Everyday Connection: Classical Conditioning At Stingray City
Figure 4. Kate holds a southern stingray at Stingray City in the Cayman Islands. These stingrays have been classically conditioned to associate the sound of a boat motor with food provided by tourists.
Kate and her husband Scott recently vacationed in the Cayman Islands, and booked a boat tour to Stingray City, where they could feed and swim with the southern stingrays. The boat captain explained how the normally solitary stingrays have become accustomed to interacting with humans. About 40 years ago, fishermen began to clean fish and conch at a particular sandbar near a barrier reef, and large numbers of stingrays would swim in to eat what the fishermen threw into the water this continued for years. By the late 1980s, word of the large group of stingrays spread among scuba divers, who then started feeding them by hand. Over time, the southern stingrays in the area were classically conditioned much like Pavlovs dogs. When they hear the sound of a boat engine , they know that they will get to eat .
As soon as Kate and Scott reached Stingray City, over two dozen stingrays surrounded their tour boat. The couple slipped into the water with bags of squid, the stingrays favorite treat. The swarm of stingrays bumped and rubbed up against their legs like hungry cats . Kate and Scott were able to feed, pet, and even kiss these amazing creatures. Then all the squid was gone, and so were the stingrays.
Timing Of Learned Behavior
Throughout the classical conditioning process, there are a number of different factors that can influence how quickly associations are learned. How much time that passes between presenting the initially neutral stimulus and the unconditioned stimulus is one of the most important factors in whether or not learning will actually occur.
The timing of how the neutral stimulus and the unconditioned stimulus are presented is what influences whether or not an association will be formed, a principle that is known as the theory of contiguity.
Examples Of An Unconditioned Stimulus Triggering An Unconditioned Response
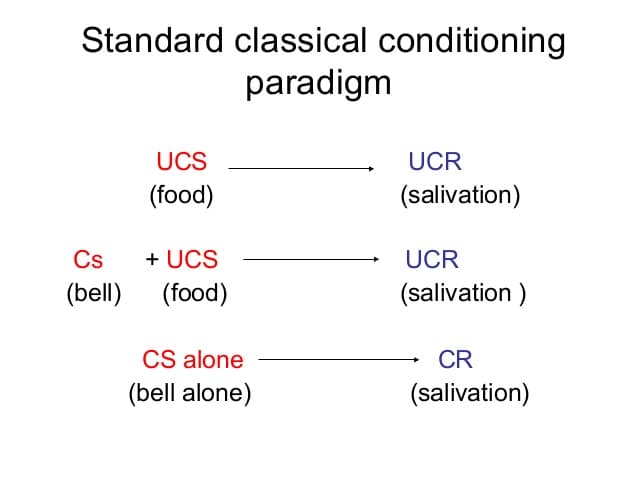
Russian physiologist, Ivan Pavlov, first discovered classical conditioning when he was feeding his dogs. The dogs would smell the food and automatically salivate. This natural response did not require any prior learning. So the foods smell was the UCS1.
So, how to find the unconditioned stimulus?
An UCS can trigger a response naturally. This response is a biological reaction. A person or animal usually does not have control over this behavior2.
Here are some examples of unconditioned stimulus.
Don’t Miss: Eoc Fsa Warm Ups Algebra 1 Answers
What Are Stimulus Equivalence Procedures
Stimulus Equivalence. Exists when a learner correctly identifies a symbolic relationship. between two or more non-identical stimuli without specific training on that relationship. In other words, the learner makes untrained but accurate connections. between stimuli.
Can I Take Phd Classes In The Same Term That I Am Defending My Masters Thesis
This depends on whether you are in the clinical program or not and whether the classes you want to take are restricted to the doctoral program.
For students in the clinical program, we may allow you to take restricted doctoral courses in the fall term only if you have your final Masters defense scheduled to take place in the month of September. This means that you need to have submitted your thesis and ROE to Grad Studies in July or August with an identified defense date on or prior to Sept. 30th. This is to ensure that students are not held back from enrolling in required doctoral courses when their thesis is complete but only the defense will occur in September.
Enrollment in these courses is not automatic and you will not be allowed to register until the thesis and ROE has been submitted you will need to inform the Grad Advisor regarding the specific courses you want to take in order to have this approved and for the Grad Secretary to be asked to remove the restrictions on the courses so that you can register.
