Compare Cellulose And Starch Structures
Cellulose: Beta glucose is the monomer unit in cellulose. As a result of the bond angles in the beta acetal linkage, cellulose is mostly a linear chain. Starch: Alpha glucose is the monomer unit in starch. As a result of the bond angles in the alpha acetal linkage, starch-amylose actually forms a spiral much like a coiled spring.
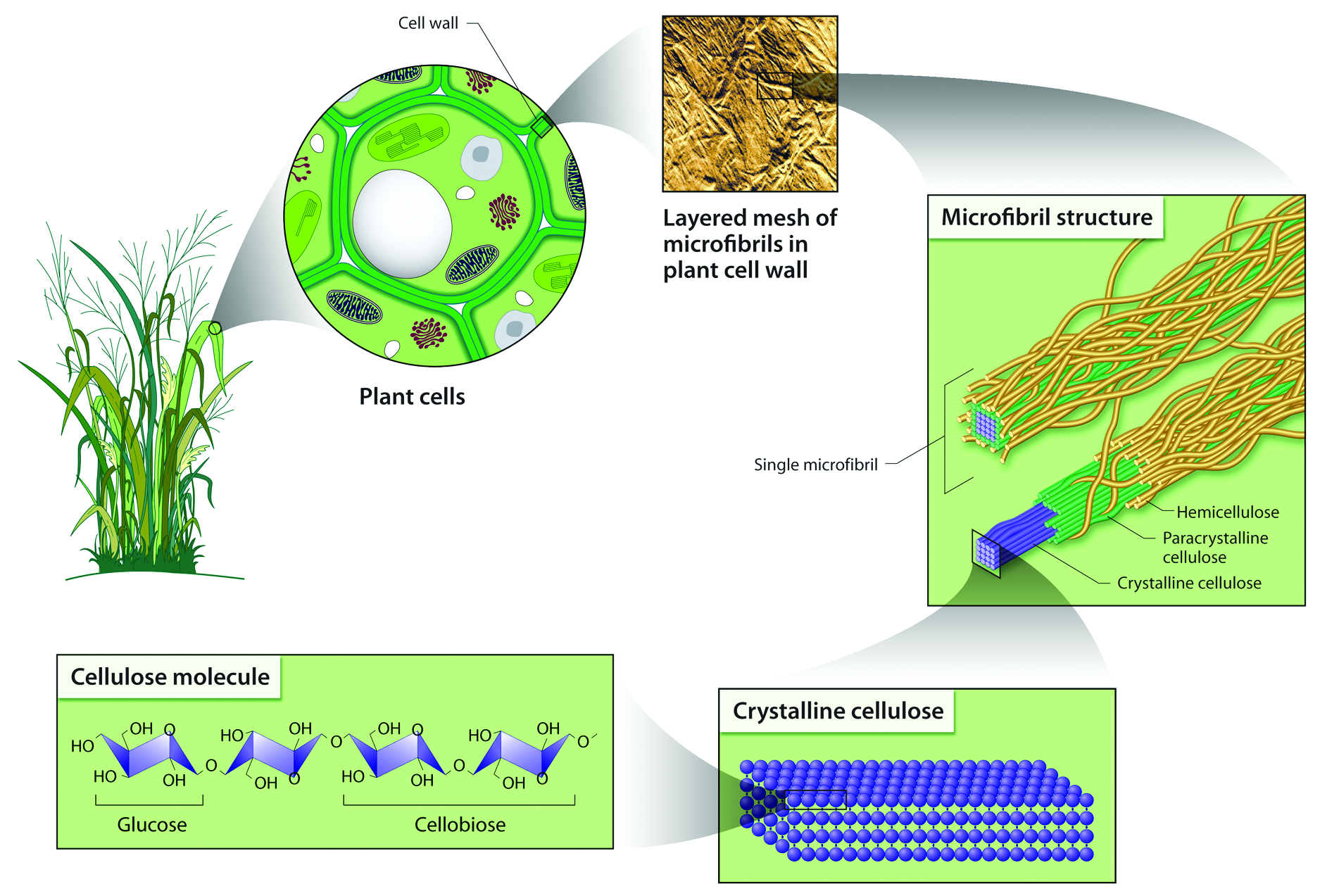
Spatial Organization Of Cellulose Microfibrils
Because cellulose microfibrils are the structural units of primary cell walls, the spatial arrangement of these microfibrils, including their bundling and packing, strongly impacts cell wall mechanics and growth. Traditionally, the mesoscale arrangement of microfibrils was studied largely by electron microscopy. The technique provided many valuable insights about the microstructure in cell walls, such as the development of network-like morphologies in growing cells of maize and oats coleoptiles . Microfibrils form a loosely reticulated network in a newly deposited cell wall, and gradually stiffen the wall with the addition of new microfibrils. Electron microscopy has also been used to study the cell wall architecture of near native onion primary cell walls at high resolution through shadowed replicas of rapidly frozen, deep-etched specimens . This study suggests hemicelluloses form the cross-links between cellulose microfibrils, and indicated a lamellate model for cellulose organization microfibrils are co-aligned within each lamellae, multiple lamellae are stacked on top of each other, but the net orientation of each lamellae is not necessarily correlated to other lamellae. Various aspects of this model were challenged by further work on native tissues, as described below.
