Preventing Unwanted Energy Transfers
Conduction Convection Energy-Efficient Homes Green Buiders Green Building Green Houses Heat Transfer Radiation Dan H 106 posts 0 comments Dan is a seasoned internet marketing guru located in Western Canada, and a staff writer for Cyber Parent Foams and insulations are also common materials used to reduce heat transfer in your home to make it more efficient. Shiny, Reflective Surfaces While reflective surfaces feel extremely hot to the touch when exposed to radiation or sunlight, the metal is actually repelling the radiation rather than transferring it
Convection refers to the process of transfer of heat or energy through a fluid from high temperature to low temperature. Convection is one of the three types of heat transfer the other two being radiation and conduction Heat transfer in fluids generally takes place via convection, in which flowing fluid carries heat from one place to another. Convection currents are produced by temperature differences. Hotter parts of the fluid rise, while cooler areas sink What is Convection. In general, convection is either the mass transfer or the heat transfer due to bulk movement of molecules within fluids such as gases and liquids. Although liquids and gases are generally not very good conductors of heat, they can transfer heat quite rapidly by convection.. Convection takes place through advection, diffusion or both
How Does Double Glazing Reduce Heat Loss
by Maghull Double Glazing | Jul 20, 2019 | Blog
Youve probably heard a lot of people raving about the benefits of double glazed windows. If youre not familiar with the term, it has nothing to do with sugar-coating. Its simply pushing two layers of glass against each other and making benefit of the air trapped in-between to reduce heat and regulate energy consumption.
The fact that more than 25% of your home energy bill is wasted, as air escapes through inefficient windows and doors should give you a hint of how important these coatings are.
While many are well-acquainted with the benefits double glazing provides, only a few are aware of its mechanism how it actually reduces heat loss. This will be our focus in this article.
Controlling Heat Transfer In Green Buildings
radiation thermal energy may be transformed into electromagnetic energy, emitted and then absorbed so that it is transformed into thermal energy again In this particular experiment the second and third mechanism, radiation and convection, are studied in some more detail In most home ovens, the convection fan is adequate to maintain uniform temperature throughout and does increase heat transfer by about 15% above what it would be with radiation plus free convection, but does not provide sufficient air velocity to raise convective heat transfer to a point where convection dominates radiation as the mechanism for transferring heat to the bread Convection heat transfer arises when heat is lost/gained by a fluid in contact We are seeking to decrease the total resistance to heat flow when surface constant and perform an energy balance on a small element of the fin..
Also Check: What Does Abiotic Mean In Biology
Ways To Reduce Heat Inside Your Home Without Using
Reducing heat transfer is one way of improving energy efficiency. Sometimes we want to keep things cool. In summer we use air conditioners to keep our homes and offices cool and comfortable Reduce heat loss with Effective Double Glazing.Putting two glass layers together with a small air or gas filled gap between them is refereed to as Double Glazing. These two panes of glass may be sealed in the factory during production Convection is when a fluid, such as air or a liquid, is heated and then travels away from the source, it carries the thermal energy along. The next way we lose body is called convection. The definition of convection is weird but I’ll explain it better Forced Convection Heat Transfer 8.1 Introduction The general definition for convection may be summarized to this definition energy transfer between the surface and fluid due to temperature difference and this energy transfer by either forced or natural convection
Double Glazing: How It Works And Why You Need It
Are you looking into double-glazing windows for your home? Whether youre planning to purchase one or you already have them installed throughout your home, you are probably wondering how it works and how does it improves to the point of becoming standard for building regulations in the UK. And its nothing like magic. In this article, were going to explain the science behind double glazing windows and the benefits of having them in your home.
According to a study, double-glazed windows could save up to 12.4% on overall households energy consumption. Its an efficient way to improve your homes insulation up to 73% and reduce the noise that enters the room by as much as 70%no wonder why its the top choice for most homeowners.
