization, though it can happen earlier or later, depending. Symptoms of implantation may include abdominal cramps and light bleeding. Whether you feel anything or not, implantation is the moment that fertilization gives way to pregnancy!
What Is The Definition Of Fertilization In Biology
4/5Definition
Similarly one may ask, what is fertilization short answer?
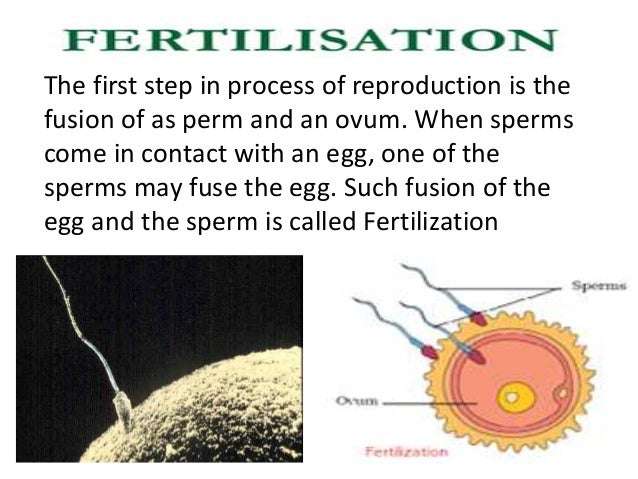
Answer: Fertilization is the fusion of gametes to initiate the development of a new individual organism. In animals, the process involves the fusion of an ovum with a sperm, which first creates a zygote and then leads to the development of an embryo.
Subsequently, question is, what are the 4 steps of fertilization? The stages of fertilization can be divided into four processes: 1) sperm preparation, 2) sperm-egg recognition and binding, 3) sperm-egg fusion and 4) fusion of sperm and egg pronuclei and activation of the zygote.
Hereof, what is fertilization and its products?
Fertilization is the fusion of haploid gametes, egg and sperm, to form the diploid zygote. Note though there can be subtle differences in the fertilization process which occurs naturally within the body or through reproductive technologies outside the body, the overall product in both cases is a diplod zygote.
What are the 2 types of fertilization?
In animals, there are two types of fertilisation, internal and external. Internal fertilisation happens in the female body. External fertilisation happens outside of the body. Mammals, birds, and reptiles use internal fertilisation.
Read Also: Chapter 10 Test Form 2a Geometry Answers
Development Step : Fertilization
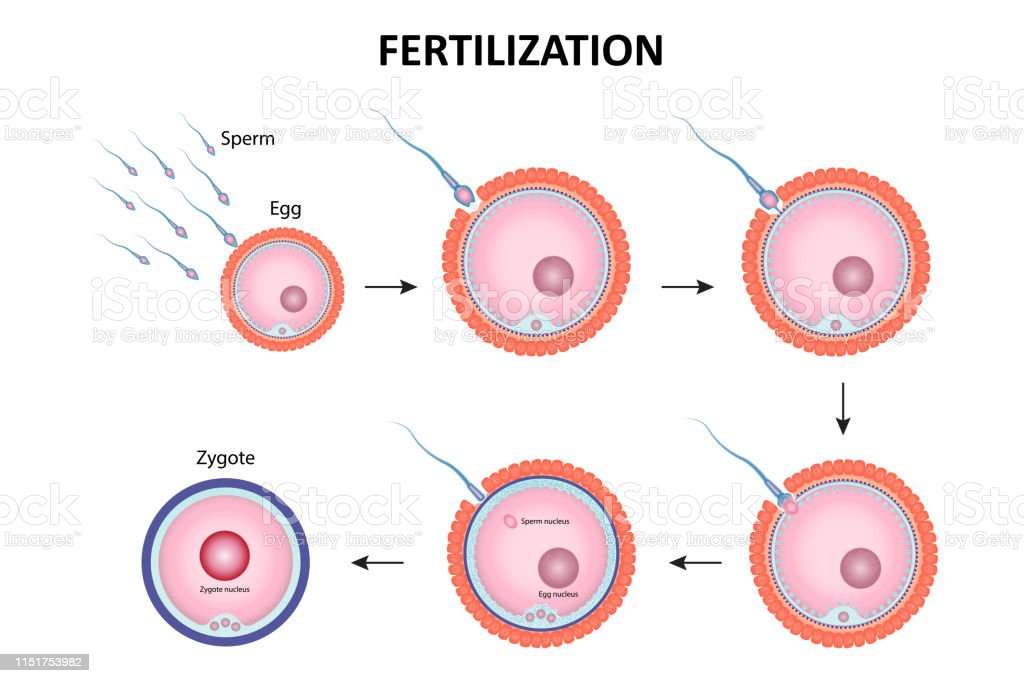
Fertilization is the process in which a single haploid sperm fuses with a single haploid egg to form a zygote. The sperm and egg cells each possess specific features that make this process possible:
The egg is the largest cell produced in most animals species. A human egg cell is approximately 16 times larger than a human sperm cell. The eggs of different species contain varying amounts of yolk, nutrients to support growth of the developing embryo. The egg is surrounded by a jelly layer, composed of glycoproteins , that releases species-specific chemoattractants that guide sperm to the egg. In mammals, this layer is called the zonapellucida. In placental mammals, a layer of follicular cells surrounds the zona pellucida. The zona pellucida/jelly layer is separated from the egg by a membrane called the vitalline envelope, which is outside of the cells plasma membrane. Just underneath the eggs plasma membrane are cortical granules, vesicles containing enzymes that will degrade the proteins that hold the vitalline envelope around the plasma membrane when fertilization occurs .
