Contributions Hela Cells Have Made To Science
In 1951, aged just 31 years, Henrietta Lacks died from an aggressive form of cervical cancer, only 10 months after first seeking treatment at Johns Hopkins for a knot in her womb. During her treatment at the hospital, samples of cancerous tissue were taken from her cervix. These cells went on to become the immortal cell line known as HeLa.HeLa cells are immortal, as they have an overactive version of the enzyme telomerase, that prevents the shortening of the chromosome telomeres, and so prevents cellular aging and cell death. HeLa cells also proliferate abnormally fast, even in comparison to other cancer cells, and have the ability to contaminate other cell lines.Over the years HeLa cells have enabled scientists around the world to make great leaps in science and medicine. This list highlights five of these remarkable contributions.
Cell Lines In Modern Cancer Research: Toward The Encyclopedia Of Cell Lines
Human cancer cell lines continue to play a critical role in modern cancer research. Indeed, they are widely used as preclinical model systems for gaining mechanistic and therapeutic insight. Notably, with the advent of -omics technologies , recent studies have provided comprehensive databases dedicated to the characterization of most existing cell lines . Furthermore, the online availability of the information that was derived from these studies created an important resource for the study of cancer cell lines and facilitated researchers in selecting the most appropriate in vitro model system for their research projects. In this context, it is important to consider a series of significant papers that have been published in less than 10 years.
Why Do We Need Immortalized Cells
Firstly, primary cells will reach senescence after limited generation. The process of frequently re-establish fresh cultures from explanted tissue is tedious and it can also add significant variation from one preparation to another. Using immortalized cell can guarantee the experiment materials’ consistent.
Next, in addition to the capacity of extended proliferation, the immortalized cells possess similar or identical genotype and phenotype to their parental tissue. Additionally, in many studies hTERT immortalized cells have been induced to become differentiated cell types, exhibiting tissue-specific features, differentiation-specific proteins, and forming structures that resemble those formed in vivo. All the mentioned above make immortalized cells become vital factor in cell biology research.
Read Also: Psychology Figure Ground
What Does Henrietta Lacks’s Story Say About Racism In Medicine
While Lacks’s HeLa cells have had a major impact on modern medicine, there’s still a lot of controversy over their usenamely that Lacks’s cells were both taken and further used without her consent or that of her family’s. But Lacks and her family aren’t the only ones who have suffered this treatment. “This is what youll see when you look at the history of the medical community, Dr. Shepherd says. Shes not the only case of peoples cells and bodies being used without their consent.
Dr. Shepherd specifically points to the US Public Health Service Syphilis Study at Tuskagee, in which 600 Black men299 who had syphilis and 201 who did not were told they were being treated for having bad blood. The study went on for 40 years, and the men with syphilis were never given proper treatment for their disease, even when it became widely available. Overall, “there were many experimental uses of peoples cells and diseases that were studied in African Americans that they were never told what it was used for, Dr. Shepherd says. “Its a moral issue as far as how we do studies and how we advance in science and medicine.
Overview Of Immortalized Cell

Immortalized cells are a population of cells from a multicellular organism due to mutation, which can escape normal cellular senescence and keep undergoing division. Thus, this kind of cells can grow in vitro for prolonged periods. The mutations required for immortality can occur naturally or be intentionally induced for experimental purposes. Immortal cell lines are a powerful tool for the biological investigator to research the biochemistry and cell biology of multicellular organisms, which plays an important role in the study of the biology of cell growth, differentiation, and senescence. And they have been applied in the research of cell biology, immunology, hematology, cancer biology, toxicology, and molecular biology.
Read Also: Beth Child Of Rage Now
Number : Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells
Chinese hamster ovary cells are clearly ovary-derived cells, but this time, we are talking mammalian cells. Similarly to Sf9 cells, they can exist both as adherent or suspension cells in culture. CHO cells are used in various applications such as recombinant protein production and studies of the epidermal growth factor receptor .
Developing A New Cell Line
Deriving a new cell line, especially when human, from fresh tissue is an expensive and time-consuming exercise. The subsequent value of the new cell line will depend on the ability to authenticate its origin and on the associated information that is available.
1.1.1. Tissue
In addition to tissue taken for culture, if donor or patient consent and/or ethical review permit , it is recommended that additional material is stored for:
Confirmation of origin . A small portion of the sample used for primary culture should be frozen or processed immediately. The tissue or DNA can then be used to demonstrate unequivocally that the cell line is derived from the putative donor. Short tandem repeat profiling is a recommended method for the purpose of authentication, although additional information on genotype mapping, or even whole-genome sequence) will sometimes help ensure identity.
1.1.2. Clinical information
If donor or patient consent and ethical reviews permit , as much of the following information as possible should be recorded and stored securely:
Age and sex of donor/patient.