Crystalline Structure Of Native Cellulose And Its Allomorphs
Six polymorphic forms of cellulose that are interconvertible have been identified . Natural cellulose is found in the form of cellulose I, which has two allomorphs cellulose I and cellulose I . Cellulose I is the dominant form in primitive organisms like bacteria and algae while Cellulose I is dominant in higher plants. The existence of these two forms was established by spectroscopic techniques while their lattice structures were revealed by diffraction techniques. Both techniques are widely used to identify the two forms of cellulose in plant cell walls and they are also used to quantify the relative abundances of the cellulose forms. This section highlights studies that revealed the cellulose unit cell parameters by diffraction techniques, and also discusses methods for identifying the two different forms most commonly found in nature.
Also Check: Prentice Hall Gold Geometry Answer Key
Induction Of Transdifferentiation And Drug Treatment
Seeds were surface sterilized with 30% bleach for 15 min, washed three times with autoclaved double-distilled H2O , and stored at 4 °C for 3â7 d. Seeds were grown for 3 d at 21 °C in the dark on vertical half-strength Murashige and Skoog plates containing 1% sucrose. Three-day-old seedlings were placed in open microfuge tubes containing half-strength MS 3% sucrose liquid medium that was supplemented with either 20 μM DEX for induced samples or an equivalent volume of the solvent, dimethyl sulfoxide , for control seedlings. Seedlings that were subjected to live-cell fluorescence imaging were observed after 24â30 h of DEX treatment. In experiments in which microtubules were pharmacologically removed, oryzalin was introduced to the liquid induction medium after 16 h of induction and seedlings were imaged 8â12 h later. Seedlings that were subjected to SFG, FE-SEM, or lignin autofluorescence imaging were treated for 60 h with DEX or DMSO. After DEX or DMSO treatment, samples for SFG analysis were frozen on MS plates containing 1% sucrose at â80 °C overnight. After thawing, groups of 20â30 seedlings were aligned parallel to close to one another in a single layer on glass slides and air dried before SFG analysis. All other analyses were conducted on fresh, never-frozen, never-dried samples.
What Is The Function Of Cellulose
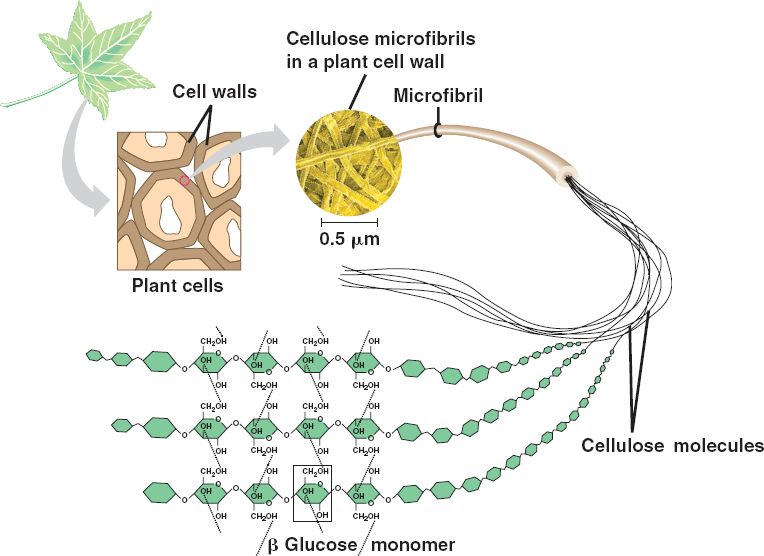
Cellulose makes up most of the tough cell walls surrounding plant cells and enables plants to stand upright, according to Education Portal. It is the major component of plants that makes the branches, stems and leaves very strong.
