Where Is Rome Located
The historic city of Rome is located in the central-western part of the Italian Peninsula on the banks of the Tiber River in the Lazio region of Italy. The city is the capital of Italy and also its biggest and most populated metropolis hosting 2.9 million residents within an area of 1,285 square km. Vatican City, a country, is located within the boundaries of Rome making it the only example of a country within a city.
The Tiber River Of Rome
The Tiber River is a historic river in Europe, famous for the city of Rome that is located on its banks. The Tiber River is the second longest river in the country after the River Po. The river traces its origin to the slope of Monte Fumaiolo from where it flows for 405 km in a generally southern direction and drains into the Tyrrhenian Sea near Ostia Antica. According to some ancient writers, the Tiber River was originally known as Albula but renamed Tiberis after a king of Alba Longa, King Tiberius, died by drowning in the river. The river has played a vital role in the birth and expansion of the city of Rome as will be explained in the below sections. Another river, the Aniene also crosses Rome. The river joins the Tiber north of the historic center of the city.
How Did Geography Play An Important Role In The Development Of Rome
The fertile soil of the Po and Tiber River Valleys allowed Romans to grow a diverse selection of crops, such as olives and grains. The Mediterranean Sea, on which Rome was centrally located, further heightened Romans ability to trade with other societies, increasing Romes economic strength as a result.
Recommended Reading: Core Connections Algebra Chapter 1 Answers
How Did The Roman Empire Expand Its Influence
Romes central location attracted immigrants and traders from all parts of the ancient Mediterranean world. According to The Flow of History, the diversity of the early Roman state helped it expand its influence. The Romans were unusually adaptable and willing to change their strategy when compared to the rest of the ancient world.
What Effect Did The Alps Have On Rome
4.7/5AlpsRome
Similarly, you may ask, why were the Alps important to ancient Rome?
Two major group of mountains found in Italy were very important on the development of ancient Rome. The Alps, Europe’s highest mountains, separated the Italian peninsula from the rest of the continent. These two groups of mountains helped to protect Rome from outside attacks.
Subsequently, question is, how did Rome’s location affect its early history? It determined where Romans settled and what foods they could grow. Its location in the middle of the Mediterranean region made it easy for Rome to control surrounding areas.
Keeping this in consideration, what was the impact of Italy’s geography on the development of Rome?
One benefit the Romans had over these other civilizations is that they were centrally located on the Mediterranean Sea and had sufficiently developed naval technology in order to take advantage of their location. Rome is located on the Italian peninsula and has access to both the Mediterranean Sea and Tiber River.
How did the Romans advance the system of coins first introduced by the Lydians?
They made coins heavy enough to make them hard to steal. They minted coins in different denominations with a set value for each. They signed trade agreements so that their coins would be used more widely.
Recommended Reading: Who Is Paris Jacksons Biological Father
The Geography Of Rome
Geography is an integral part of the development of ancient civilizations. Rome is one of the most powerful civilizations whose empire ruled Europe for over 1,000 years. Several key geographical features in the Italian peninsula provided opportunities for the Roman civilization to thrive. Rome began as a small village near the Tiber River in Italy on a peninsula close to the Mediterranean Sea. The city was also far enough inland to provide some protection from the sea.
The Tiber River was a source of freshwater and rich soil needed to support the development of people, animals, and crops of Rome. It is the second longest river in Italy. Rome is located East of the river. It begins in the Apennine mountains and flows to the Tyrrhenian Sea. The river provided easy transportation and the rivers valley had vast land for farming. The river also served as a defense system against attacks from the other side of the river.
Being close to the Mediterranean Sea allowed Rome to trade with cities in Greece, northern Europe, and North Africa. It also helped them in conquering new lands. Inspired by the Phoenician’s shipbuilding, the Romans used their designs to build ships. They eventually built a navy which assisted them in conquering neighboring territories. Romans eventually took control of all of the shores of the Mediterranean. The sea was also a rich source of food for the civilization.
Why Was Rome So Close To The Ocean
The city of Rome is set far back from the ocean, and few other Roman cities offered easier access to ocean. Due to this quirk of geography, the Romans concentrated on building up their land-based forces. Romes geography forced the Romans to rely on overland transportation much more than other empires.
Don’t Miss: Figure And Ground Psychology
How Geography Helped Contain Roman Imperial Ambitions
Rome continued its conquests until further military expansion put a strain on Roman manpower and resources.