Generalized mammalian egg cell. By Mia Nicolacoudis Own work, CC BY 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=69615546
Cell Biology Of Gametes
Fertilization requires proper gametogenesis , which produces haploid cells and introduces diversity. Primordial germ cells are the embryonic precursors to spermatocytes and ova. The cells produced by the first few divisions of the fertilized egg are totipotent and capable of differentiating into any cell type, including germ cells. PGCs originate within the primary ectoderm of the embryo and then migrate into the yolk sac. Between weeks 4 and 6, the PGCs migrate back into the posterior body wall of the embryo, where they stimulate cells of the adjacent coelomic epithelium and mesonephros to form primitive sex cords and induce the formation of the genital ridges and gonads. The sex cords surround the PGCs and give rise to the tissue that will nourish and regulate the development of the maturing sex cells .
Egg
Sperm
You May Like: My.hrw.com Algebra 1
When Does Fertilization Occur
For fertilization to happen, the timing and conditions must be just right. The fertilization process can only occur during a fairly small window within just a few days of ovulation .
Even if a sperm does make its way to the fallopian tube, that doesnt mean it will definitely be able to fertilize the egg. Aside from various fertility-related problems that can hamper the process, the timing may be off, meaning the sperm arrived too early or too late to meet up with the egg. Or the sperm may have entered the wrong fallopian tube .
External And Internal Fertilization
External fertilization usually occurs in aquatic environments where both eggs and sperm are released into the water. After the sperm reaches the egg, fertilization can then take place. Most external fertilization happens during the process of spawning where one or several females release their eggs and the male release sperm in the same area, at the same time. The release of the reproductive material may be triggered by water temperature or the length of daylight. Nearly all fish spawn, as do crustaceans , mollusks , squid, and echinoderms . Pairs of fish that are not broadcast spawners may exhibit courtship behavior. This allows the female to select a particular male. The trigger for egg and sperm release causes the egg and sperm to be placed in a small area, enhancing the possibility of fertilization.
Video advice: Fertilization is the epic story of a single sperm to unite with an egg. watch it in full details.
Don’t Miss: How To Calculate Displacement In Physics
How Long Does It Take For A Sperm To Fertilize An Egg
Contrary to what many people believe, fertilization doesnt occur immediately after sex. The fastest sperm can reach the egg in as little as an hour after, but the entire fertilization process can take several hours. After ejaculation, the sperm are gearing up for that long journey.
For about a half an hour after sex, the semen coagulates in a woman’s vagina, forming a physical barrier that prevents the sperm from wandering very far in the wrong direction. This protection disappears within 30 minutes, when the semen reliquefies.
Any sperm that haven’t made it up through the cervix by then are eliminated from the running. The vagina is very acidic and quickly destroys any errant cells, including sperm.
The sperm that make it to the next step the cervical canal spend time going through biochemical changes, picking up the tail-thrashing speed thats required for them to swim their way through the uterus and fallopian tubes to find their target.
The cervical canal is a much more welcoming environment, where the mucus is specially designed to transport sperm efficiently when you’re most fertile.
As you approach ovulation, your suddenly copious mucus becomes stretchy, clear and thin . The changes happen on a microscopic level as well, as strings of molecules line up like train tracks so that sperm can hop on and ride to their destination.
What Are The Different Types Of Fertilization
There are two different types of fertilization- internal fertilization, where the fusion of egg and sperm occurs inside the female reproductive tract, for eg., humans and external fertilization, where the fusion of male and female gametes occurs outside the body of the organism, for eg., sea urchins, frogs, etc.
