Other Ways To Classify Plant Tissue
There are other ways to classify the basic plant tissue types, if the above separation seems too complicated. Some choose to classify three types of plant tissue, ground tissue, vascular tissue, and dermal tissue. This is basically the same as above, although it separates the epidermis and related tissue into the dermal category. The remaining tissues which are not vascular, it refers to as ground tissue.
Another way to classify plant tissue is based on its function. Certain tissues are only used for the purposes of photosynthesis and growth. Theses tissues can be referred to as vegetative tissue. The more specialized organs of the plant, such as flowers, fruits, and seeds, are all reproductive tissue. This method of classifying plant tissues is often used by those interested in plant genetics and reproduction, as these forms of the plant are often vastly different, genetically speaking, than the vegetative portions of the plant. Plants have a life-cycle which exhibits the alternation of generations, in which the internal portions of the flower are actually small, multicellular organisms differing genetically from the parent plant. For this reason, some scientists choose to view these tissues as separate.
Aging Changes In Organs Tissue And Cells
All vital organs begin to lose some function as you age. Aging changes occur in all of the body’s cells, tissues, and organs, and these changes affect the functioning of all body systems.
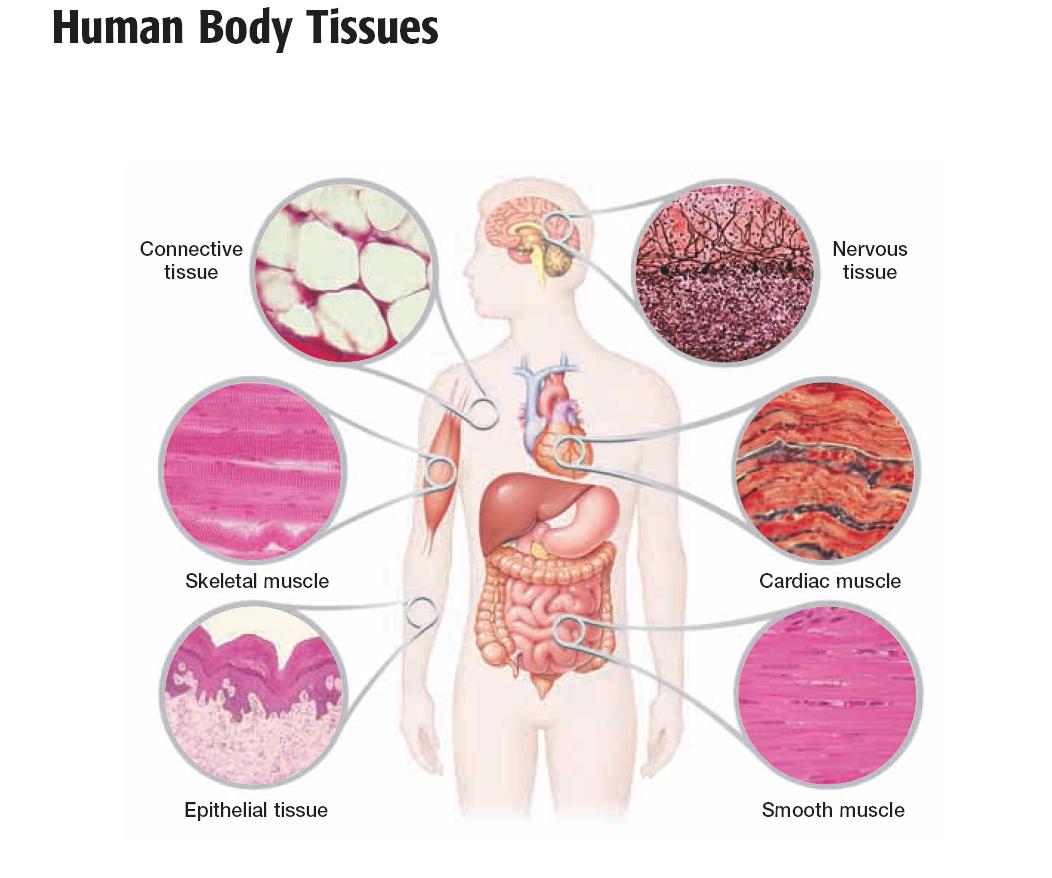
Living tissue is made up of cells. There are many different types of cells, but all have the same basic structure. Tissues are layers of similar cells that perform a specific function. The different kinds of tissues group together to form organs.
