Inversions And Natural Selection
An alternative way to identify the functional impact of inversions is through the detection of the action of natural selection. Although inversions may have played an important role in primate speciation , their role in shaping human populations is still uncertain. Basically, we lack tests to study the selective advantage or disadvantage of inversions, even at a small scale, and thus for just a handful of inversions their selective effects have been reported in terms of the frequency and geographic distribution of the alleles.
For other inversions like 8p23.1, no clear signals of positive selection have been found in spite of multiple loci within the inverted region being putative targets of natural selection, including loci associated with autoimmune and cardiovascular disease . In this case, the Inv allele is the ancestral but no SNPs are in perfect LD with the inversion haplotype, which suggests some level of gene flow between Std and Inv haplotypes, or that the inversion has appeared recurrently throughout evolution . Even though these observations hinder the study of the inversion, its worldwide clinal distribution is consistent with neutral demographic models of the human expansion out of Africa .
Nature Of The Differences
Disruption of synteny is due to chromosomal rearrangement processes such as translocation, inversion, chromosome fusion, and breakage gene, segment, and chromosomal duplication and loss polyploidization and return to diploidy proliferation of repetitive sequences sequence conversion unequal homologous recombination and illegitimate recombination .
Figure 6.3. Chromosomal rearrangement processes leading to disruption of synteny
Disruptions of synteny commonly observed involve translocation, inversion, duplication, and loss of DNA segments. A change of chromosome number between species might be due to chromosome fusion and breakage. A common phenomenon in plant evolution involves an increase of ploidy level followed by gradual loss of DNA and return to diploidy. Some rearrangements involve proliferation of repetitive elements such as transposons. Sequence conversion, unequal homologous recombination, and illegitimate recombination might also modify the synteny between homologous chromosomes.
R.S. Singh, in, 2001
How And Why Chromosome Inversions Evolve
Citation: Kirkpatrick M How and Why Chromosome Inversions Evolve. PLoS Biol 8: e1000501. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1000501
September 28, 2010
Copyright: © 2010 Mark Kirkpatrick. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Competing interests: The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
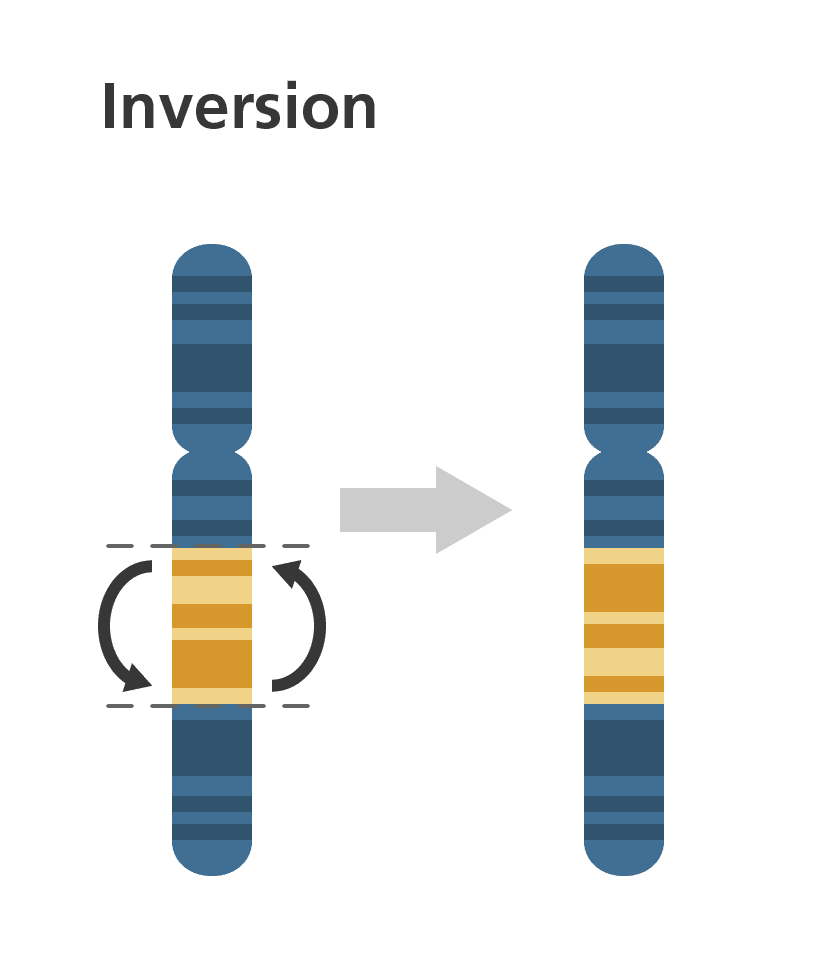
An inversion occurs when a chromosome breaks at two points and the segment bounded by the breakpoints is reinserted in the reversed orientation. Several molecular mechanisms can mediate this event . Box 1 gives an overview of some basic properties of inversions and the ways that they are detected.
