Positive Punishment And Operant Conditioning
Shereen Lehman, MS, is a healthcare journalist and fact checker.;She has co-authored two books for the popular Dummies Series .
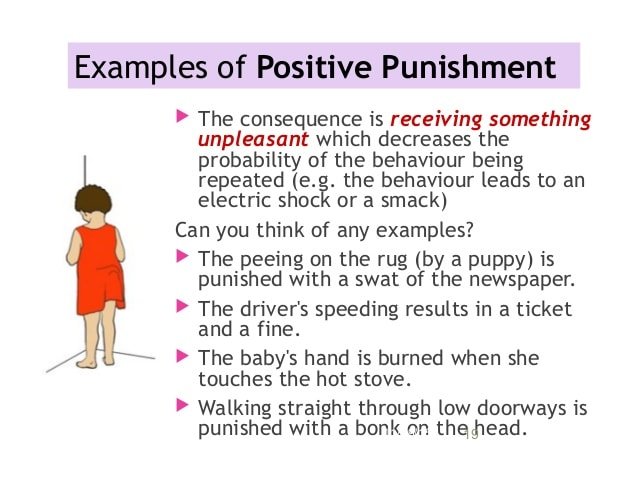
Positive punishment is a concept used in B.F. Skinner’s;theory of operant conditioning. How exactly does the positive punishment process work? The goal of any type of punishment is to decrease the behavior that it follows. In the case of positive punishment, it involves presenting an unfavorable outcome or event following an undesirable behavior.
When the subject performs an unwanted action, some type of negative outcome is purposefully applied. So, if you are training your dog to stop chewing on your favorite slippers, you might scold the animal every time you catch them gnawing on your footwear. Because the dog exhibited an unwanted behavior , you applied an aversive outcome .
The concept of positive punishment can be difficult to remember, especially because it seems like a contradiction. How can punishment be positive? The easiest way to remember this concept is to note that it involves an aversive stimulus that is added to the situation. For this reason, positive punishment is sometimes referred to as punishment by the application.
The Psychology Of Positive Reinforcement Theory
Although it sounds like a simple idea, it was not always the go-to method for teaching. Punishment has always been a popular method for teachingwhether it was for training children, pets, or adults.
In fact, positive reinforcement is only one of the four types of conditioning according to famed behaviorist B. F. Skinners model.
What Is Punishment Psychology And Should You Use It
Medically Reviewed By: Tanya Harell
We were all punished when we were younger at one time or another. However, it is how we are punished that can shape how we will behave in the future. Believe it or not, whether you got a spanking for hitting your sister or a pat on the back can decide what kind of person you will be. In;operant conditioning, punishment isa change in surroundings after a certain behavior is shown that will prompt the subject to stop using that sort of behavior. Whether the punishment is positive or negative depends on the subject and the type of behavior you are trying to discontinue.
The Law Of Effect
Dr. Burrhus Frederic Skinner, or B.F. Skinner, was a psychologist who thought classical conditioning was too simple to be an accurate explanation of human behavior. Therefore, he decided to use the causes of action and consequence to determine why we do what we do. However, Skinner based his operant conditioning onDr. Edward Thorndike’s;Law of Effect.
The Law of Effect was a theory that satisfying responses cause an individual’s actions to be repeated, and unwelcome responses cause these actions to occur less often. For example, if you inadvertently did something nice for someone and they praised you for it, you would be more likely to do it again, right? Dr. Skinner found three different operant responses that follow certain behaviors. These include:
Positive Punishment Versus Negative Punishment Psychology
Punishment Psychology Definition
You May Like: Eoc Fsa Practice Test Answers
Positive Punishment And Skinners Operant Conditioning Theory
Skinner was a behaviorist who developed the theory of operant conditioning . Since he firmly believed that nurture, i.e., external factors affect peoples behavior, he conducted various experiments in his attempt to offer a model that explains why and how people behave under certain circumstances.