Site of origin and nature of tissue specimen.
Stage and grade of cancer or other syndrome, or pathology.
Additional information such as tumour marker status, genetic information and family data etc.
Evidence of informed consent and waiver of commercial rights by donor.
1.1.3. Accessory information
1.1.4. Cell line designation
1.1.5. Publication
Also Check: Do You Need Chemistry For Psychology
Polyclonal Vs Monoclonal Antibodies
What Is the Difference Between Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibodies?
Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are secreted by B cells to neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses. The classical representation of an antibody is a Y-shaped molecule composed of four polypeptides-two heavy chains and two light chains. Each tip of the “Y” contains a paratope that is specific for one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. The ability of binding to an antigen has led to their ubiquitous use in a variety of life science and medical science. These antibodies can be classified into two primary types by the means in which they are created from lymphocytes. Each of them has important role in the immune system, diagnostic exams, and treatments.
This overview will describe the synthesis of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies, their differentiating properties, and their role in clinical diagnostics and therapeutics.
Fig 1. The structure of the antibody
Polyclonal Antibodies vs. Monoclonal Antibodies: Production.
Polyclonal antibodies are mixture of heterogeneous which are usually produced by different B cell clones in the body. They can recognize and bind to many different epitopes of a single antigen.
Fig 2. The process to generate the polyclonal antibody
Fig 3. The process to generate the monoclonal antibody
Polyclonal Antibodies vs. Monoclonal Antibodies: Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Lobsters: Impressive But Not Immortal
What initially attracted the attention to lobsters and created the “immortal lobster” hype, was their ability to keep growing even after reaching maturity. We already mentioned the telomerase enzyme in regards to cancer cells that can keep dividing without limit. Most vertebrate animals can produce telomerase only in their early developmental stages. It appears that lobsters have a constant supply of it throughout their life.
However, the problem they encountered on their path to immortality is their protective exoskeleton. While other cells divide and the animal grows, its rigid exoskeleton does not. Lobsters have to get rid of it as it becomes too tight, and this process in itself is taxing. So all lobsters reach the point when they no longer can withstand the effort of molting and die of exhaustion.
Also Check: Simplifying Radicals Imaginary Numbers Worksheet Kuta Software
Introduce A Viral Gene That Overrides The Cell Cycle
Many viral genes affect the cell cycle and thus can be used to overcome senescence by removing the biological brakes on proliferative control. Many of these are tumor suppressor genes, since they require suppression for tumorigenesis to occur. The most common of these is over-expression of the Large T-antigen of the simian virus , which represses the retinoblastoma and p53 genes, both critical controllers of the cell cycle.
One example of a cell line immortalized with SV40 is HEK293T, which are also known as 293T cells, a cell line widely used to express viral particles and for many cellular assays, since they are very easily transfected. Other viral genes include those from the human papilloma virus such as E6 and E7, which also target Rb and p53.
Excerpt: ‘the Immortal Life Of Henrietta Lacks’
Rebecca Skloot
The Immortal Life of Henrietta LacksBy Rebecca Skloot
PROLOGUE
The Woman in the Photograph
There’s a photo on my wall of a woman I’ve never met, its left corner torn and patched together with tape. She looks straight into the camera and smiles, hands on hips, dress suit neatly pressed, lips painted deep red. It’s the late 1940s and she hasn’t yet reached the age of thirty. Her light brown skin is smooth, her eyes still young and playful, oblivious to the tumor growing inside her a tumor that would leave her five children motherless and change the future of medicine. Beneath the photo, a caption says her name is “Henrietta Lacks, Helen Lane or Helen Larson.”
No one knows who took that picture, but it’s appeared hundreds of times in magazines and science textbooks, on blogs and laboratory walls. She’s usually identified as Helen Lane, but often she has no name at all. She’s simply called HeLa, the code name given to the world’s first immortal human cells her cells, cut from her cervix just months before she died.
Her real name is Henrietta Lacks.
I was a kid who’d failed freshman year at the regular public high school because she never showed up. I’d transferred to an alternative school that offered dream studies instead of biology, so I was taking Defler’s class for high-school credit, which meant that I was sitting in a college lecture hall at sixteen with words like mitosis and kinase inhibitors flying around. I was completely lost.
You May Like: Who Is Paris Jackson Father
How Did Henrietta Lacks’s Hela Cells Contribute To Medicine
Because HeLa cells could be grown continuously in labs, researchers started to rely heavily on them for their experiments, according to the National Institutes of Health . HeLa cells became the go-to human cell line for scientists working laboratories. By now, it’s no longer the only immortalized cell line, but its still the most widely used cell line in biomedical research, showing up in more than 110,000 scientific publications, the NIH says.