Cellulose is a valuable polysaccharide and the most abundant organic compound in the planet, notes Education Portal. All plants are composed of polysaccharides, which are large sugar molecules consisting of single sugar units. The four common polysaccharides are cellulose, chitin, glycogen and starch. Cellulose has a unique, rigid structure that serves an important function in plants. Its molecules are joined together using hydrogen bonds and are arranged parallel to one another, forming a long, cable-like structure that merges with other cellulose molecules. This creates the strong support structure that allows plants to stand upright.
Education Portal explains that the strength of cellulose makes it useful in various synthetic products, including plastics, fabrics, cosmetics, lotion and carpeting. Cellulose is also an essential component of paper, cotton fabric and lumber. Moreover, cellulose plays a key role in digestion, as it is an insoluble fiber that does not break down when passing through the digestive system. Insoluble fiber is important in a persons diet, because it allows the digestive tract to keep moving.
You May Like: Regression To The Mean Psychology
Cellulose: Structure & Function
- Cellulose is a polysaccharide
- Polysaccharides are macromolecules that are polymers formed by many monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds in a condensation reaction to form chains. These chains may be:
- Branched or unbranched
- Folded
- Straight or coiled
- Polysaccharides are insoluble in water
Cellulose structure
- Is a polymer consisting of long chains of -glucose joined together by 1,4 glycosidic bonds
- As -glucose is an isomer of -glucose to form the 1,4 glycosidic bonds consecutive -glucose molecules must be rotated 180° to each other
To form the 1,4 glycosidic bond between two -glucose molecules, the glucose molecules must be rotated to 180° to each other
- Due to the inversion of the -glucose molecules manyhydrogenbonds form between the long chains giving cellulose its strength
Cellulose is used as a structural component due to the strength it has from the many hydrogen bonds that form between the long chains of -glucose molecules
Cellulose function
The strength and insolubility of cellulose fibres means it is a suitable molecule to construct cell walls
Exam Tip
Learn the monomer for cellulose, the arrangement of the glycosidic bond and that cellulose exists in parallel chains bonded by many hydrogen bonds giving it high mechanical strength.
Opportunities In Structural Characterization Of Plant Cell Walls
The on-going development of instrumentation and techniques for the study of soft matter structure leads to new opportunities in the structural characterization of cell walls. In this section, we highlight some emerging techniques based on diffraction/scattering, imaging, and spectroscopy that may facilitate the creation of new knowledge on cell wall structure and assembly.
Also Check: Do You Have To Memorize Physics Equations For The Mcat
What Is The Difference In Structure Between Starch And Cellulose
Cellulose is mostly linear chains of glucose molecules bound by beta 1,4 glycosidic bonds while starch is present in both linear and branched chains. Starch and cellulose are two Polymers that are very similar. In addition, they are both made from the same monomer, glucose, and have the same glucose-based repeat units.
What Are The Characteristics Of Cellulose
It has the following properties
- Cellulose is the most abundant carbohydrate present in nature.
- It is insoluble in water.
- Cellulose is a crystalline solid having a white powdery appearance.
- It has high tensile strength due to firm hydrogen bonds between the individual chains in cellulose microfibrils.
You May Like: Ap Human Geography Self Study
How Is Cellulose Important For Humans
Cellulose is a polysaccharide that makes 30% of the plant cell wall. It helps in connecting cells to form tissues and signals the cells to grow and divide. Humans cannot digest cellulose. However, it is consumed in the diet as fibre. Fibre helps the digestive system to keep the food moving through the gut and moves the waste out of the body.