He wanted to prove that Pavlovs theory on classical conditioning did not offer a detailed explanation of complex behavior tendencies.
The Operant Conditioning Theory rests upon the idea that when a behavior is rewarded, it tends to be repeated, when it is punished, it is discouraged.
Behaviorists firmly believe that humans behave based on the input and the influence they get from the environment where they reside.
He defined four possible alternatives that result in a behavior change and deliver different outcomes.
I would like to unlock the full potential of:
Incapacitation And Societal Protection
Incapacitation as a justification of punishment refers to the offender’s ability to commit further offences being removed. Imprisonment separates offenders from the community, for example, Australia was a dumping ground for early British criminals. This was their way of removing or reducing the offenders ability to carry out certain crimes. The death penalty does this in a permanent way. In some societies, people who stole have been punished by having their hands amputated.
Criminal activities typically give a benefit to the offender and a loss to the victim. Punishment has been justified as a measure of retributive justice, in which the goal is to try to rebalance any unjust advantage gained by ensuring that the offender also suffers a loss. Sometimes viewed as a way of “getting even” with a wrongdoerthe suffering of the wrongdoer is seen as a desired goal in itself, even if it has no restorative benefits for the victim. One reason societies have administered punishments is to diminish the perceived need for retaliatory “street justice”, blood feud, and vigilantism.
You May Like: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet
Positive Punishment Vs Negative Punishment
Positive punishment works by presenting an undesirable consequence after the negative behavior is exhibited. In other words, you are following up your childs bad behavior with a negative consequence.
Image: Shutterstock
Negative punishment is one where a desirable stimulus is removed after the unwanted behavior is exhibited. You are removing a positive thing from your childs life as a punishment.
Here are subtle differences between positive and negative punishments:
| Positive punishment | Negative punishment |
|---|---|
| Positive punishment is giving something negative to the child, such as spanking or scolding them. | Negative punishment is taking away something nice from the child, such as cutting off their TV time or playtime. |
| Differentiation through examples: | |
| The boy breaks the toy or dismantles the toy parts and the parent spanks him every time he does that. | Two brothers have a fight over a toy as to who gets to play with it first; the mother takes the toy away. |
| The teenagers phone rings during the class, and he is scolded for talking over the phone during the class. | The teenagers phone rings during a session. As a result, the phone is taken away from him. |
| The girl wears her favorite accessories to school; the principal reprimands her in front of everyone for not following the rules. | The girl enjoys her music class, but she misbehaves during the class; the teacher dismisses her from the class for misbehaving. |
Everyday Connection: Behavior Modification In Children
Parents and teachers often use behavior modification to change a childs behavior. Behavior modification uses the principles of operant conditioning to accomplish behavior change so that undesirable behaviors are switched for more socially acceptable ones. Some teachers and parents create a sticker chart, in which several behaviors are listed . Sticker charts are a form of token economies, as described in the text. Each time children perform the behavior, they get a sticker, and after a certain number of stickers, they get a prize, or reinforcer. The goal is to increase acceptable behaviors and decrease misbehavior. Remember, it is best to reinforce desired behaviors, rather than to use punishment. In the classroom, the teacher can reinforce a wide range of behaviors, from students raising their hands, to walking quietly in the hall, to turning in their homework. At home, parents might create a behavior chart that rewards children for things such as putting away toys, brushing their teeth, and helping with dinner. In order for behavior modification to be effective, the reinforcement needs to be connected with the behavior; the reinforcement must matter to the child and be done consistently.
Figure 1. Sticker charts are a form of positive reinforcement and a tool for behavior modification. Once this little girl earns a certain number of stickers for demonstrating a desired behavior, she will be rewarded with a trip to the ice cream parlor.
Also Check: Geometry Chapter 4 Practice Workbook Answers
Primary And Secondary Reinforcers
Rewards such as stickers, praise, money, toys, and more can be used to reinforce learning. Lets go back to Skinners rats again. How did the rats learn to press the lever in the Skinner box? They were rewarded with food each time they pressed the lever. For animals, food would be an obvious reinforcer.
