Students’ Conceptions And Their Implications For Teaching
The results of the interviews about pollination imply that students have difficulties explaining the interactions between plants and animals and how they evolved. However, the documented conceptions of the students from the fifth grade of adaptation confirmed the findings of Baalmann et al. who analyzed students’ conceptions of adaptation in older students . Including the evolutionary perspective to provide explanations for specific behavior or morphological features seems to be crucial, not only regarding students’ conceptions of evolution but also regarding their ideas of a deliberate pollination. It is also necessary to differentiate between flower visit and pollination , because not every visit to a flower results in pollination. This differentiation might help students to understand why animals visit flowers and how pollination occurs as a side effect in most cases. One student in the interview study was confused, because pollen is collected by bees for the offspring but is at the same time transferred to flowers. Therefore, it might be helpful to differentiate between pollen the insects collect and bring to their offspring and pollen that gets caught in insects’ fur and thus cannot be used as food but serves pollination. Based on our results, we suggest avoiding metaphors that indicate a deliberate behavior and use evolutionary explanations instead.
Disadvantages Of Asexual Reproduction
The major disadvantages of asexual reproduction are:
- Lack of diversity. Since the offsprings are genetically identical to the parent they are more susceptible to the same diseases and nutrient deficiencies as the parent. All the negative mutations persist for generations.
- Since only one organism is involved, the diversity among the organisms is limited.
- They are unable to adapt to the changing environment.
- A single change in the environment would eliminate the entire species.
Understanding Students’ Conceptions Of Plant Reproduction To Better Teach Plant Biology In Schools
Austrian Educational Competence Centre for Biology , University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Botanical Garden of the University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Correspondence
Peter Lampert, Austrian Educational Competence Centre for Biology , University of Vienna, Porzellangasse 4, 1090 Vienna, Austria.
Austrian Educational Competence Centre for Biology , University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Botanical Garden of the University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Austrian Educational Competence Centre for Biology , University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Botanical Garden of the University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Austrian Educational Competence Centre for Biology , University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Botanical Garden of the University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Correspondence
Peter Lampert, Austrian Educational Competence Centre for Biology , University of Vienna, Porzellangasse 4, 1090 Vienna, Austria.
Austrian Educational Competence Centre for Biology , University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Botanical Garden of the University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Austrian Educational Competence Centre for Biology , University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Botanical Garden of the University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Also Check: Chapter 6 Test Form 2c Algebra 1
What Is The Meaning Of Reproduction
1 : the act or process of reproducing specifically : the process by which plants and animals give rise to offspring and which fundamentally consists of the segregation of a portion of the parental body by a sexual or an asexual process and its subsequent growth and differentiation into a new individual. 2 : something reproduced : copy.
What Is Reproduction In Biology
Reproduction is the production of offspring. There are two main forms: sexual and asexual reproduction. In sexual reproduction, an organism combines the genetic information from each of its parents and is genetically unique. In asexual reproduction, one parent copies itself to form a genetically identical offspring.
You May Like: What Happened To Beth Child Of Rage
Task N: Description Of A Given Life Cycle
Task N°2 uses an illustration of a life cycle of a plant. Illustrations of this kind are often used in books or worksheets to give an overview of the different stages of the life cycle of a plant. The illustration shows a life cycle of B. rapa, which is used in the fast plant project . The illustration is derived from a booklet for primary school teachers but the descriptions of the stages have been removed so that only the illustrations of the plants with connecting arrows are left. The included illustration of a flying insect refers to the process of pollination without naming this process explicitly.
We used Task N°2 to find out, how students interpret illustrations of life cycles without textual guidance. We also were interested if students describe the connecting processes between the stages, particularly when it comes to sexual reproduction. This task was also included because various studies show that students have difficulties in understanding plant development and reproduction as a cycle . We assumed that students who have difficulties in understanding the life cycle of plants would only describe the stages that can be seen in the illustration and do not deal with the processes connecting them.