Examples Of Cellulose In A Sentence
celluloseWiredcellulose Robb Reportcellulose NBC NewscelluloseWiredcellulose Wiredcellulose refinery29.comcelluloseSmithsonian Magazinecellulose oregonlive
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘cellulose.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
Recommended Reading: Abiotic Science Definition
Spinning Disk Confocal Microscopy Imaging
Seedlings were imaged between two glass coverslips. Transdifferentiating seedlings were prepared as described above, and slides were prepared with the induction medium described above. Imaging of CSC markers during PCW synthesis was conducted in epidermal cells 1â2 mm below the apical hook of 3-d-old dark grown seedlings, a common model tissue for PCW synthesis. Seedlings used for imaging during PCW synthesis were grown on half-strength MS plates with 0% sucrose, and slides were prepared with half-strength MS liquid medium with 0% sucrose.
Images were acquired every 5 s for periods of 5â8.5 min to generate time-lapse movies to assess the localization, dynamics, and distribution of fluorescent protein-tagged proteins of interest. Photobleaching was caused by three rapid pulses with a 405-nm laser in designed ROIs. In lateral photobleaching experiments designed to visualize the directional movement of GFP-CESA particles , the two lateral regions of cells were bleached during time-lapse imaging. In these experiments, the bleach event occurred at the 2-min time point of 7-min time-lapse acquisition. In photobleaching experiments designed to measure the delivery rate of CSCs , a region that was â¼20 μm long and spanned the entire width of the cell was bleached at the 30-s time point of 8.5-min time-lapse acquisitions.
How Do You Test For Carb Intolerance
When carbohydrate intolerance is suspected, the diagnosis can be confirmed using oral tolerance tests. The carbohydrate being investigated is given by mouth in liquid form. Several blood levels are measured and compared to normal values. This helps evaluate the individuals ability to digest the sugar.
Recommended Reading: Hawkes Learning College Algebra
How Is Cellulose Useful
Cellulose is a molecule, consisting of hundreds and sometimes even thousands of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. Cellulose is the main substance in the walls of plant cells, helping plants to remain stiff and upright.
Humans cannot digest cellulose, but it is important in the diet as fibre. Fibre assists your digestive system keeping food moving through the gut and pushing waste out of the body.
Animals, such as cows, sheep and horses, can digest cellulose, which is why they can get the energy and nutrients they need from grass.
Cellulose has many uses. In cotton, it makes clothes like t-shirts and jeans. Paper-making needs huge quantities of cellulose, obtained mainly from wood.
Does Cellulose Make You Poop
The key to good poops, Chutkan says, is straightforward: What really makes a good stool is large amounts of the indigestible plant matter that feed gut bacteria. This plant fiber mostly cellulose also directly adds bulk to poop, so a plant-heavy diet is critical for nice, solid bowel movements.
Read Also: Exponential Growth And Decay Common Core Algebra 1 Homework Answer Key
What Is The Structure And Function Of Cellulose
Cellulose is a structural protein in plants and algae. Cellulose fibers are enmeshed in a polysaccharide matrix to support plant cell walls. Plant stems and wood are supported by cellulose fibers distributed in a lignin matrix, where the cellulose acts like reinforcing bars and the lignin acts like concrete.
Progress And Opportunities In The Characterization Of Cellulose An Important Regulator Of Cell Wall Growth And Mechanics
- 1Department of Chemical Engineering, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, United States
- 2Department of Materials Science and Engineering, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, United States
- 3Materials Research Institute, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, United States
- 4Department of Biomedical Engineering, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, United States
Recommended Reading: Electron Dot Structure Of Ccl4
Cellulose Synthesis In Higher Plants
Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology
Vol. 22:53-78 First published online as a Review in Advance on July 6, 2006
Chris Somerville
Department of Plant Biology, Carnegie Institution, and Department of Biological Sciences, Stanford University, Stanford, California 94305 email:
Cellulose Microfibril Size And Organization
Direct visualization of the cell wall through light microscopy shows the existence of cellulose in a bundled fibrillar structure. High resolution electron microscopy reveals microfibrils that are aggregated, such that individual microfibrils have cross-sections of 24 nm and lengths of 100 nm or more . Complete understanding of this fibrillar network requires the characterization of structural parameters, including fibril length, lateral size and shape, as well as the spatial arrangement of microfibrils. These parameters have a strong influence on the mechanical and physicochemical properties of cellulose and its derivatives. The following section discusses the characterization of the abovementioned parameters through different techniques such as microscopy, diffraction/scattering, spectroscopy, and chemical methods. We cover examples from studies of bacterial cellulose, primary cell walls, and secondary cell walls.