Also Check: Figure Definition Psychology
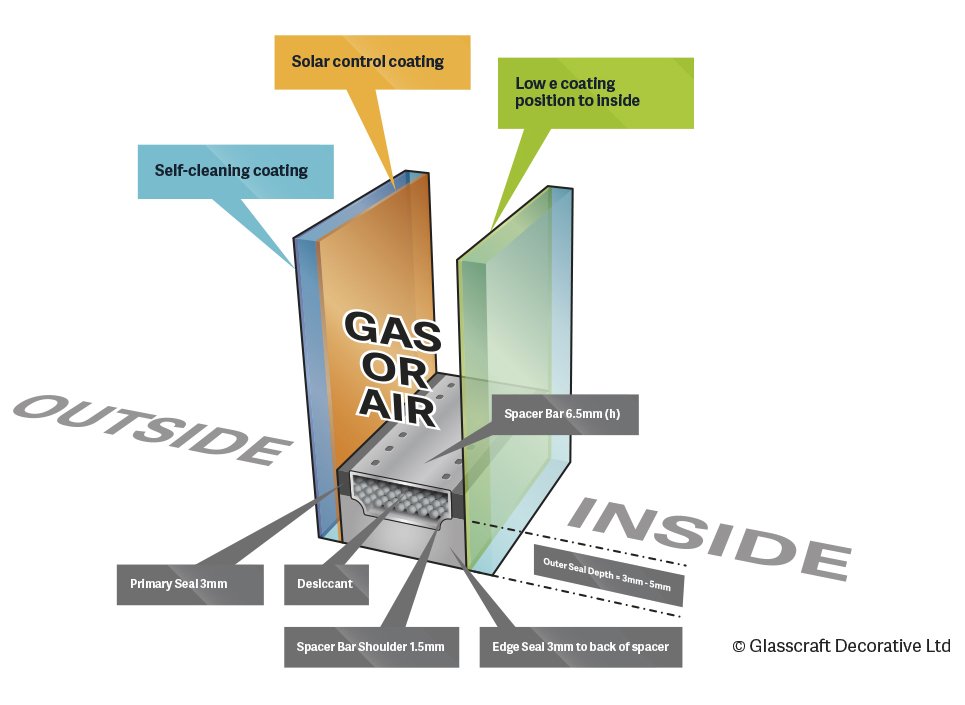
Spacer Bar And Desiccant
A spacer bar, sometimes also called a profile, is a continuous hollow frame that separates the two panes of glass in a double glazed window. Most spacer bars are made out of aluminum, because it is reasonably priced and flexible which makes it easy to work with.
A double glazed windows spacer bar is filled with a desiccant. The desiccant which can be a variety of products, including silica pellets and zeolite spheroids, absorbs any humidity from the weather or washing that manages to creep in between the panes of glass. This keeps condensation from building up and obstructing the view through the window.
Why Are The Double Glazed Units Filled With Argon Gas
An improvement that can be made to the thermal performance of insulating glazing units is to reduce the conductance of the air space between the layers of glass. In most double glazing units, the space is filled with air or flushed with dry nitrogen just prior to sealing. In a standard sealed glass insulating unit, air currents between the two panes of glazing carry heat to the top of the unit and settle into cold pools at the bottom.
Filling the space with a less conductive, more viscous, or slow-moving gas such as Argon minimises the convection currents within the space, conduction through the gas is reduced, and the overall transfer of heat between the inside and outside is reduced. This phenomenon results from the fact that the density of the gas is greater than the density of the air.
All of the double glazed units we use at Bond Homes are filled with Argon gas*. This type of double glazing has a marked improvement, in thermal performance over standard double glazing.
Don’t Miss: Segment Addition Postulate Answers
Insulation Edexcel Gcse Physics Revision Note
How Do I Reduce Or Eliminate Convection
Regions that contain higher kinetic energy transfer the energy to regions with lower kinetic energy. Simply put, heat transfer can be grouped into three broad categories: conduction, convection. A lesson focusing on reducing energy loss from domestic situations using forms of insulation. The PPT introduces typical types of insulation and learners then have opportunity to complete differentiated activities in explaining how double glazing, cavity wall and loft insulation etc. reduce heat transfer Heat-reflecting roofs, insulation, and energy efficient windows will help to reduce that heat conduction. Radiation is heat traveling in the form of visible and non-visible light. Sunlight is an obvious source of heat for homes In cooling seasons, cellular shades can reduce unwanted solar heat through windows by up to 80%, reducing the total solar gain to 15% or less when installed with a tight fit. Cellular shades that operate on side tracks are most effective at increasing the R-value of windows, and those that open from both the top and bottom allow users to most effectively control daylight entering the home
Recommended Reading: What Does K Mean In Physics
How Does Insulation Conserve Energy Home Guides Sf Gat
Energy efficient windows also reduce the peak heating and cooling load, which can reduce the size of an air conditioning system by 30%, leading to further cost savings. The Australian Window Association has developed a tool that calculates the savings that may be achieved by energy efficient glazing Insulation saves money, increases home comfort, and protects the environment by reducing energy use. According to the U.S. Department of Energy , the typical U.S. family spends close to $1,500 each year on energy bills. DOE statistics show that, typically, 44% of a homeowner’s utility bill goes for heating and cooling costs
How Does Double Glazing Work
Double glazing uses two panes of glass separated by a layer of argon gas to keep your home more energy efficient and reduce sound. The argon gas is a poor heat conductor and therefore keeps warm air from escaping, while the second pane of glass acts as a barrier to noise.
Find out exactly how double glazing and triple glazing works, the ins and outs of their energy ratings and how improving your windows will help you save money and reduce sound pollution.
If you still have any additional questions after youve had a read, or would like more information, speak to a member of our team today.
