What Is A Revetment In Geography
4/5Revetmentsrevetmentanswer here
A groyne is a rigid hydraulic structure built from an ocean shore or from a bank that interrupts water flow and limits the movement of sediment. In the ocean, groynes create beaches or prevent them being washed away by longshore drift.
Similarly, what are the advantages of revetments? Revetments
| Advantages Absorb wave energy through the slats Effective for many years Can be cheap compared to other techniques | Disadvantages Not effective in stormy conditions Can make the beach inaccessible for tourists Regular maintenance is required Visually obtrusive |
| Evaluation Used in Happisburgh |
Considering this, what causes slumping geography?
Movement is characterized by sliding along a concave-upward or planar surface. Causes of slumping include earthquake shocks, thorough wetting, freezing and thawing, undercutting, and loading of a slope. Translational slumps occur when a detached landmass moves along a planar surface.
What is rock Armour in geography?
Rock armour or rip-rap involves placing large boulders in front of a cliff or sea wall to absorb the energy of waves. Rock armour is a cheaper solution than seawalls to deflect the wave energy.
To Test If Longshore Drift Is Taking Place Along Deal Beach On The Day Of Our Visit And If So In Which Direction The Longshore Drift Is Taking Place
Extracts from this document…
Introduction
Karl Bowers 11Bu Friday 25th June 2004 Aim 2- To Test if Longshore drift is taking place along Deal Beach on the Day of our visit and if so in which direction the Longshore Drift is taking place. Aim 2a For this aim, we measured the wave angle. To do this, I laid a protractor on the floor, and watched for about 5 minutes in which direction the waves were travelling. I would look down on the protractor, and note down the angle of the waves. I then worked out the average angle. We had to do measure the wave angle because it would show us in which direction the longshore drift was taking place, therefore resulting back to the title of the aim. Aim 2b Weather Data: Wave Angle = 150 Wave Direction = South East Wind: Time Wind Speed Wind Direction 10:45am 6.3 South East 10:50am 6.1 South East 10:55am 5.8 South East 11:00am 6.7 South East 11:05am 6.6 South East 11:10am 6.6 South East 11:15am 6.8 South East On the day of the visit, the weather conditions were probably the worst conditions of the week. There was rain early on in the morning and when we arrived, so we had to wait in the minibus for the rain to stop. …read more.
Middle
This student written piece of work is one of many that can be found in our AS and A Level Coastal Landforms section.
What Is Longshore Drift Geography
longshore drift
. Besides, what is longshore drift and how does it work?
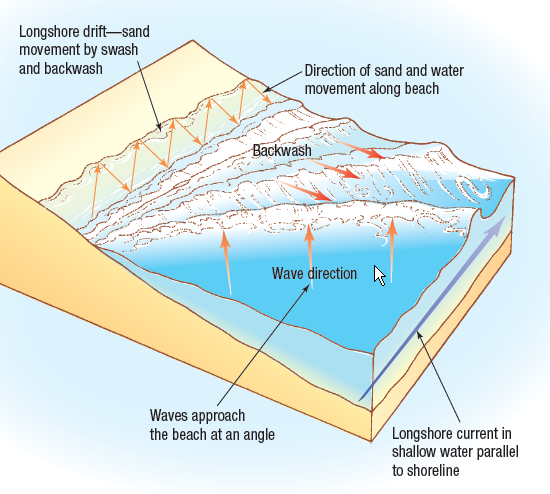
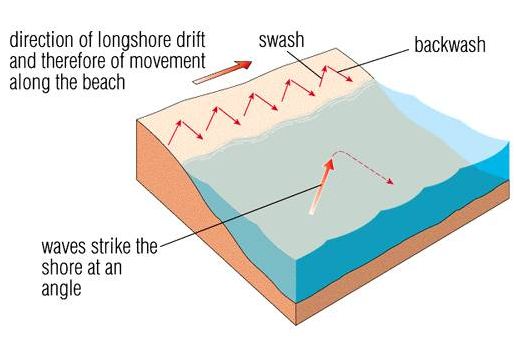
Longshore drift happens when waves moves towards the coast at an angle. The swash carries material up and along the beach. The backwash carries material back down the beach at right angles. This is the result of gravity.
Similarly, what is the process of longshore drift? Long shore drift is the process of deposition and transportation where sediment zig-zags along a coastline. This occurs when the prevailing wind hits the shoreline and an angle, or the waves are deflected.
Beside above, what is Longshore Drift A level geography?
Longshore Drift Longshore drift is a process responsible for moving significant amounts of sediment along the coast. The swash moves beach material along the beach and the backwash, under gravity, pulls the material back down the beach at right angles to the coastline.
What is Longshore Drift BBC Bitesize?