HeLa cells have been used to better understand the processes behind cell growth, differentiation, and death, to try to help researchers understand a range of diseases. Theyve also helped serve as the foundation for developing modern vaccines, and been used to develop medical techniques like in vitro fertilization, the NIH says. HeLa cells even contributed to the HPV vaccine,Jessica Shepherd, MD, a womens health expert and ob-gyn in Texas, tells Health. They helped us understand HPV and its cancer-causing cells. That was incredible as far as what we were able to do.
Cancer research in generalnot just that to understand HPV and cervical cancerhas benefitted from HeLa cells, too. “A tremendous amount of what we know about cancer and cancer biology is directly attributed to the use of Henrietta Lacks cells, Nicole C. Woitowich, PhD, associate director of the Center for Reproductive Science and a research assistant professor at Northwestern University, tells Health.
The Importance Of Hela Cells
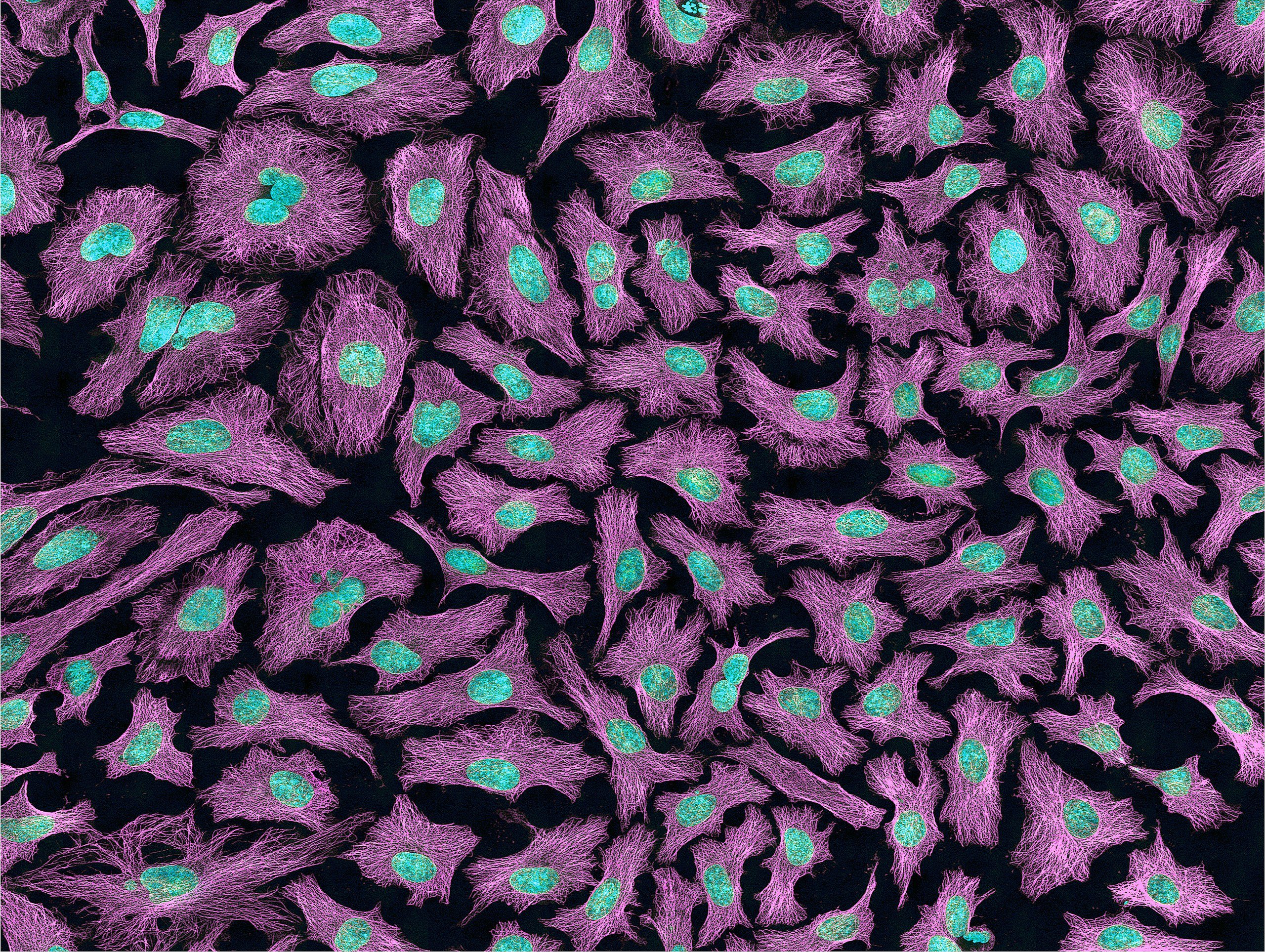
Among the important scientific discoveries of the last century was the first immortal human cell line known as HeLa a remarkably durable and prolific line of cells obtained during the treatment of Henriettas cancer by Johns Hopkins researcher Dr. George Gey in 1951.