There are four basic types of tissue:
Connective tissue supports other tissues and binds them together. This includes bone, blood, and lymph tissues, as well as the tissues that give support and structure to the skin and internal organs.
Epithelial tissue provides a covering for superficial and deeper body layers. The skin and the linings of the passages inside the body, such as the gastrointestinal system, are made of epithelial tissue.
Muscle tissue includes three types of tissue:
- Striated muscles, such as those that move the skeleton
- Smooth muscles , such as the muscles contained in the stomach and other internal organs like the female uterus
- Cardiac muscle, which makes up most of the heart wall
Nerve tissue is made up of nerve cells and is used to carry messages to and from various parts of the body. The brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves are made of nerve tissue.
AGING CHANGES
Many tissues lose mass. This process is called atrophy. Some tissues become lumpy or more rigid.
AGING THEORY
Atrophy:
Hypertrophy:
How Do Tissue Engineering And Regenerative Medicine Work
Cells are the building blocks of tissue, and tissues are the basic unit of function in the body. Generally, groups of cells make and secrete their own support structures, called extra-cellular matrix. This matrix, or scaffold, does more than just support the cells it also acts as a relay station for various signaling molecules. Thus, cells receive messages from many sources that become available from the local environment. Each signal can start a chain of responses that determine what happens to the cell. By understanding how individual cells respond to signals, interact with their environment, and organize into tissues and organisms, researchers have been able to manipulate these processes to mend damaged tissues or even create new ones.
The process often begins with building a scaffold from a wide set of possible sources, from proteins to plastics. Once scaffolds are created, cells with or without a cocktail of growth factors can be introduced. If the environment is right, a tissue develops. In some cases, the cells, scaffolds, and growth factors are all mixed together at once, allowing the tissue to self-assemble.
Also Check: Does Organic Chemistry Have Math
Patient Discussion About Tissue
Q. I could feel hard tissues in my breasts.I suspect it the other way, any idea what it may be? I could feel hard tissues in my breasts. While reading article about breast cancer, I happened to note that these may be simple cyst and there is nothing to worry. My friend too had cyst and treated by the doctor with needle by removing the fluid out. But I suspect it the other way, any idea what it may be?
A.
Q. I want to get cure for asthma and develop my cardiac tissue. What is the best exercise for me to do? This is Daron, 20/m. I have had asthma since I was 3 yrs old, and suffer from exercise induced asthma as well as weather and food. Running is the worst thing that induces asthma in me. I want to get cure for asthma and develop my cardiac tissue to ensure fitness. What is the best exercise for me to do? I will be very thankful if I get suitable suggestion or advice..
A.
Q. I developed an AV Fistula after a heart catherization procedure. I am bleeding through the tissues in left arm I am on coumadin, but currently have a lower than usual INR. Corrective surgery was scheduled for yesterday, but had to be delayed. I am concerned that I have a large amount of blood bleeding though the tissues right under the skin in my left arm. Should I seek immediate medical attention? The bleeding is over approximately a 3 and 1/2″ area on my left arm. Came about in a period of a few minutes.
A.
How Do Tissue Engineering And Regenerative Medicine Fit In With Current Medical Practices
A biomaterial made from pigs’ intestines which can be used to heal wounds in humans. When moistened, the material, which is called SIS, is flexible and easy to handle.Source: Stephen Badylak, University of Pittsburgh.
Currently, tissue engineering plays a relatively small role in patient treatment. Supplemental bladders, small arteries, skin grafts, cartilage, and even a full trachea have been implanted in patients, but the procedures are still experimental and very costly. While more complex organ tissues like heart, lung, and liver tissue have been successfully recreated in the lab, they are a long way from being fully reproducible and ready to implant into a patient. These tissues, however, can be quite useful in research, especially in drug development. Using functioning human tissue to help screen medication candidates could speed up development and provide key tools for facilitating personalized medicine while saving money and reducing the number of animals used for research.