You May Like: Exponential Growth And Decay Worksheet Answer Key
Why The Extra Pane
Double glazed windows have two panes close together, hence the name double glazing. There is a glass pane on the outside, a glass pane on the inside, and a small space in the centre known as an air gap or tight air pocket.
When heat energy is transferred from hot spaces to cold spaces we call it convection, but it requires a good conductor. The trapped air in-between the glass cannot circulate, so it is therefore a poor conductor, reducing the rate of heat loss from inside the house. With less heat able to leave the room through the window pane, the room stays warmer for longer.
Many double glazed windows are manufactured with PVCu or aluminium frames, which are both durable and efficient materials. There should be no small gaps around the window frames to allow cold air to enter the house.
The Science Behind Double Glazing: How Does It Work

Energy efficiency is a hot topic for homeowners for two reasons: energy efficient home improvements can reduce household bills and increase house value, and they will also reduce your carbon footprint. As the UK and Europe scramble to try and achieve their carbon reduction targets, its imperative that we stop relying on gas and other fossil fuels for our energy, and start using renewable sources. Any efficient home improvements we can make will lower our gas consumption.
Double glazed windows are one of the top property improvements chosen by homeowners, because they keep homes at a warmer temperature. Double glazing also reduces outside noise which is another added benefit. But how is this type of window so much more efficient than a single pane window?
Double glazing works in three ways:
- It prevents heat loss through the window
- It stops draughts through the window and the frame
- It works as an insulator in the same way as cavity wall insulation
Recommended Reading: Imagine Math Login
Ways To Reduce Energy Transfer
There are some simple ways to reduce energy transfers from a house, including fitting:
- carpets and curtains
- reflective foil on the inside walls
- double glazing
Double glazing involves having two panes of glass in the window instead of just one. There is air or an even better insulator such as argon gas between the two panes of glass. This reduces energy transfer by conduction.
Energy loss through walls can be reduced using cavity wall insulation. This involves blowing insulating material into the gap between the outside wall and the inside wall to reduce conduction. Loft insulation works in a similar way.
How people and animals use insulation to keep warm
What Does Double Glazing Do
Double glazing has many benefits, and there is a real science behind how well it performs. Some systems will perform better than others, however what is outlined below will be common through all double glazing systems.
Firstly, double glazing will reduce noise. Different sounds travel at different frequencies. When a sound is emitted and meets an object, in this situation glass a percentage of sound is reflected, a percentage is absorbed, and a percentage is transmitted through the glass to the other side. In a double glazed system sound needs to travel through two panes of glass instead of just one. The second pane of glass acts as another layer of insulation, reducing the amount of sound waves that travel through the system. In addition to this, a wider cavity between the two panes of glass, preferably filled with a pressurised gas significantly reduces the travel of sound. Windows are the one of the weakest sound proofing points in a home, because sound travels through the path of least resistance. This is why it is essential to have windows that have a proper seal.
Also Check: Reversible Figure Ground Relationship
The Science Behind Double Glazed Windows
You probably know the benefits of double glazed windows, but do you understand the science behind them? In this post, we are going tell you about the 5 components of double glazed windows and how they work together to efficiently:
- Insulate your home and decrease energy bills
- Give you a better view
- Increase security
- Filter out noise
The Science Behind The Process
When molecules are heated they move quickly and conduct heat to each other. In the case of molecules trapped within a thin layer between two glass surfaces molecules are tight and close to each other. This, in turn, allows for easier heat transfer.
On the other side, regular molecules that are spread widely in the air are far apart from each other, so they have much slower heat transferring rate. Hence, the thin layer of air of double glazed windows acts as a heat insulator.
In other words, making an extremely thin gap for air to prevent it from circulating properly results in lower heat conduction. So, it reduces the overall heat loss. Technically speaking, the heat loss is not avoided, its just slowed down.
You May Like: Eoc Fsa Warm Ups Algebra 1 Answers
Diy Fixes For The Main Forms Of Home Heat Loss
If your home is not properly maintained to keep heat indoors, your heaters will have to work much harder and longer to keep you warm. This will result in a waste of energy and money. So, if you want to do something that’s good for your wallet and the environment, check your home for ways to reduce heat loss.
- plumbing vents
- recessed lighting
apply caulk or weather stripping to seal the leak.
Double Glazing Heat Loss Mechanics
The mechanics of that concept are summed up in how conduction works. For heat to be lost through your window, itll need a surface to get transferred or conducted through. Double-glazed windows are made out of two planes of glass with Argon gas in between them.
Argon is a poor conductor of heat. So the heat doesnt really make it through to the opposite plane of glass, meaning that its not fully transferred to the other side of the window. The same thing happens with noise.
Now that weve discussed all the mechanics that play a role in reducing heat loss, we should discuss how these mechanics actually function.
Also Check: Who Are Paris Jackson’s Biological Parents