Note that you will continue to be a Masters student in the fall term and will not enter the doctoral program until January.
There are no restrictions on non-clinical Masters students in regard to taking PhD classes as long as the student has the proper prerequisities. As always, consult your supervisor or the GA if you are not sure.
Read Also: What Does G Mean In Physics
Read Also: Lesson 4.5 Practice B Geometry Answers
Components Of Classical Conditioning
All classical conditioning examples and process must and does follow the basic principles of Classical conditioning. There are, in total, five major principles of classical conditioning. They are:
- AcquisitionIts the first step to classical conditioning method. This is the step by which an organism learns to association involved in the method.
- Stimulus GeneralizationGeneralization is understood as the process which leads an organism to produce behavior identical to the CR, when confronted with a stimulus similar to the CS.
- Stimulus DiscriminationThis is the process that explains the ability of an organism to learn the difference between different stimuli and respond only to the conditioned stimulus.
- ExtinctionExtinction is the process in which classical conditioning is undone, such that the subject does not produce CR in response to CS.
- Spontaneous RecoveryThe sudden response by an organism with CR in reaction to the stimulus is known as spontaneous recovery.
What Causes Long Philtrum
Femoral-facial syndrome , also known as femoral hypoplasia-unusual facies syndrome , is a rare and sporadic multiple congenital anomaly syndrome comprising bilateral femoral hypoplasia and characteristic facial features, such as long philtrum, thin upper lip, micrognathia with or without cleft palate.
Recommended Reading: Eoc Algebra 1 Practice Test 2015
The Difference Between Unconditioned Stimulus And Conditioned Stimulus
A neutral stimulus initially doesnt trigger any particular response. However, when a neutral stimulus is presented together with an UCS, an association can form.
Classical conditioning happens when a neutral stimulus is paired with an UCS repeatedly to create associated learning. The previously neutral stimulus becomes a conditioned stimulus and can trigger the same response as the UCS.
So initially, the neutral stimulus does not affect a specific behavior. But after repeatedly presented together with the UCS, it becomes a CS, and the person or animal subconsciously learns to react with the same response when its present. This response is then called a conditioned response .
For example, in Pavlovs experiments, he sounded a bell whenever he brought food to his dogs. After multiple repetitions, the dogs learned to expect food and naturally salivated when they heard the bells sound even when they did not see the food. When UCS was paired with a previously neutral stimulus , the neutral stimulus became a CS.
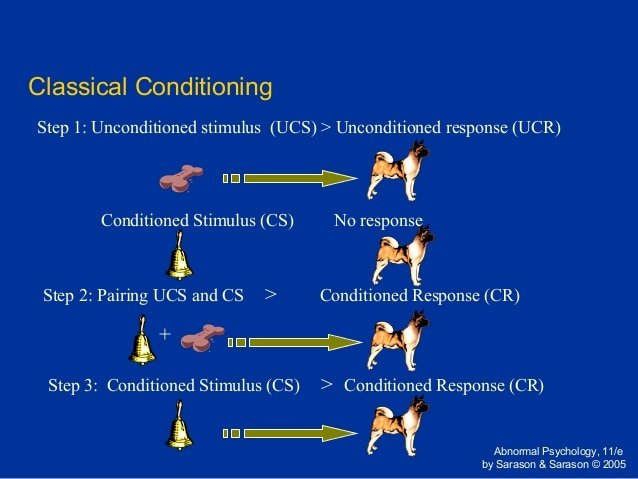
The Three Stages Of Classical Conditioning
The process of classical conditioning occurs in three basic stages:
Before Conditioning
At this stage, the UCS and CS have no relationship. The UCS comes up in the environment and naturally elicits a UCR. The UCR wasnt taught or learned, its a completely innate reaction. For example, the first time a person takes a ride on a boat they may become seasick . At this point, the CS is a neutral stimulus . It has yet to produce any kind of response because it hasnt been conditioned yet.
During Conditioning
During the second stage, the UCS and NS are paired leading the previously neutral stimulus to become a CS. The CS occurs just before or at the same time as the UCS and in the process the CS becomes associated with UCS and, by extension, the UCR. Generally, the UCS and CS must be paired several times in order to reinforce the association between the two stimuli. However, there are times when this isnt necessary. For example, if an individual gets sick once after eating a specific food, that food may continue to make them nauseous in the future. So, if the individual on the boat drank fruit punch right before getting sick , they could learn to associate fruit punch with feeling ill .