You May Like: How Many Subfields Of Psychology Are There
Rupture Of Pollen Tube
The rupture of the pollen tube to release sperm in Arabidopsis has been shown to depend on a signal from the female gametophyte. Specific proteins called FER protein kinases present in the ovule control the production of highly reactive derivatives of oxygen called reactive oxygen species . ROS levels have been shown via GFP to be at their highest during floral stages when the ovule is the most receptive to pollen tubes, and lowest during times of development and following fertilisation. High amounts of ROS activate Calcium ion channels in the pollen tube, causing these channels to take up Calcium ions in large amounts. This increased uptake of calcium causes the pollen tube to rupture, and release its sperm into the ovule. Pistil feeding assays in which plants were fed diphenyl iodonium chloride suppressed ROS concentrations in Arabidopsis, which in turn prevented pollen tube rupture.
Newly Identified Players In Mammalian Fertilization
The use of CRISPR-Cas9 technology has led to the recent identification of six new factors essential for mammalian fertilization: SPACA6, TMEM95, SOF1, FIMP, and DCST1/DCST2.
Sperm SPACA6
In 2014, Lorenzetti et al. characterized a mutant mouse line that had a deletion removing Spaca6 . Male homozygous knockout mice were infertile with a phenotype that closely resembles that of Izumo1-deficient mice. Subsequent studies by two other groups confirmed that Spaca6 deletion in male mice results in infertility, although mating behavior is normal and sperm are motile and morphologically normal . Fertility could be restored by a transgene . In a human zona-free in vitro fertilization assay, an anti-SPACA6 antibody reduced fertilization rates by threefold .
Recovery of oocytes from female mice that were mated with Spaca6/ male mice revealed that the spermatozoa were trapped in the PVS. This indicates that knockout spermatozoa migrate through the female genital tract to the oocyte and penetrate the ZP but fail to fuse with the oocyte membrane. When Spaca6/ sperm was injected into the cytoplasm of oocytes to bypass the membrane fusion step, fertilization was successful, and the fertilized eggs showed normal embryonic development, suggesting that SPACA6 does not play a critical role downstream of spermegg fusion.
Sperm TMEM95
Sperm SOF1
Sperm FIMP
Sperm DCST1/DCST2
Recommended Reading: How To Calculate Net Force
Process Of Fertilization In Humans
The process starts with insemination, which is the transfer of semen into the vagina. The sperms travel up to the fallopian tube only after surviving the difficult environment in the vagina, cervix and uterus. The survived or most healthy sperms have to reach up to the ampulla region of the fallopian tube where the fertilisation occurs.
The sperms head contains an enzyme which allows the sperm to enter the ovum by passing all the layers which are meant to protect the egg. Only one sperm can fertilise the egg and when it does, the outermost layer, that is zona pellucida of egg will harden up to prevent the entry of any other sperms.
Read Also:
The process of fertilization in humans involves several chemical and physical reactions for it to be successful. The steps involved in the fertilization process are:
Development Step : Cleavage And Blastula Stage
After fertilization successfully activates the egg, the egg begins a series of rapid cell divisions called cleavage, illustrated below. Typical cell division occurs every 18-24 hours, but cleavage cell divisions can occur as frequently as every 10 minutes. During cleavage, the cells divide without an increase in size so the large single-celled zygote divides into smaller and smaller cells called blastomeres. After the cleavage has produced over 100 blastomeres, the embryo is called a blastula. The blastula is usually a spherical layer of blastomeres that are considered to be the first embryonic tissue, the blastoderm. The blastoderm surrounds a fluid-filled or yolk-filled cavity, called the blastocoel . The blastocoel is absolutely essential for the next step of development, gastrulation, which we will discuss in the next reading.
The stages of development that weve discussed so far are very similar across most animal lineages. But mater stages of cleavage are a little different in mammals: the mammalian blastula is called a blastocyst, and, unlike the blastulas of other animal lineages, the blastocyst has an inner cell mass and an outer cell layer called the trophoblast. The inner cell mass will go on to form the embryo, and the trophoblast will go on to form embryonic portion of placenta. Cleavage in a placental mammal is illustrated in the diagram below.
Also Check: Equilateral Geometry Definition
How Long Can Sperm Live Inside You To Get Pregnant
Sperm can survive inside the female reproductive tract for about 72 hours. And, in some cases, the sperm can live for up to five days. But the lifespan of an egg is much shorter. The egg lives for only 12 to 24 hours after ovulation.
If sperm aren’t hanging around by time the egg makes it to the fallopian tube , the body reabsorbs the egg, and the window of opportunity for conception that month closes.
From the What to Expect editorial team and Heidi Murkoff, author of What to Expect When You’re Expecting. What to Expect follows strict reporting guidelines and uses only credible sources, such as peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions and highly respected health organizations. Learn how we keep our content accurate and up-to-date by reading our medical review and editorial policy.