What would be a good reinforce for humans? For your daughter Sydney, it was the promise of a toy if she cleaned her room. How about Joaquin, the soccer player? If you gave Joaquin a piece of candy every time he made a goal, you would be using a primary reinforcer. Primary reinforcers are reinforcers that have innate reinforcing qualities. These kinds of reinforcers are not learned. Water, food, sleep, shelter, sex, and touch, among others, are primary reinforcers. Pleasure is also a primary reinforcer. Organisms do not lose their drive for these things. For most people, jumping in a cool lake on a very hot day would be reinforcing and the cool lake would be innately reinforcingthe water would cool the person off , as well as provide pleasure.
What Is A Negative Punishment In Psychology
Negative punishment is an important concept in B. F. Skinners theory of operant conditioning. In behavioral psychology, the goal of punishment is to decrease unwanted behavior. In the case of negative punishment, it involves taking something good or desirable away to reduce the occurrence of a particular behavior.
You May Like: Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet
What Is Negative Punishment
Negative punishment happens when a certain reinforcing stimulus is removed after a particular undesired behavior is exhibited, resulting in the behavior happening less often in the future.
The following are some examples of negative punishment:
- A child kicks a peer , and is removed from his/her favorite activity
- A child yells out in class , loses a token for good behavior on his/her token board; that could have later be cashed in for a prize.
- A child fights with her brother and has her favorite toy taken away .
With punishment, always remember that the end result is to try to decrease the undesired behavior. Positive punishment involves adding an aversive consequence after an undesired behavior is emitted to decrease future responses. Negative punishment includes taking away a certain reinforcing item after the undesired behavior happens in order to decrease future responses.
It should be noted that research shows that positive consequences are more powerful than negative consequences for improving behavior. Therefore, it is always suggested that these interventions be tried prior to negative consequences. Do you have any experiences with reinforcement or punishment that you would like to share in the comment section below?
So Should I Try These Types Of Punishments Or Not
Like any other form of discipline or so many aspects of raising responsible children, positive and negative punishments only work as well as they are administered. If the punishment follows the guidelines listed above and also includes thoughtful discourse and relevant reinforcement techniques, then it has a better chance of doing what it is intended to do: deter unwanted behavior.
When administering punishment or any other form of discipline, it is important to focus on the behavior as undesirable rather than the child. Consider the difference between saying, You are a bad girl and Im disappointed that a child of mine would act that way, and That behavior is not acceptable, and your friend is hurt because you kicked her.;
In the first example, the words are focused on two people the child and the parent. The child is bad, the parent is disappointed that they have a bad child. In the second example, the focus is on the action and the immediate result of that unacceptable action, i.e., that the friend is hurt. This distinction is important, and although it may seem like semantics, words and the actions we tie to them resonate in children and affect how they perceive themselves, their parents and caregivers, and the world in general.;
Recommended Reading: Fsa Algebra 1 Eoc Review Functions And Modeling-answer Key
Making Connections Between Theory And Reality
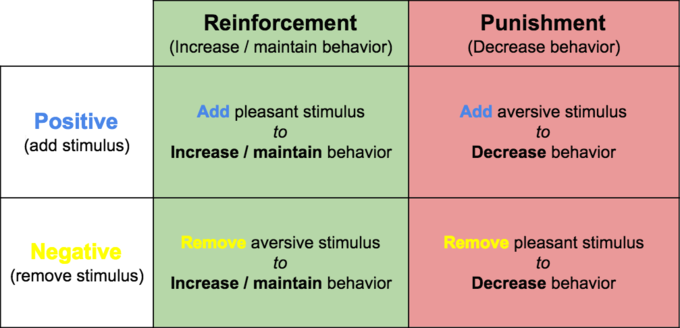
Punishment is considered an adverse event that decreases the behavior that it follows. Operant conditioning is conditioning in which the subject forms associations between behaviors and resulting events. Punishment is used in operant conditioning to decrease the likelihood of an unwanted behavior. Its different than positive and negative reinforcement, which is also used in operant conditioning, because reinforcement aims to increase a behavior whereas punishment aims to diminish a behavior. The terms positive and negative in regards to punishment can be confusing because they do not mean good or bad. ;Positive punishment involves presenting an aversive stimulus after a behavior as occurred. In other words adding a stimulus after the undesired behavior occurs that discourages the behavior from happening again. ;This would be like getting a parking ticket after parking illegally. The parking ticket is a stimulus that is added to reduce the unwanted behavior of illegally parking. Negative punishment is taking away a desirable stimulus after an unwanted behavior as occurred. This would be like taking away a video game from a kid who talked back to his parents. The kid would then no longer talk back to his parents for fear of losing his video game, thus decreasing the unwanted behavior.