Don’t Miss: Algebra 2 Escape Challenge Answers
Active Cscs Are Evenly Distributed Early In Transdifferentiation And Are Later Distributed Within Confined Hoops During The Synthesis Of Scw Thickenings
Active CSCs exhibit bidirectional movement along tracks during PCW synthesis and directionally coherent movement along tracks during SCW synthesis. GFP-CESA3 cesa3je5 was imaged in nontransdifferentiating cells as a CSC marker during PCW synthesis , and GFP-CESA7 cesa7irx3-1 35S::VND7-GR was imaged during two stages of xylem cell transdifferentiation, before hoop formation and during hoop formation , as a CSC marker during SCW synthesis . The influence of CMTs on GFP-CESA7 particle behavior was assessed via 8â12 h treatment with 25 μM oryzalin. Representative single-frame images and 7-min projection images show the distribution and trajectories of GFP-CESA particles, respectively. Arrows indicate the apical direction. Kymographs were derived from the indicated tracks in each 7-min projection image and the directions of particle movements along the track were color-coded in schematic kymographs. Images from 5 s and 5 min after photobleaching the lateral sides of cells are shown to depict the direction of particle movement along tracks of interest. Upper images are raw images, and lower images are highlighted to show the bleached regions , the particles within tracks of interest , and the favored direction of particle movements . The frequency of particle direction along individual tracks was quantified . Error bars are standard errors of the mean n ⥠48 tracks and 6 seedlings per data point. *P< 0.0001.
Digestion Of Cellulose In Termites
Termites have mastigophorans in their gut which brings about digestion of cellulose. Herbivorous animals, on the other hand, are ruminants. They have different compartments in their stomach to carry out digestion.
The rumen is the first compartment where ingested food containing cellulose is stored temporarily and later regurgitated to chew their cud. They are able to digest cellulose because of the presence of bacteria and enzymes in the rumen where anaerobic bacterial digestion occurs. A by-product of this type of digestion releases methane which is foul-smelling and causes the destruction of the ozone layer of the Earth.
See also: Role Of Digestive Enzymes
You May Like: Unit 1 Test Study Guide Geometry Basics Answers
Sfg Vibrational Spectroscopy Analysis
The broadband SFG spectroscopy system and common SFG spectra collecting procedures were previously described . SFG spectroscopic probing was performed in the reflection geometry and s-polarized sum frequency output, s-polarized visible input, and p-polarized IR input polarization combination. To account for inherent heterogeneity within each sample, SFG data collection was performed at four different locations on each sample and averaged to generate a representative SFG spectrum for each sample.
Mutations In Other Genes Affecting Cellulose Synthesis
Because of the importance of cellulose synthesis in plant development, many mutants have been isolated that have a cellulose deficiency. Despite this, many of these mutants are affected in general âhousekeepingâ roles and are not specific to cellulose synthesis. These include mutations in steps in the pathway for N-linked glycosylation . Only mutations directly affecting cellulose synthesis will be described here.