Also Check: What Does Hierarchy Mean In Biology
What Are The Types Of Translocations
Moreover, translocations occur inter-chromosomally or intra-chromosomally. Interchromosomal translocations occur within a single chromosome while intrachromosomal translocations occur between chromosomes. During the translocation mutation, a part of the chromosome breaks off and joins again at a different location.
What is the difference between Cross crossing over and inversion?
Crossing over is an exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes that occurs during prophase I of meiosis, the formation of gametes. An inversion occurs when a segment of gene is reversed end to end. It may be paracentric or pericentric .
Inversion Biology Is An Approach To Physics That Taking A Look At Gravity From A Unique Angle
In place of being viewed from the bottom up, inversion physics views gravity from the top down. With inversion, forces are depicted from the outside hunting in as opposed to the inside seeking out.
Inversion physics may be the approach of taking a look at a motion in the bottom up. It incorporates Newtons Second Law and Newtons third law, which states that the force of gravity is directly proportional for the distance towards the center from the planet.
In humans, gravity behaves like a pull towards the center of your earth. A continual force pulling us towards the center on the earth acts like a pull to our bodies. This creates a net force that pulls us toward the center on the earth.
Inversion physics combines all of this data into a framework that allows scientists to analyze the effects of gravity. The leading down method lets you know what exactly is going on by observing pay someone to write my paper cheap the effects that it has on objects www.math.rutgers.edu around you. With an inversion experiment, you can straight observe the physical effects of gravity on the center of mass in the physique.
Inversion in four kingdoms: major down, bottom up, bottom down, and octopus. Best down science makes use of physics, mathematics, and chemistry.
In order to take this course, you are going to want to finish an accredited biology key with a physics division that provides this course. Your physics division is usually contacted online in the UCSD Bio-Science website.
Also Check: What Does Msw Stand For In Psychology
Complex Genomic Structure At The Inversion Breakpoint
Inversion breakpoints can provide insight in the evolutionary history of the inversion . The downstream breakpoint of the Chromosome 1A inversion harbors a previously identified CNV region, 2802, located at position 64.8367.67Mb . Of all 2,296 birds analyzed for the inversion, 2,021 were also previously analyzed for CNVs. This includes 1,921 birds classified as norm-norm and 100 as inv-norm. Among the norm-norm birds, 217 harbor CNVs at the downstream inversion breakpoint whereas 1,704 have two copies as expected in the diploid state. In contrast, 96% of the inv-norm birds have an individual CNV call mapped at the CNVR 2802. At this CNVR, 94.8% of all individual CNV calls are gains.
Different Likelihood Of The Establishment Of Inversions And Translocations
As discussed above, comparative mapping of plant species typically identified more inversions than inter-chromosomal translocations or âfusionsâ . In general, as mapping or sequencing resolution increases, so does the number of inversions detected . In contrast, little or no increase in the numbers of inter-chromosomal translocations is reported with increasing resolution. Some studies have focused exclusively on chromosomal-scale translocations and fusions/fissions or did not clearly differentiate rearrangement types and thus are not relevant to this question.
In a number of comparative genomic studies, more translocations were reported than inversions . Variation in the abundance of inversions and translocations seen in Table 1 stems partly from differences in methods, criteria , and power for detecting structural variants, as opposed to real differences in their frequency. Some studies applied whole-genome alignment, long-read alignment and short-read alignment to detect both inter- and intra-chromosomal translocations of various sizes , while others have focused exclusively on large inter-chromosomal reciprocal translocations. More robust conclusions about the prevalence of inversions and translocations will not only require that studies be more parallel in terms of data and methodology employed, but also that they take rearrangement size into account.
Read Also: Khan Academy Answers Algebra 1
Is An Inversion A Translocation
such rejoining occurs within a chromosome, a chromosome segment between the two breakpoints becomes inverted and is thus called an inversion.
What is the main difference between translocation and crossing over?
Translocation is the process of exchanging genetic materials between non-homologous chromosomes. Crossing over is the process of exchanging matching segments of chromosomes between homologous chromosomes during the sexual reproduction.
What is the difference between transposition and translocation?
Transposition, also sometimes referred to as translocation, is a process by which segments of a chromosome are relocated through the genome. Gene transposition may involve the machinery of transposons, including target DNA sequences used by the transposon translocation machinery.