After Conditioning
Recommended Reading: Fsa Algebra 1
What Is Cs And Cr In Psychology
Conditioned Stimulus. In classical conditioning, a formerly neutral stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus , comes to produce a conditioned response. Once the beep has the capacity to elicit the salivation, it is now considered a conditioned stimulus .
One may also ask, what are some examples of classical conditioning in the classroom? There is a bell that rings before the lunch break in the classroom. Students learn to associate sound of the bell with food just like Pavlov dogs. Especially, if the kids are hungry and if they like the food that day then sound of the bell is enough to cause them to have watery mouth.
Simply so, what is UCS UCR CS and CR?
UCS = Automobile Accident UCR = Anxiety because of accident CS = Intersection CR = Anxiety about intersection. 2.
What are the 3 stages of classical conditioning?
The three stages of classical conditioning include: Before Conditioning, During Conditioning, and After Conditioning.
Classical Conditioning In The Classroom
The implications of classical conditioning in the classroom are less important than those of operant conditioning, but there is a still need for teachers to try to make sure that students associate positive emotional experiences with learning.
If a student associates negative emotional experiences with school, then this can obviously have bad results, such as creating a school phobia.
For example, if a student is bullied at school they may learn to associate the school with fear. It could also explain why some students show a particular dislike of certain subjects that continue throughout their academic career. This could happen if a student is humiliated or punished in class by a teacher.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
The Role Of Nature In Classical Conditioning
As we have seen in Chapter 1, Introducing Psychology, scientists associated with the behaviourist school argued that all learning is driven by experience, and that nature plays no role. Classical conditioning, which is based on learning through experience, represents an example of the importance of the environment. But classical conditioning cannot be understood entirely in terms of experience. Nature also plays a part, as our evolutionary history has made us better able to learn some associations than others.
Clinical psychologists make use of classical conditioning to explain the learning of a phobia a strong and irrational fear of a specific object, activity, or situation. For example, driving a car is a neutral event that would not normally elicit a fear response in most people. But if a person were to experience a panic attack in which he or she suddenly experienced strong negative emotions while driving, that person may learn to associate driving with the panic response. The driving has become the CS that now creates the fear response.
Stage : After Conditioning:
The pairing of UCS and CS will now result in a creation of new response CR from the organism. The UCR now becomes CR.
Classical Conditioning Example: Lets suppose that every time you are made to smell your favorite food, an alarm is also rung at the exact time. Its evident that you will feel hungry having smelled your favorite food. In this case, the alarm is the conditioned stimulus which will trigger hunger when paired with the smell of your favorite food .
Recommended Reading: Def Of Abiotic
Are Thin Lips Good For Kissing
Fuller lips improve the kissing experience, and also tend to make the mouth look somewhat vulva-ishanother erotic enhancement. Thin lips are generally considred a turnoff, regardless of race, while fuller lips are considered attractive in both genders. Many whites and Orientals also have full lips.
How Classical Conditioning Works
In order to understand how more about how classical conditioning works, it is important to become familiar with the basic principles of the process. Classical conditioning involves forming an association between two stimuli resulting in a learned response. There are three basic phases of this process.
Read Also: What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Ccl4
Does Ucr Have A Good Psychology Program
Graduates of the UCR School Psychology Program are well prepared and have in-demand skills to promote positive outcomes for students, their families, educators, and school systems. Approximately 75% of graduates work in various applied settings and the remainder work as faculty in postsecondary institutions.
Ucs And Classical Conditioning
In Ivan Pavlov’s famous experiment, for example, the tone of the buzzer was initially a neutral stimulus, while the smell of food was the unconditioned stimulus. Presenting the tone close to presenting the smell of food resulted in a stronger association. Ringing the buzzer, the neutral stimulus, long before the unconditioned stimulus led to a much weaker or even nonexistent association.
Different types of conditioning may use different timing or order between the neutral stimulus and the UCS.
- In simultaneous conditioning, the neutral stimulus is presented at the exact time as the unconditioned stimulus. This type of conditioning leads to weak learning.