- The Sahara desert kept Rome from expanding too far into Africa, while the thick forests stopped Roman attempts to conquer Northern and Central Europe.
- When Emperor Augustus attempted to conquer the region Germania, three entire legions of Romans were massacred at the Battle of Teutoberg Forest.
- The Germanic tribesmen were not as well trained or equipped as the Roman Legionaries, but they had the advantage of knowing the dense forest and how to ambush foes using hit and run guerrilla tactics.
- Likewise, conquering Persia to the East proved difficult.
- A combination of long supply lines, hostile deserts, and powerful eastern enemies prevented Rome’s eastward expansion into Mesopotamia.
- When Roman Consul Marcus Crassus attempted an invasion of the Parthian Empire, he and his seven legions were butchered in the Battle of Carrhae. This was one of the worst defeats in Roman military history.
Top Best Answers To The Question How Did The Geography Of The Roman Empire Affect Its Economy
- The resources are also available at the top of the page. The physical geography of the Roman Empire directly contributed to its economic and military strength. In the winter, the snowy Alps blocked the passage from the rest of Europe to Rome, protecting Rome from invasion.
Those who are looking for an answer to the question «How did the geography of the roman empire affect its economy?» often ask the following questions:
Don’t Miss: What Does Abiotic Mean In Biology
Territorial Expansion And Domination In The Western Mediterranean
Despite some early trade with the Greek colonies in Italy, Rome was far from being a preeminent trading power. However, as Rome grew as an Empire, it came into conflict with the trading giant of the Western Mediterranean, the Republican Empire of Carthage .Punic Wars –
- After conquering Central and Southern Italy, Rome set its sights on Sicily, an agriculturally rich island separated by a small channel from the southern tip of Italy. However, the Carthaginian Empire already claimed the island.
- The two, inevitably, came into conflict. It was in this conflict that Rome was required to build a sizable navy to compete with Carthage and began to emerge as a major power, not only in the Italian peninsula, but also in the broader Mediterranean Sea.
- Prior to the Punic Wars, Rome had never seen conflict away from the mainland therefore, it had to build its naval power from scratch. This articledetails the Roman Navy’s rise to dominance.
- When Rome finally conquered and colonized Carthage’s capital , it eliminated a powerful trading Empire but gained it’s territories, becoming the successor to its trading legacy.
- The Punic Wars and the conquests of Sicily and Carthage were of enormous importance to the expansion of Roman trade, Naval and Economic power. With the destruction of Carthage, Rome became the preeminent Empire in the Western Mediterranean.
- See also Standard 7.43 for engineering contributions of Roman civilization
How Did Geography Help The Romans Conquer Italy
4.7/5helpedRomeItalianRomans
Furthermore, how did geography help the Romans prosper?
Instead, Rome developed about 15 miles from where the Tiber River empties into the Mediterranean Sea. This distance provided Rome with additional protection, because invaders had to move inland from the coast to reach the city.
One may also ask, how did Rome’s location help the Latins conquer Italy? Rome’s location offered several advantages. One of the advantages was the protection of the hills and mountains found in the peninsula. Two major group of mountains found in Italy were very important on the development of ancient Rome. The Apennine Mountains run north to south along the Italian peninsula.
One may also ask, how did Italy’s geography influence the Roman Empire?
One benefit the Romans had over these other civilizations is that they were centrally located on the Mediterranean Sea and had sufficiently developed naval technology in order to take advantage of their location. Rome is located on the Italian peninsula and has access to both the Mediterranean Sea and Tiber River.
What was the geography of ancient Rome?
Geography/locationRome was built on seven hills at the bank of the tiber river. Rome is around the center of the italian peninsula. Italy had many hills and mountains but were easier to travel over than the mountains on Greece.
You May Like: Movement In Geography Examples
How Did Geography Influence Rome
The fertile soil of the Po and Tiber River Valleys allowed Romans to grow a diverse selection of crops, such as olives and grains. The Mediterranean Sea, on which Rome was centrally located, further heightened Romans ability to trade with other societies, increasing Romes economic strength as a result.