Life Cycles Of Plants
Most life histories, except perhaps for the simplest and smallest organisms, consist of different epochs. A large tree has a period of seed formation that involves many cell divisions after fertilization and the laying down of a small embryo in a hard resistant shell, or seed coat. There then follows a period of dormancy, sometimes prolonged, after which the seed germinates, and the adult form slowly emerges as the shoots and roots grow at the tips and the stem thickens. In some trees the leaves of the juvenile plant have a shape that is quite different from that of the taller, more mature individuals. Thus, even the growth phase may be subdivided into epochs, the final one being the flowering or gametebearing period. Some of the parasitic fungi have much more complex life histories. The wheat rust parasite, for example, has alternate hosts. While living on wheat, it produces two kinds of spores it produces a third kind of spore when it invades its other host, the barberry, on which it winters and undergoes the sexual part of its life cycle.
Don’t Miss: What Is Dimensional Analysis In Chemistry
What Is Reproduction Biology
4.7/5Reproductionbiologicalreproductionreproduction
Thereof, what is reproduction Short answer?
Answer: The process by which an organism produces its offspring is called reproduction. Answer: When a single parent is involved in reproduction and gamete formation does not happen, it is called asexual reproduction.
Secondly, what is reproduction and types of reproduction? Reproduction is the process by which organisms give rise to offspring. It is one of the defining characteristics of living things. There are two basic types of reproduction: asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
Then, what is reproduction and why is it important?
Reproduction ensures the continuity of various species on the Earth. In the absence of reproduction, the species will not be able to exist for a long time and may soon get extinct. Reproduction is important for the survival of all living things. Without a mechanism for reproduction, life would come to an end.
What is the purpose of reproduction in biology?
Reproduction is the biological process by which new offspring are produced from their parents. In sexual reproduction, the genetic material of two individuals from the same species combines to produce genetically-different offspring this ensures mixing of the gene pool of the species.
Choose The Right Synonym For Reproduction
reproduction, duplicate, copy, facsimile, replica mean a thing made to closely resemble another. reproduction implies an exact or close imitation of an existing thing. reproductions from the museum’s furniture collectionduplicate implies a double or counterpart exactly corresponding to another thing. a duplicate of a house key copy applies especially to one of a number of things reproduced mechanically. printed 1000 copies of the lithograph facsimile suggests a close reproduction often of graphic matter that may differ in scale. a facsimile of a rare book replica implies the exact reproduction of a particular item in all details a replica of the Mayflower but not always in the same scale. miniature replicas of classic cars
Recommended Reading: Slader Geometry Workbook
Sexual Reproduction In Plants And Animals:
The mode of reproduction which involves the formation of male and female gametes either by the same individuals or by different individuals of opposite sex is known as sexual reproduction. These gametes fuse to form a new cell called zygote, which grows and develops into a new individual.
Sexual reproduction is exhibited by all the flowering plants and most of the animals. Before an organism starts to reproduce sexually, it has to attain a certain level of growth and maturity. This period during which an organism grows to attain the sexual maturity is called juvenile phase or vegetative phase . This phase is followed by another phase called reproductive phase.
The end of reproductive phase is marked by the onset of another phase called senescent phase. After this phase, the organism dies. In both plants and animals, hormones regulate the transitions between these three phases. Interaction between hormones and certain environmental factors regulate the reproductive processes and the associated behavioural expressions of organisms.
Points related to the attainment of sexuality in plants are:
1. Annuals and biennial plants exhibit clear cut vegetative, reproductive and senescent phases.
2. In perennials, these phases cannot be defined clearly.
3. Some plants show unusual behaviour for flowering, e.g., Strobilanthus kunthiana plant flowers once in 12 years, whereas bamboo plants flower only once in their life time.
Sexuality in Plants:
Sexuality in Animals:
Bisexual:
Types Of Asexual Reproduction
There are many different ways to reproduce asexually. These include:
1. Binary fission. This method, in which a cell simply copies its DNA and then splits in two, giving a copy of its DNA to each daughter cell, is used by bacteria and archaebacteria.
2. Budding. Some organisms split off a small part of themselves to grow into a new organism. This is practiced by many plants and sea creatures, and some single-celled eukaryotes such as yeast.
3. Vegetative propagation. Much like budding, this process involves a plant growing a new shoot which is capable of becoming a whole new organism. Strawberries are an example of plants that reproduce using runners, which grow outward from a parent plant and later become separate, independent plants.