Read Also: What Does S Stand For In Chemistry
Examples Of Plant Tissues
What is tissue in plant biology? We already know that biological tissue is made up of a number of cells performing a specific function. In plants, tissues are similarly made up of cells that perform a particular function. Below are some of the examples of plant tissues that perform a particular function. For example, the plant epidermis is the tissue that renders protection. The ground tissues are the tissues consisting of fundamental plant cells that perform a distinct function. The vascular tissues are the plant tissues involved in the transport of nutrients throughout the plant body. Lets take a closer look at them below.
Interplay Between Absorption And Scattering In Turbid Media
Biological tissue is strongly scattering for optical radiation. This fact leads to two major problems in the application of laser techniques in biomedicine. 1) The scattering results in the optical pathlength through the medium investigated being undefined part of the light travels shorter distances, part substantially longer distances. Thus, the Beer-Lambert law as stated in Eq. 10.3 is no longer valid. 2) The strong multiple scattering leads to blurring of images taken through tissue layers.
In analytical chemistry the turbidity of a sample, i.e. a pharmaceutical preparation, leads to difficulties in a direct assessment of drug constituent concentrations because of the scattering. Classical spectroscopic measurements are therefore combined with multivariate techniques, which, after calibration with known samples, still provide possibilities for quantitative analysis.15
As an alternative, launching light into a medium and detecting emerging light at successively increasing distance from the injection site can yield separate information on absorption and scattering however, only when certain assumptions are fulfilled.18 Further, it was noted by Bigio et al. that, for a particular magic separation between injection and detection points, absorption data become largely independent of scattering,19 making the construction of relatively simple tissue diagnostic probes possible.
Y.L. Chan, … N.M. King, in, 2012
Also Check: Geometry 3.5 Worksheet Answers
Examples Of Tissue In A Sentence
tissuetissuetissuestissuetissue Glamourtissue San Diego Union-Tribunetissue USA TODAYtissue clevelandtissue Smithsonian Magazinetissue altissueThe Courier-JournaltissueSmithsonian Magazine
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ’tissue.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
Viewed From The Surface
Lab-2 28
The image to the left shows a model of pseudostratified columnar epithelium. This type of tissue consists of a single layer of cells resting on a noncellular basement membrane that secures the epithelium. The tissue appears stratified because the cells are not all the same height and because their nuclei are located at different levels. Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium lines the trachea and larger respiratory passage ways.
Lab-2 29
Skeletal muscle is the most abundant type of muscle tissue found in the vertebrate body, making up at least 40% of its mass. Although it is often activated by reflexes that function in automatically in response to an outside stimulus, skeletal muscle is also called voluntary muscle because it is the only type subject to conscious control. Because skeletal muscle fibers have obvious bands called striations that can be observed under a microscope, it is also called striated muscle. Note that skeletal muscle cells are multinucleate, that is, each cell has more than one nucleus.
Lab-2 30
Lab-2 31
Cardiac muscle is striated like skeletal muscle but adapted for involuntary, rhythmic contractions like smooth muscle. The myofibrils are transversely striated, but each cell has only one centrally located nucleus. Note the dark blue transverse bands on the model called intercalated disks that mark the boundaries between the ends of the muscle cells. These specialized junctional zones are unique to cardiac muscle.
Lab-2 32
Lab-2 33
Read Also: Find The Value Of Each Variable Geometry
What Are Tissue Engineering And Regenerative Medicine
A mini bioengineered human liver that can be implanted into mice. Source: Sangeeta Bhatia, MIT
Tissue engineering evolved from the field of biomaterials development and refers to the practice of combining scaffolds, cells, and biologically active molecules into functional tissues. The goal of tissue engineering is to assemble functional constructs that restore, maintain, or improve damaged tissues or whole organs. Artificial skin and cartilage are examples of engineered tissues that have been approved by the FDA however, currently they have limited use in human patients.
Regenerative medicine is a broad field that includes tissue engineering but also incorporates research on self-healing where the body uses its own systems, sometimes with help foreign biological material to recreate cells and rebuild tissues and organs. The terms tissue engineering and regenerative medicine have become largely interchangeable, as the field hopes to focus on cures instead of treatments for complex, often chronic, diseases.
This field continues to evolve. In addition to medical applications, non-therapeutic applications include using tissues as biosensors to detect biological or chemical threat agents, and tissue chips that can be used to test the toxicity of an experimental medication.