Longshore drift is a process of transportation that shifts eroded material along the coastline. Waves approach the coast at an angle. Swash carries sediment up the beach at an angle. Backwash carries sediment down the beach with gravity at right angles to the beach.
Read Also: Who Are Paris Jacksons Biological Parents
What Is Longshore Drift Bbc Bitesize
Longshore drift
What is longshore drift gcse?
The movement of the material is known as longshore drift . Waves approach the coast at an angle because of the direction of prevailing wind. The swash will carry the material towards the beach at an angle. The backwash then flows back to the sea, down the slope of the beach.
What is the process of longshore drift?Long shore driftprocess
Contents
What Is A Drift In Geography
What is a drift in geography? In geology, drift is the name for all material of glacial origin found anywhere on land or at sea, including sediment and large rocks . Glacial origin refers to erosion, transportation and deposition by glaciers.
What is a longshore drift in geography? Sediment is moved along the coastline in a process known as longshore drift. This results in a zigzag motion as sediment is transported along the coastline. This process means that over time beaches can change shape.
What is glacial drift in geography? Glacial drift. A general term applied to all rock material transported by a glacier and deposited directly by or from the ice, or by running water emanating from a glacier. This category is also used for Glacial sediment.
What is a drift area? Coordinates:43.5°N 91°WThe Driftless Area comprises southwestern Wisconsin, southeastern Minnesota, northeastern Iowa, and the extreme northwestern corner of Illinois in the American Midwest. It was never covered by ice during the last ice age, and therefore lacks glacial deposits, also termed drift.
Also Check: Holt Geometry Workbook Answers
Longshore Drift Facts For Kids
Longshore drift is the process of the ocean currents forcing sand and other material down a beach.
The material is first pulled into the currents by the backwash and is then pushed back up the beach by the swash . Longshore drift always moves in the direction of the main wind. If longshore drift continues for a long time, beaches can be changed quite a bit. The changes depend on the details, and vary from place to place. Longshore drift is the net movement of sand grains across a beach in a zig-zag motion.
- The waves carry the rock material up the beach at an angle.
- The backwash carries the material directly down into the sea or it stays there.
- This process goes again.
There are many inexpensive and effective ways of controlling longshore drift. The most common method is groynes . Some people dislike groynes because they interfere with walking along the beach, and the look of the beach.
Features Of Shoreline Change
Longshore drift plays a large role in the evolution of a shoreline, as if there is a slight change of sediment supply, wind direction, or any other coastal influence longshore drift can change dramatically, affecting the formation and evolution of a beach system or profile. These changes do not occur due to one factor within the coastal system, in fact there are numerous alterations that can occur within the coastal system that may affect the distribution and impact of longshore drift. Some of these are:
Read Also: Holt Geometry Workbook Answer Key
Technique 4 Measuring Longshore Drift
Using a float, such as an orange, ball or cork you can identify the rate of longshore drift at a location of choice. To begin with, you should decide on the distance you will measure longshore drift over, for example, 10 metres. Measure your start and finish points using a tape measure as close to the watermark as you can. Put your float into the water at the start point. Record the time it takes for the float to be transported to the finish point. You could also measure longshore drift by recording the distance the float travels over a set period of time e.g. 5 minutes.
When measuring longshore drift you should also consider recording wind speed and direction as these can affect longshore drift.
Technique 4 Measuring the impact of groynes on longshore drift
A popular fieldwork technique is to investigate the impact of groynes on longshore drift. The difference in height of the beach either side of the groyne will give an indication of the effectiveness of groynes in trapping material being transported by longshore drift. The more effective the groyne the greater the distance between beach levels either side of the groyne. To do this:
Technique 1 Beach Profiles
A beach profile shows the cross-sectional shape of a beach, usually from the edge of the sea to the base of the cliff.
To create a beach profile follow a straight transect line from the edge of the sea to the end of the active beach. Split the line into sections where the slope angle changes. You need to measure the length of each section and its angle. To do this:
- Person A stands at a safe distance from the edge of the sea holding a ranging pole
- Person B holds a second ranging pole further up the beach where there is a break of slope
- The distance between the two ranging poles is measured using a tape measure
- The angle between matching markers on each ranging pole is measured using a clinometer or an app such as Theodolite.
- Repeat this process at each break of slope until the top of the beach is reached
Beach Transect
Beach profiles can also be used to calculate cross-sectional area and the amount of beach material present.
Read Also: Course 3 Chapter 7 Congruence And Similarity Answers
What Is The Process Of Long Shore Drift
Long shore drift is the process of deposition and transportation where sediment zig-zags along a coastline. This occurs when the prevailing wind hits the shoreline and an angle, or the waves are deflected. During the swash , sediment is transported up the beach at the same angle as the waves’ swash. This is then deposited. The back wash pulls sediment down the beach perpendicular to the coastline, due to gravity.