4. Sporogenesis. Sporogenesis is the production of reproductive cells, called spores, which can grow into a new organism.
Spores often use similar strategies to those of seeds. But unlike seeds, spores can be created without fertilization by a sexual partner. Spores are also more likely to spread autonomously, such as via wind, than to rely on other organisms such as animal carriers to spread.
5. Fragmentation. In fragmentation, a parent organism is split into multiple parts, each of which grows to become a complete, independent offspring organism. This process resembles budding and vegetative propagation, but with some differences.
Read Also: Geography Definition Of Movement
New Mexico Whiptail Lizards
This species of lizard was created by the hybridization of two neighboring species. Genetic incompatibility between the hybrid parents made it impossible for healthy males to be born: however, the female hybrids were capable of parthenogenesis, making them a reproductively independent population.
All New Mexico whiptail lizards are female. New members of the species can be created through hybridization of the parent species, or through parthenogenesis by female New Mexico whiptails.
Possibly as a remnant of their sexually reproducing past, New Mexico whiptail lizards do have a mating behavior which they must go through to reproduce. Members of this species are mated with by other members, and the lizard playing the female role will go onto lay eggs.
It is thought that the mating behavior stimulates ovulation, which can then result in a parthenogenic pregnancy. The lizard playing the male role in the courtship does not lay eggs.
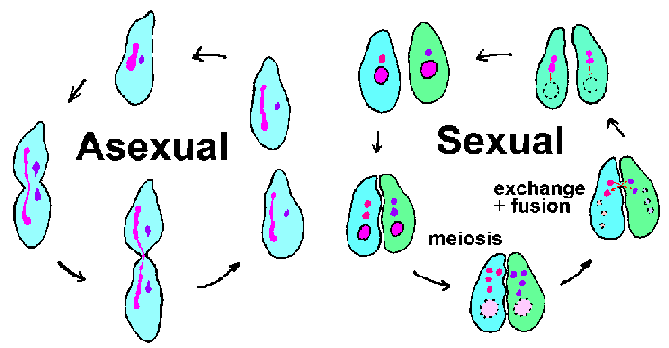
Asexual Versus Sexual Reproduction
Organisms that reproduce through asexual reproduction tend to grow in number exponentially. However, because they rely on mutation for variations in their DNA, all members of the species have similar vulnerabilities. Organisms that reproduce sexually yield a smaller number of offspring, but the large amount of variation in their genes makes them less susceptible to disease.
Many organisms can reproduce sexually as well as asexually. Aphids, slime molds, sea anemones, and some species of starfish are examples of animal species with this ability. When environmental factors are favorable, asexual reproduction is employed to exploit suitable conditions for survival, such as an abundant food supply, adequate shelter, favorable climate, disease, optimum pH, or a proper mix of other lifestyle requirements. Populations of these organisms increase exponentially via asexual reproductive strategies to take full advantage of the rich supply resources. When food sources have been depleted, the climate becomes hostile, or individual survival is jeopardized by some other adverse change in living conditions, these organisms switch to sexual forms of reproduction.
You May Like: Segment Addition Postulate Kuta
Definition Of Sexual Reproduction
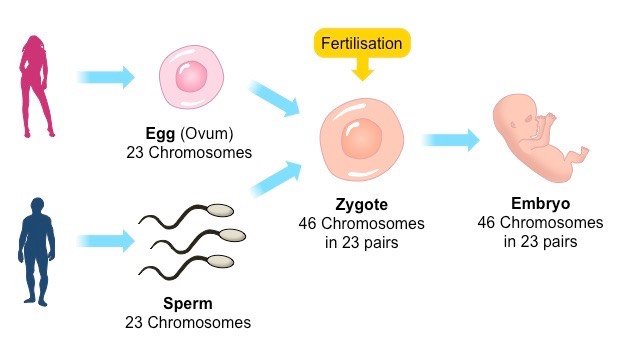
Sexual reproduction is the process in which new organisms are created, by combining the genetic information from two individuals of different sexes. The genetic information is carried on chromosomes within the nucleus of specialized sex cells called gametes. In males, these gametes are called sperm and in females the gametes are called eggs. During sexual reproduction the two gametes join together in a fusion process known as fertilization, to create a zygote, which is the precursor to an embryooffspring, taking half of its DNA from each of its parents. In humans, a zygote contains 46 chromosomes: 23 from its mother and 23 from its father. The combination of these chromosomes produces an offspring that is similar to both its mother and father but is not identical to either.