Function Of Muscle Tissue
Muscle tissue functions as a single unit, and is often connected to the same nerve bundles. A nerve impulse traveling from the brain or another outside signal tells the muscle to contract. The nerve impulse is transferred almost instantaneously to all the nerve cells in the muscle tissue, and the entire muscle contracts.
At the cellular level, each muscle cell has a complex of proteins containing actin and myosin. These proteins slide past one another when the signal to contract is received. The filaments are connected to the ends of the cells, and as they slide past one another, the cell contracts in length. A single cell can contract up to 70% in length, which shortens the entire muscle when contraction happens. Muscle tissue can be used to move bones, compress chambers, or squeeze various organs. These different types of muscle tissue are discussed below.
Don’t Miss: What Is Magnitude Of Displacement In Physics
Key Takeaways: Tissue Definition In Biology
- A tissue is a group of cells with the same origin that serve a similar function.
- Tissues are found in animals and plants.
- The four main types of animal tissues are connective, nervous, muscle, and epithelial tissues.
- The three main tissue systems in plants are the epidermis, ground tissue, and vascular tissue.
Types Of Plant And Animal Tissues
Steve Gschmeissner / Getty Images
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
In biology, a tissue is a group of cells and their extracellular matrix that share the same embryonic origin and perform a similar function. Multiple tissues then form organs. The study of animal tissues is called histology, or histopathology when it is concerned with diseases. The study of plant tissues is called plant anatomy. The word “tissue” comes from the French word “tissu,” which means “woven.” French anatomist and pathologist Marie François Xavier Bichat introduced the term in 1801, stating that body functions could be understood better if they were studied at the level of tissues rather than organs.
You May Like: What Are Lysosomes In Biology
Types Of Animal Tissues
Animal tissues are grouped into four types:
- Connective Tissue
- Epithelial Tissue
The collection of tissues are joined in structural units to serve a standard function of organs. The primary purpose of these four types of tissue differs depending on the type of organism.
For example, the origin of the cells comprising a particular tissue type also differs.
The Modified Beerlambert Law
Biological tissue is a complex heterogeneous medium comprising multiple absorbers and scatterers . The generic BeerLambert law does not consider the scattering effect, hence is not valid in the biological medium. The law was corrected for the scattering and has been extensively used for applications in near-infrared spectroscopy by Delpy and his team .
In an absorption only medium, the sample thickness equals to the optical pathlength . However, in a scattering-absorbing medium like tissue, the optical pathlength is not equal to the material thickness, rather related by a multiplicative term known as the differential pathlength factor DPF . The differential pathlength factor is a parameter dependent on the optical wavelength and the tissue anatomy . It has been found that the value of a DPF is always greater than 1 which means that the optical pathlength in tissue is always higher than the source-detector separation.
The modified BeerLambert law defines the absorbance of light through a scattering-absorbing medium at a certain wavelength using the following equations:
Melissa K. McHale, … Jennifer L. West, in, 2013
Don’t Miss: Is High School Chemistry Required For College
What Are Tissues
In simple terms, tissue can be defined as a group of cells with similar shape and function are termed as tissues. They form a cellular organizational level, intermediate between the cells and organ system. Organs are then created by combining the functional groups of tissues.
Let us learn in detail about the types of tissues in different organs.
The study of tissue is known as histology and study of disease-related to tissue is known as histopathology. The standard tools for studying tissues is by embedding and sectioning using the paraffin block.
What Are Nih
Research supported by NIBIB includes development of new scaffold materials and new tools to fabricate, image, monitor, and preserve engineered tissues. Some examples of research in this area are described below.
- Controlling stem cells through their environment:For many years, scientists have searched for ways to control how stems cells develop into other cell types, in the hopes of creating new therapies. Two NIBIB researchers have grown pluripotent cellsstem cells that have the ability to turn into any kind of cellin different types of defined spaces and found that this confinement triggered very specific gene networks that determined the ultimate fate for the cells. Most other medical research on pluripotent stem cells has focused on modifying the combination of growth solutions in which the cells are placed. The discovery that there is a biomechanical element to controlling how stem cells transform into other cell types is an important piece of the puzzle as scientists try to harness stems cells for medical uses.
Human Livers in Mice Aid Therapeutics
Don’t Miss: What Is Work Measured In Physics