Also Check: Define Relation In Math Terms
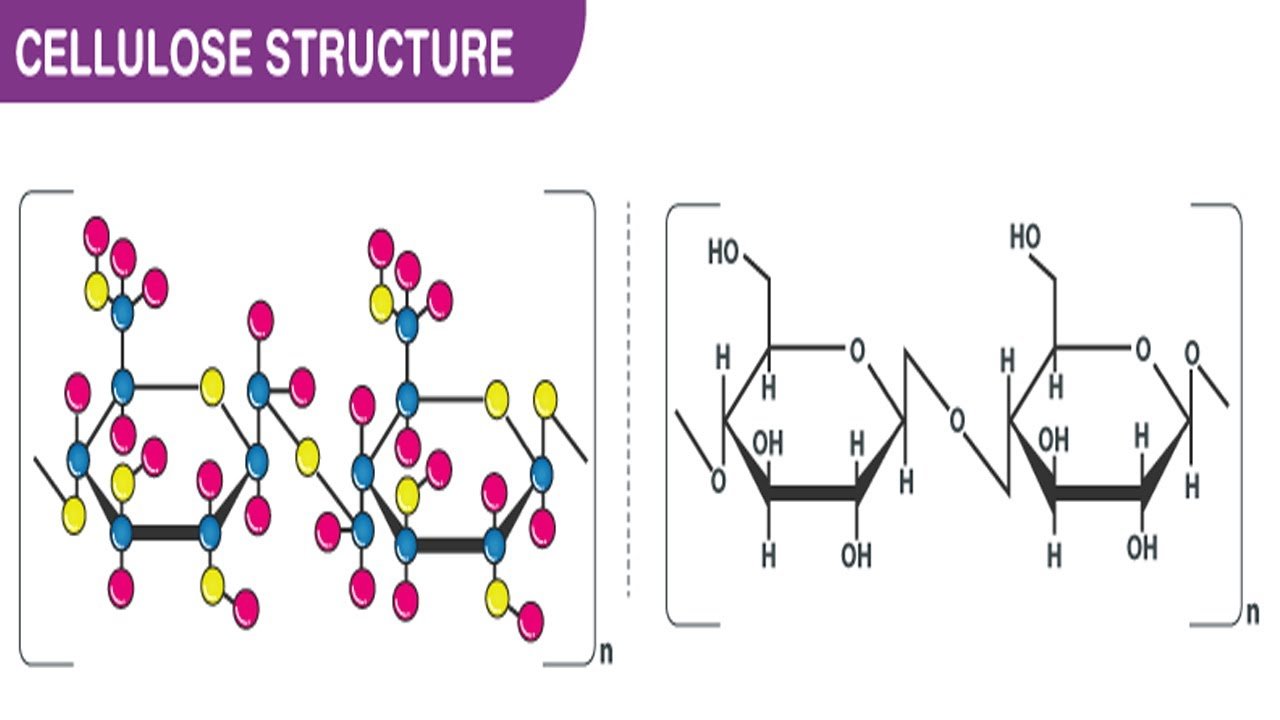
Chemical Structure And Properties
Cellulose forms via -glycosidic bonds between D-glucose units. In contrast, starch and glycogen form by -glycosidic bonds between glucose molecules. The linkages in cellulose make it a straight chain polymer. The hydroxyl groups on the glucose molecules form hydrogen bonds with oxygen atoms, holding the chains in place and conferring high tensile strength to the fibers. In plant cell walls, multiple chains bond together to form microfibrils.
Pure cellulose is odorless, flavorless, hydrophilic, insoluble in water, and biodegradable. It has melting point of 467 degrees Celsius and can be degraded into glucose by acid treatment at high temperature.
How Can I Eat Carbs Without Bloating
Eating plenty of fruits and vegetables is a healthy way to help meet your carbohydrate needs without consuming wheat or gluten. Go for starchy veggies like squash and sweet potato or choose fruit for a snack. Getting your five-a-day is definitely a great way to beat the bloat
Read Also: Unit 1 Geometry Basics Homework 4 Angle Addition Postulate
Iv Mutations Affecting Cellulose Synthesis
Much of our knowledge about cellulose synthesis has been derived from the identification of mutants in A. thaliana. These mutants have been isolated from a variety of genetic screens that reflect the importance of cellulose synthesis in plant growth and development. It has become clear that cellulose synthesis in the primary and secondary cell walls, while sharing some components, use a different set of cellulose synthases. Hence cellulose-deficient mutants can be conveniently divided into mutations in CesA genes that affect either primary or secondary cell walls, and mutations in other genes affecting cellulose synthesis. Because of the diversity of mutant screens that has yielded mutations in CesAs, there is a wide range of mutant allele names. To minimize confusion, the nomenclature for specific mutants used here will be the CesA number with the particular allele following .