Although these were the first cells that could be easily shared and multiplied in a lab setting, Johns Hopkins has never sold or profited from the discovery or distribution of HeLa cells and does not own the rights to the HeLa cell line. Rather, Johns Hopkins offered HeLa cells freely and widely for scientific research.
Over the past several decades, this cell line has contributed to many medical breakthroughs, from research on the effects of zero gravity in outer space and the development of polio and COVID-19 vaccines, to the study of leukemia, the AIDS virus and cancer worldwide.
Although many other cell lines are in use today, HeLa cells have supported advances in most fields of medical research in the years since HeLa cells were isolated.
Recommended Reading: 100 Day Countdown To The 5th Grade Math Fsa (1-50) Answer Key
Henrietta Lacks: Science Must Right A Historical Wrong
Nobody asked Henrietta Lacks for consent to use her cells in research in 1951 and, shockingly, consent is still not always required in the United States today.Credit: Jonathan Newton/The Washington Post/Getty
That day in Erika Johnsons high-school biology class, some 20 years ago, is seared into her memory. The teacher was leading the students through experiments involving cells from a widely used line known as HeLa. The cell line originated from tissue taken from a woman named Henrietta Lacks and Johnsons mother was a Lacks. This is my great-grandmother Im holding in my hand, Johnson remembers feeling. It was a very surreal situation.
But the story of Henrietta Lacks also illustrates the racial inequities that are embedded in the US research and health-care systems. Lacks was a Black woman. The hospital where her cells were collected was one of only a few that provided medical care to Black people. None of the biotechnology or other companies that profited from her cells passed any money back to her family. And, for decades after her death, doctors and scientists repeatedly failed to ask her family for consent as they revealed Lackss name publicly, gave her medical records to the media, and even published her cells genome online. Nature later published the genome of another HeLa line after the Lacks family reached an agreement with the US National Institutes of Health to approve its release.
Number : Sf9 Insect Epithelial Cells
Well, we didnt say that it would just be human cell lines, did we?
Derived from the ovaries of the fall armyworm moth , these cells are probably related to all insect cell lines in labs worldwide . Sf9 cells can be cultured as adherent or suspension cells. Most cell lines are adherent cells, which grow only on the surfaces of culture vessels. This limits the amount of cells you can expect to obtain from each culture. Similarly to E.coli, suspension cells can grow in the entire volume of the medium, thus increasing the amount of cells that can be harvested from a vessel. Furthermore, and because of the high volume: cell number ratio, suspension cultures allow a much more effective use of medium than adherent cultures. Sf9/baculovirus systems are typically preferred for large-scale protein production including industrial manufacture of mammalian proteins, including the vaccine for cervical cancer CERVARIX® .
Also Check: Define Consistent In Math
How You Handle Primary Cells Determines Success
Human primary cell cultures can be initiated from healthy cells or cancer cells. They come from healthy donors, organ donation, surgical specimens, fetal tissues or post-mortem donors. When planning your experiments, keep in mind that the source of human primary cells is limited. This means you might not be able to get extra material from the same donor. Also, primary cultures derived from tissue explants are a mix of different cells at different stages, so if you want to initiate more homogeneous cultures, you might need to purify specific cell types. Because primary cells are more sensitive than cell lines, they often require additional nutrients and growth factors.
Uk Legal And Ethical Requirements
These may be summarised as follows:
Research involving human tissue samples will require ethical approval. To this end the Human Tissue Act 2004 legislates on the use of human tissue samples for a number of scheduled purposes including research. Informed patient consent may be required to store and use human tissue samples for research purposes and a Human Tissue Authority licence may be required to store human tissue samples for research purposes. Once a human cell line is established it is no longer covered by the Act.
Any patient data where the patient name is recorded should be managed under the Caldicott Principles. These require the laboratory to have a Caldicott Guardian to assure compliance with these guidelines .
The Human Fertilisation and Embryology Act 1990 legislates on research using early human embryos up to 14 days of development or the first signs of primitive streak formation and is regulated and licensed by the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority . The HFEA is not concerned with tissues from later-stage embryos or foetuses .
Clinical trials of cell-based medicinal products are regulated by the Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency in compliance with the Medicines for Human Use Regulations 2004 .
An MTA should accompany all transfers of created cell lines between organisations and should define specific details including ownership, intellectual property rights and patent rights.
2.1.2. The Human Tissue Act 2004
You May Like: What Is Mode In Math Terms