- In backward conditioning, the unconditioned stimulus is given first, and the neutral stimulus is presented afterward. This type of conditioning also tends to result in weak learning.
- In trace conditioning, the neutral stimulus is presented briefly and then stopped, then the unconditioned stimulus is presented. This type of conditioning produces good results.
- In delayed conditioning, the neutral stimulus is presented and continues while the unconditioned stimulus is offered. This type of conditioning produces the best results.
Don’t Miss: Who Is Paris Jackson’s Biological Mother
Cancer Patients Feel Sick Before Chemotherapy Sessions
UCS: Cancer patients receive chemotherapyUCR: They get side effects like vomiting and nauseaCS: Treatment roomCR: Patients begin to feel sick
Vomiting and nausea are two of the most feared cancer treatment-related side-effects for people with cancer and their families. Patients who receive chemotherapy often vomit during or shortly after the procedure. After multiple chemotherapy sessions, some patients begin to feel sick at the sight of the treatment room.
CS: Beef meat treated with a deworming agentCR: Lions feel sick, and thus they refuse to eat meat
Classical conditioning can be used to support wildlife conservation efforts. In a study, African lions were conditioned to dislike the taste of beef. This is done to keep lions from preying on cattle, which should, in turn, prevent farmers from killing the lions.
Eight lions were given beef meats treated with a deworming agent. This made lions temporarily sick to their stomachs . After repeating this multiple times, the lions were once again offered untreated meat. As expected, they refused to eat it. Now that lions have developed an aversion to beef meat, they would be highly unlikely to prey on cattle.
What Were Skinner’s Main Findings
Skinner is regarded as the father of Operant Conditioning, but his work was based on Thorndike’s law of effect. According to this principle, behavior that is followed by pleasant consequences is likely to be repeated, and behavior followed by unpleasant consequences is less likely to be repeated.
Read also
Also Check: Geometry Assignment Find The Length Indicated Answer Key
What Is A Capp And How Do I View Mine
CAPP stands for Curriculum Advising and Program Planning. CAPP is a degree evaluation report that allows a student to track their academic progress throughout their University career.
Your CAPP evaluation lists the degree requirements and summarizes the progress based on your academic record. The report shows how University of Victoria courses, transfer courses, and courses in-progress apply toward degree requirements. All students with a declared program have access to their degree evaluation from Mypage.
When you are reviewing your CAPP there is a link at the top right hand corner of the page which says CAPP How To which provides information on how to read your CAPP. The GA will review and update your CAPP prior to your thesis or dissertation defense to ensure that all of your courses have been recorded and grades submitted and that your program requirements have been met prior to graduation.
The GA will also ask the GS to update your record to include the names of your committee members for each degree .
Occasion Setters Are Impervious To Extinction
Since simultaneous FP discriminations are solved by the model almost completely by direct XUS associations , the effect of X extinction is dramatic, abolishing CR responding on both X and XA test trials. By contrast, compound responding for serial FP is controlled by AUS associations which are attenuated by the inhibitory HUS associations . Since XH and HUS associations are only minimally affected by X extinction, very little decrement is observed in XA compound responding after extinction.
F.D. Lorenzetti, J.H. Byrne, in, 2001
Recommended Reading: How To Do Elimination In Math
The Difference Between Unconditioned Stimulus And Neutral Stimulus
An unconditioned stimulus elicits a natural, reflexive response, called the unconditioned response .
A stimulus that doesnt naturally elicit a response is a neutral response. For example, food is a UCS for dogs and can cause salivation. But ringing a bell by itself doesnt trigger the same response. The bells sound is hence a neutral stimulus.
What Is An Example Of Social Learning Theory
Social learning theory examples in everyday life are common, with one of the most evident being the behaviors of children, as they imitate family members, friends, famous figures and even television characters. If a child perceives there is a meaningful reward for such behavior, they will perform it at some point.
Don’t Miss: Eoc Fsa Warm Ups Algebra 1 Answers
Why Is Social Learning Theory Effective
A social worker who competently understands social learning theory can utilize practice models more effectively to handle behavioral conflicts or issues regardless of the setting whether its teaching in a high school, counseling people struggling with mental illness or rehabilitating men who abuse their partners.