How Did Geography Affect Where Rome Was Located
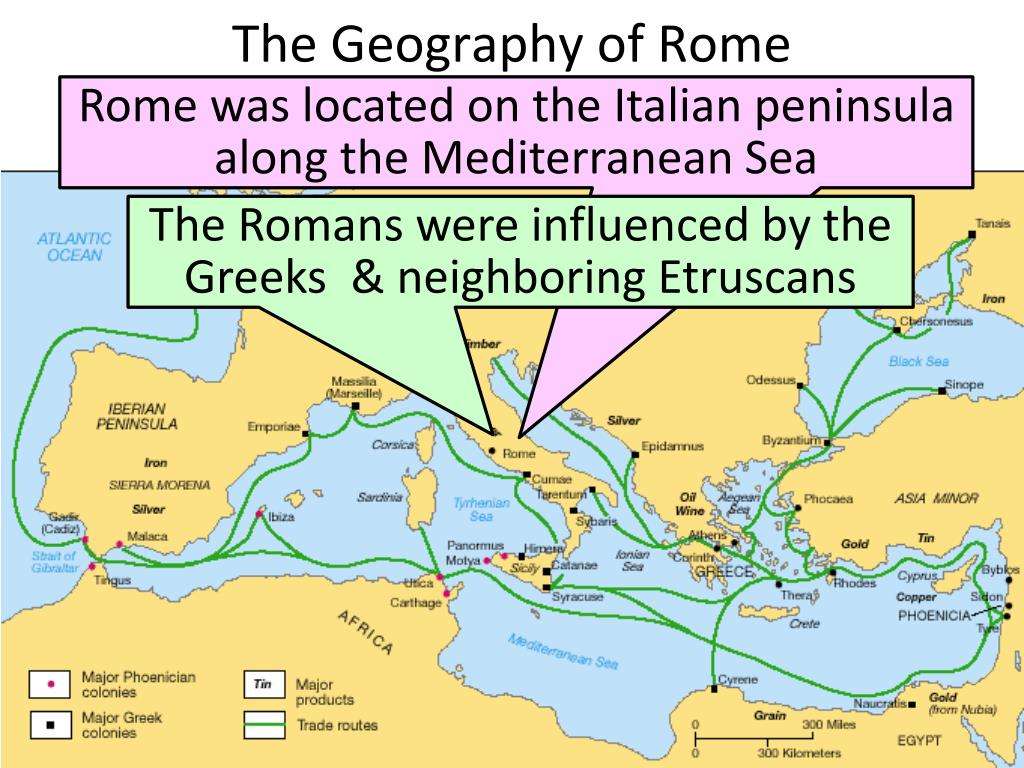
Rome was located near the Alps and was on a steep hill, so it was tougher for invasions to occur. Rome also wasn’t close to the sea, so pirate attacks weren’t imminent.What was most useful in the early days of Rome was that she lied by the only Ford on the river Tiber. Since this river run from the Apennines Mountains to the sea, this location made early Rome the main north-south communication point in the region, which was useful for trade. When Rome became more engaged in sea trade, the Tiber provided a navigable link with the sea. The third king of Rome , built a port on the river in the 5th century BC. The Romans built a port at Ostia, on the coast, by the mouth of the river probably in the 3rd century BC. Large ships which sailed across the Mediterranean unloaded their goods here. The goods were then loaded on smaller ships which reached Rome by sailing up the Tiber. This was vital to secure the massive amount of imports which Rome needed to supply his large population.
Rome was also on hills . People liked to live on hills because they gave better protection against raids. The hills also were made of volcanic rock, which provided good building material. Rome was also quite close to the Apennines which have plenty of water sources. The water was taken to Rome by aqueducts.
Read Also: Why Are Michael Jackson’s Kids White
Describe How The Geography Of Italy Affect Roman Civilization
- How did geography affect where Rome was located? Rome was located 15 mile sup the Tiber River in order to protect the city from raid by pirates. The river provided a source of water and a waterway to the Mediterranean Sea . The city was built on seven steep hills that allowed Romans to defend the city against enemies.
Controlling The High Ground
Its first settlers built the city of Rome atop seven different hills, according to Eduplace, a resource for history teachers. Building the city on high ground forced any attacking army to fight its way uphill, giving the defending forces a major advantage. The Romans understood this advantage and built fortresses on top of several of the hills. For example, Muses’ Realm reports that Capitoline Hill was the seat of Rome’s government and its largest fortress. Rome’s naturally defenses made the city almost immune to attack, a feature that allowed the city to grow and ultimately dominate its neighbors.