This process repeats, resulting in sediment being pushed at an angle up the beach and pulled down the beach perpendicular to the coastline. Resulting in the net movement of sediment along the coast. This results in the build up of sediment up the coastline.
Why Is Longshore Drift Bad
Longshore drift can be very destructive to manmade structures. In either case, the water in a longshore current flows up onto the beach, and back into the ocean, as it moves in a sheet formation. As this sheet of water moves on and off the beach, it can capture and transport beach sediment back out to sea.
Read Also: Geometry Dash Hack Steam
What Is Suspension In Geography
BSL Geography Glossary Suspension definition Definition: Suspension is a method of transporting very fine sediment in a river. The sediment is probably eroded from larger rocks upstream and is then carried in the water. When the sediment is deposited from the water it is known as silt. Suspension.
Is Drifting Illegal In Usa
You wont to be able to just drift in your neighborhood, or on any streets for that matter as its completely illegal. But, there are many race tracks that allow you to legally race, drift, and compete against others. So you will want to look locally in your yellow pages, or a quick Google search will help.
You May Like: Who Is Paris Jackson’s Mom
What Is Longshore Drift And How Does It Work
Longshore drift happens when waves moves towards the coast at an angle. The swash carries material up and along the beach. The backwash carries material back down the beach at right angles. This is the result of gravity.
What is a longshore drift in geography?
The transport of sand and pebbles along the coast is called longshore drift. The prevailing wind causes waves to approach the coast at an angle. The swash carries the sand and pebbles up the beach at the same angle .
Technique 3 Fine Sediment Analysis
Fine sediments, such as clay, silt and sand, will need to be taken from the beach to the lab. Each sample will need to be sealed separately and labelled accurately.
Using graduated sieves sort the sediment samples into size categories .
Arrange the sieves into decreasing mesh diameter. Please the sediment sample into the top sieve. Then shake the sieve and sort the sediment. Record the mass of the contents of each sieve. Calculate the percentage of the sample in each sieve.
Also Check: What Is Dimensional Analysis In Chemistry
What Drifts In Longshore Drift
Longshore drift from longshore current is a geological process that consists of the transportation of sediments along a coast parallel to the shoreline, which is dependent on the angle incoming wave direction. The process is also known as littoral drift.
Formulas Used In Calculating Longshore Drift
There are about six formulas that are used in calculating the factors that are considered to cause longshore drift. All of the formulas give a different view into the procedures involved in generating longshore drift. Some of the usual factors considered by these formulas include: breaking and non-breaking waves, bed load and suspended transport, and the flow associated with waves.
Don’t Miss: Physics Vs Chemistry Which Is Harder
What Is The Difference Between A Bar And A Spit
A bar develops by the process of Longshore drift,which occurs due to waves meeting at the beach at an angle and backwashing perpendicular to the shore, moving sediment down the beach on a zigzag pattern. A spit is a deposition landform found off coasts. At one end, spits connect to land and extend into the sea.
Technique 2 Course Sediment Analysis
Beach sediment, such as sand, gravel and pebbles, can be analysed by random, systematic and/or stratified sampling. The size of the sediments determines the measuring technique.
Measuring size
Coarse sediments on the beach can be measured by their size and shape. This should be done on the beach, never take sediments from the beach.
To measure this material use a ruler or callipers to determine their a, b and c axes. The a-axis is the longest axis. The b-axis is the widest axis at right angles to the a-axis. The shortest axis is the c-axis.
Measuring shape
Powers Scale of Roundness is the easiest way to record pebble shape. You can judge by eye whether a stone is very angular, angular, sub-angular, sub-rounded, rounded or very rounded.
Powers Scale of Roundness
Use a concentric circle card or protractor to measure the minimum radius of the curvature. This is the sharpest corner of the a-axis.
Don’t Miss: Prentice Hall Gold Geometry Teaching Resources Answer Key
What Is Longshore Drift
Longshore drift is a geological process responsible for transporting sediments such as shingle, silt, clay, and sand along a coast that is aligned to the shoreline, relying on prevailing oblique winds. The prevailing oblique winds send water down the coast generating a water current which in turn advances parallel to the coast. Therefore, longshore drift can be simply defined as sediment transported by the longshore current. The sediment and current movement take place within the surf zone. Numerous sediment sizes are affected by the longshore drift since it works in slightly distinct ways depending on the sediment. For instance, there is a difference in longshore drift between sediments from a shingle beach and those from a sandy beach. Since shingle beaches tend to be much steeper than sandy beaches, a longshore drift is likely to form plunging breakers. In this case, since shingle beaches lack an extended surf zone, a majority of longshore movement will take place in the swash zone. On the other hand, movement of sand sediments on sandy beaches tend to move down the beach in a zigzag manner.