Positive Reinforcement In The Workplace
As noted earlier, positive reinforcement is a common practice in the workplace, where the promise of monetary rewards, increased responsibilities, and higher status act as effective motivators for desired behavior.
A recent study on positive reinforcement in organizations provided further evidence that it is an effective method for employees; both intrinsic rewards and extrinsic rewards were effective motivators and correlated positively with the efficiency and effectiveness of employees .
Punishment can also be an effective tool for improving efficiency and effectiveness, but it often has the downside of reducing morale; on the other hand, verbal positive reinforcement is effective in both increasing the likelihood of desired behavior and encouraging enthusiasm, engagement, and satisfaction among staff .
Read Also: Exponential Growth And Decay Common Core Algebra 1 Homework Answer Key
Positive Reinforcement In Psychology
- 27-02-2021
If you read our earlier piece on positive punishment, you know that there are different methods of teaching and instilling good habits and behaviors.
One of the most powerful and effective methods is one that youre probably at least somewhat familiar with: positive reinforcement.
Before you read on, we thought you might like to .These science-based exercises will explore fundamental aspects of positive psychology including strengths, values and self-compassion and will give you the tools to enhance the wellbeing of your clients, students or employees.
You can download the free PDF here.
Positive Reinforcement In The Classroom
One of our examples given for positive reinforcement was a teacher handing out gold stars to students who turn their work in on time; this is just one of the many ways positive reinforcement can be applied in the classroom.
Some teachers may choose to hand out stickers, others might be generous with their praise or high-fives, and others may hand out candy or other small treats when students behave appropriately.
Positive reinforcement can be extra effective in the classroom because of one important factor: social atmosphere, or peer pressure. Children often want to do the right thing and may get embarrassed if caught doing something wrong in front of their friends and peers. When there is a whole classroom of students watching, children are more receptive than usual to a reward.
If youre a teacher who would like to implement positive reinforcement in the classroom, keep these tips from the University of Minnesotas College of Education and Human Development in mind.
When choosing a reinforcer:
When delivering a reinforcer;
Don’t Miss: Homework 5 Angle Addition Postulate Answer Key
Pros & Cons Of Punishment
Punishment is widely used in ABA therapy to help clients, but it is not without some controversy.
An article in Psychology Today warns that if applied improperly or inconsistently, the client will not understand the connection between their behavior and the imposition of the punishment. Furthering the punishment at this point could be very traumatic for the client.
Additionally, while the concept of punishment has a very distinct meaning in psychology, that meaning is lost in translation when people outside the field hear the word. This can set a very inaccurate and misleading tone for the therapy, creating a significant barrier that some parents might not be willing to cross.
Research And Studies: 5 Interesting Facts And Statistics
We know that positive reinforcement is effective in encouraging the behavior we want to see, but the findings get even more interesting when we dive a little deeper into how and why it works. Check out these 5 fascinating facts and statistics about positive reinforcement that we have learned from research on the subject:
To see more information and find sources for some of these facts,;.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4