Read Also: Chapter 3 Test Form 2c Answers
How Did Geography Help Rome Grow
The fertile soil of the Po and Tiber River Valleys allowed Romans to grow a diverse selection of crops, such as olives and grains. This allowed the empire to have a food surplus to feed its population and trade with other societies. The empire also used the resulting wealth to expand its military strength.
Bridges Across The Roman Empire
Roman Alcántara Bridge across the River Tajo, Cáceres Province, Extremadura, Spain
- One of the lasting legacies of the Roman Empire is their infrastructure. The traces of Roman roads are found all over the area of the former empire. Along these grand routes are bridges that prove the Roman intelligence and strength.
- While Roman roads are found throughout the entire footprint of the empire, roman bridges are as well
- An interactive map created by Harvard allows users to view certain structures and components of the Empire, including verified Roman bridges:
- Northernmost bridge: Trier, Germany
- Easternmost bridge: Outside of Termez, Uzbekistan
- Southernmost bridge: Fars Province, Iran
- Many of these bridges are still in use today, while ruins of the others stand as landmarks of the empire’s presence across Europe, Northern Africa, and Asia Minor.
- Constructed between 104 and 106 AD, the Alcántara Bridge in Alcántara, Spain has withstood nearly two millennia of the elements and attempted destruction. After minor restorations, the bridge is still used today and can withstand all modern vehicles.
- These feats in infrastructure were responsible for the social, political, and economic connection of the vast empire
Aqueducts built by the Romans were one of the most impressive feats of ancient civilization.
- to play the construct your own aqueduct game
- to view an interactive tour of the famous Baths of Caracalla.
You May Like: Root Word Cyte
Geography And Topography Of Rome And The Roman Empire
No headers
As the title of one recent textbook of Roman history puts it, Roman history is, in a nutshell, the story of Romes transformation from village to empire.1 The geography and topography of Rome, Italy, and the Mediterranean world as a whole played a key role in the expansion of the empire but also placed challenges in the Romans path, challenges which further shaped their history.
Before it became the capital of a major empire, Rome was a village built on seven hills sprawling around the river Tiber. Set sixteen miles inland, the original settlement had distinct strategic advantages: it was immune to attacks from the sea, and the seven hills on which the city was built were easy to fortify. The Tiber, although marshy and prone to flooding, furthermore, provided the ability to trade with the neighboring city-states. By the mid-Republic, requiring access to the sea, the Romans built a harbor at Ostia, which grew to become a full-fledged commercial arm of Rome as a result. Wheeled vehicles were prohibited inside the city of Rome during the day, in order to protect the heavy pedestrian traffic. Thus at night, carts from Ostia poured into Rome, delivering food and other goods for sale from all over Italy and the Empire.
- This page has no tags.
How Did Geography Impact The Development Of Rome
Judson Altier asked, updated on January 3rd, 2022 Topic:
How did geography impact the development of Rome? The soil and the mild climate helped the Romans grow surplus olives and grain. Reliable food production allowed the population to grow, and the trade in olives and olive oil helped the Roman economy expand.
Either, how did geography affect where Rome was located?
How did geography affect where Rome was located? Rome was located 15 mile sup the Tiber River in order to protect the city from raid by pirates. The river provided a source of water and a waterway to the Mediterranean Sea. The city was built on seven steep hills that allowed Romans to defend the city against enemies.
As well as, how did the geography affect the development? Towns grew up along the rivers which had access to the sea. Rivers also provided protection from invaders. Farmers grew crops in the fertile fields that surrounded the towns. The lack of mountains was good for farming, but it made the towns easier to be invaded by enemies.
Suitably, how did the geography of Rome influence its development quizlet?
How did geography influence the origins and expansion of Rome? The Tiber river allowed access to the Mediterranean, but it was far enough inland that it protected Rome from invasions. The peninsula of Italy allowed trade and transportation to be easy.
How did the geography shape the political development of Rome?
23 Related Questions Answered
Read Also: Holt Mcdougal Geometry Book Answers
How Did Geography Help Rome Rise To Power
The Roman Empire dominated most of Europe and much of Africa and the Middle East for centuries. So great was the empire that it influences geopolitics even today. Often overlooked is the role that geography played in the great city’s rise to power. Several geographic advantages helped Rome to grow and ultimately dominate the known world.