Phenotype traits, such as physical adaptions to an organisms environment and genotype traits, such as resistance to disease, are passed down from each parent during sexual reproduction. Natural selection, whereby individuals with favorable adaptions to their environment are able to survive and successfully reproduce, drives the evolution process. Sexual reproduction increases the diversity of genotypes and phenotypes within a population, allowing natural selection to select for the individuals best suited to an environment.
Task N: Open Description Of Plant Reproduction
Task N°1 is based on Schussler and Winslow who describe an easy way of investigating students’ ideas of plant reproduction. In their study, students were advised to draw a life cycle of a plant starting with a seed. In the discussion, the authors point out that it would be helpful to encourage students to make written notes in addition to mere drawings, to make analyses easier . This is also a recommendation of Wilson and Bradbury , who showed the potential of combined written and drawn representations for evaluating students’ thinking. Combining writing and drawing allows students to include their meaning to their own drawings, which is important to grasp students’ conceptions . Thus, we integrated both drawings and written explanations in the task and additionally encouraged students to add comments in their drawings.
Instead of asking for a drawing of a life cycle starting with a seed, no explanation was given except the statement in the beginning. This statement outlines a âproblemâ and encourages students to think about the possibilities of plant reproduction and dispersal. We also avoided content-specific terms, such as âseedâ or specific examples to minimize guidance and bias through the method of assessment. With task N°1 we simply wanted to find out what comes to studentsâ minds when they think about plant reproduction. Which processes to they describe? Which specific terms do they use? Which vectors do they mention?
Don’t Miss: Parallax Errors
Asexual Reproduction In Animals
Besides sexual reproduction, the other major type of reproduction seen in the animal kingdom is asexual reproduction. This type of reproduction is mostly observed in lower organisms and unicellular microbes.
It is the process in which a new individual is formed by the involvement of a single parent without the involvement of the gamete formation. The individuals produced are genetically and morphologically similar. It occurs in unicellular organisms. The cells divide by mitotic division and no fertilization takes place. The division occurs very rapidly.
What Is Reproduction In Living Organisms
Reproduction is the process by which new organisms are generated from older generations. It is a fundamental feature of all living beings. Sometimes a cell may produce another of its kind and that is also defined as reproduction. Like regenerating a part of tissue, or the healing of a wound.
Reproduction to produce another independent living organism, can either be sexual or asexual, in the plant or animal kingdom.
Recommended Reading: Rationalizing The Denominator Worksheet Kuta
Can Snakes Have Babies Without Mating
There are Eggs but No Babies or Babies but No Eggs In rare cases, a snake may lay a clutch of eggs without mating, which are infertile if she isnt able to fertilize them herself. These eggs are called slugs and wont hatch.
Human reproduction is the effort of a male and female that involves four functions of the reproductive systems. According to Librarythinkquest.org, these functions are production of egg and sperm cells, transportation and sustenance of cells, development and nurturing of offspring and production of hormones.
Asexual Vs Sexual Reproduction
twofold cost of sexual reproduction
Organisms that reproduce through asexual reproduction tend to grow in number exponentially. However, because they rely on mutation for variations in their DNA, all members of the species have similar vulnerabilities. Organisms that reproduce sexually yield a smaller number of offspring, but the large amount of variation in their genes makes them less susceptible to disease.
Many organisms can reproduce sexually as well as asexually. Aphids, slime molds, sea anemones, some species of starfish ” rel=”nofollow”> fragmentation), and many plants are examples. When environmental factors are favorable, asexual reproduction is employed to exploit suitable conditions for survival such as an abundant food supply, adequate shelter, favorable climate, disease, optimum pH or a proper mix of other lifestyle requirements. Populations of these organisms increase exponentially via asexual reproductive strategies to take full advantage of the rich supply resources.
Read Also: Vsepr Ccl4