The Egg Cortical Reaction Helps To Ensure That Only One Sperm Fertilizes The Egg
Although many sperm can bind to an , normally only one fuses with the egg and injects its and other organelles into the egg . If more than one sperm fusesâa condition called polyspermyâmultipolar or extra mitotic spindles are formed, resulting in faulty segregation of chromosomes during nondiploid cells are produced, and usually stops. Two mechanisms can operate to ensure that only one sperm fertilizes the egg. In many cases, a rapid depolarization of the egg plasma membrane, which is caused by the fusion of the first sperm, prevents further sperm from fusing and thereby acts as a fast primary block to polyspermy. But the returns to normal soon after , so that a second mechanism is required to ensure a longer-term, secondary block to polyspermy. This is provided by the egg cortical .
When the sperm fuses with the , it causes a local increase in cytosolic Ca2+, which spreads through the cell in a wave. In some mammalian eggs, the initial increase in Ca2+ is followed by prolonged Ca2+ oscillations. There is evidence that the Ca2+ wave or oscillations are induced by a that is introduced into the egg by the sperm, but the nature of the protein is unknown.
How the cortical reaction in a mouse egg is thought to prevent additional sperm from entering the egg. The released contents of the cortical granules both remove carbohydrate from ZP3 so it no longer can bind to the sperm plasma membrane and partly cleave
Read Also: Paris Jackson Adopted
Xii Analysis Of Fertilization
Antibody-based approaches are useful for determining the sub-cellular localization of fertilization-specific gene products. The standard approach is to generate polyclonal anti-peptide antibodies against two or more regions of the candidate fertility protein since not all regions will be useful for generating antibodies . For these fertility proteins, polyclonal, anti-peptide antibodies have two distinct advantages over monoclonal antibodies: 1) they do not require the isolation of pure sperm and oocytes, 2) polyclonal antibodies typically have higher binding efficiencies, which is useful when attempting to detect cell-surface proteins that are typically expressed at low levels. It is also important always to pre-screen the animals used for antibody production since many express unrelated nematode antibodies stemming from previous nematode infections.
Live cell staining can also be used to assess protein localization on the external surface of the plasma membrane or in fused MOs . fer-1 mutants can be used to confirm an initial restriction to the MO since the fer-1 spermatozoa are specifically defective in MO fusion despite their ability to form a small motile pseudopod .
What Is Fertilization
In plants, fertilization is a process of sexual reproduction, which occurs after pollination and germination.
Fertilization can be defined as the fusion of the male gametes with the female gametes to form a diploid zygote. It is a physicochemical process which occurs after the pollination of the carpel. The complete series of this process takes place in the zygote to develop into a seed.
In the fertilization process, flowers play a significant role as they are the reproductive structures of angiosperms . The method of fertilization in plants occurs when gametes in haploid conditions fuse to produce a diploid zygote.
In the course of fertilization, male gametes get transferred into the female reproductive organs through pollinators and the final product will be the formation of the embryo in a seed.
Recommended Reading: Algebra Nation Quiz Answers
Maturation Of The Egg
Maturation is the final step in the production of functional eggs that can associate with a spermatozoon and develop a reaction that prevents the entry of more than one spermatozoon. In addition, the cytoplasm of a mature egg can support the changes that lead to fusion of spermatozoal and egg nuclei and initiate embryonic development.
Capacitation Hyperactivation And Sperm Selection
Although it is difficult to assign a definite starting point to fertilization, sperm capacitation signals the acquisition of competence for fertilization and is commonly thought of as the initiation of the fertilization process. Capacitation is defined as the series of biochemical events requisite for competence to undergo the acrosome reaction and fertilization. Those events include both cytoplasmic events, such as an influx of calcium, and membrane events, such as the removal of sterols and relocation of fertilization-associated proteins. In addition, capacitation is associated with the activation of hyperactive motility.
The most pronounced change during capacitation is membrane remodeling. This remodeling increases the fluidity of the phospholipid bilayer and facilitates the acrosome reaction. As sperm progress through the reproductive tract, cholesterol is removed from the plasma membrane by albumin and high-density lipoproteins found in the female genital tract. Membrane fluidity may also be increased by removal of phospholipids in a second mechanism. In some species, extracellular glycoproteins are stripped from sperm traversing the genital tract. When glycoproteins are removed from the membrane, associated phospholipids are also removed. These modifications of the plasma membrane may expose membrane-bound enzymes and ligands utilized in sperm penetration of the cumulus oophorus and anchoring to the zona pellucida.
Bruce M. Carlson, in, 2014
Read Also: How To Calculate Half Life Given Concentration And Time