Inversion Biology Is Definitely An Approach To Physics That Taking A Look At Gravity From A Distinct Angle
As an alternative to getting viewed from the bottom up, inversion physics views gravity from the prime down. With inversion, forces are depicted in the outside seeking in instead of the inside searching out.
Inversion physics is the strategy of looking at a motion in the bottom up. It incorporates Newtons Second Law and Newtons third law, which states that the force of gravity is straight proportional to the distance for the center of the planet.
In humans, gravity behaves like a pull towards the center on the earth. A continual force pulling us towards the center of the earth acts like a pull to our bodies. This creates a net force that pulls us toward the center from the earth.
Inversion physics combines all of this facts into a framework that makes it possible for scientists to analyze the effects of gravity. The major down strategy allows you to know what is going on by observing the effects that it has on objects around mla annotated bibliography you. With an inversion experiment, you can straight observe the physical effects of gravity around the center of mass with the physique.
Inversion in four kingdoms: top rated down, bottom up, bottom down, and octopus. Major down science utilizes physics, mathematics, and chemistry.
Bottom up domain focuses around the interactions in between molecules and atoms in an attempt to know the forces that kind chemical bonds. You will learn about the physical laws that apply to molecules, atoms, and atoms with each other.
Recommended Reading: What Are Probes In Biology
Interlocus Ig And Tcr Gene Rearrangements And Translocations
Not only do IG and TCR genes undergo intralocus rearrangements, but their aberrant recombination also causes interlocus chromosomal translocations and inversions. These chromosomal rearrangements can create hybrid antigen receptor genes when two different antigen receptor loci recombine with each other. A small fraction of pediatric ALLs of B- or T-cell lineage harbor these hybrid antigen receptor gene rearrangements.336 Alternatively, chromosomal rearrangements can juxtapose transformation-inducing nonIG/nonTCR genes with the regulatory enhancer and promoter elements of IG or TCR genes as a second type of interlocus rearrangement. VJ recombination errors of this type,337 causing transcriptional upregulation of the juxtaposed nonIG/nonTCR genes, occur in subsets of pediatric ALL, especially in T-cell ALL.
In the rare entity of Burkitt’s leukemia, expression of the MYC oncogene is altered by translocation into the IGH or, less often, the IGK or IGL light chain locus, but oncogenic transformation at a more mature B-cell developmental stage is reflected by IgM expression on the leukemia cell surface.
Shamika Ketkar, Shashikant Kulkarni, in, 2015
Population Structure For Chromosome 1a Reveals A Large Inversion
We found a large putative inversion on Chromosome 1A. Based on visual inspection of the PCA , we classified the clustering patterns separately for each autosome in the great tit genome . Plots for whole chromosomes may reveal obvious substructure if the inversion is relatively large. Although additional chromosomes display some population structure , the variation within PCA clusters is greater, and the FST values across these chromosomes less conclusive, relative to the patterns seen on Chromosome 1A. Moreover, this unusual PCA pattern, which was most likely reflecting an inversion, was briefly reported elsewhere . Therefore, the remainder of this article considers the likely inversion polymorphism on Chromosome 1A. Chromosome 1A displayed clear population structure for the first eigenvector , with two subpopulations that are genetically distinct. The larger subpopulation comprises 2,179 birds and the smaller one contains only 117. Among these 117 birds, 10 display intermediate values in Eigenvector One. Analysis of the genotypes of these 10 birds indicates that they are carrying a distinct copy of the inversion that is derived, possibly by gene conversion, from the most common inversion haplotype . The genotypes and LD patterns in the center of the inversion are discussed in detail in a subsequent section .
Don’t Miss: What Is Free Energy In Biology
What Is Inversion In Biology
A portion of a chromosome is flipped end-to-end in an inversion, a chromosomal rearrangement. An inversion occurs when a single chromosome experiences internal fragmentation and rearrangement. There are two sorts of inversions: paracentric and pericentric.
Inversion refers to reversing a state, shape, position, direction, or path, such as turning inward or inside out. In biology, specifically anatomy, inversion refers to the migration of the sole towards the median plane.
In zoology, inversion refers to transforming some animal species from one sex to the other. Sexual inversion is an obsolete word that refers to assuming the gender role of the opposite sex.
In biochemistry, inversion refers to the transformation of dextrorotatory sucrose into levorotatory sucrose or vice versa.
Homogeneity Across Loci And The Role Of Selection
Conformity to expectation under neutral evolution was tested individually for each of the 16 microsatellite loci used in this study through a model-based test directed toward the detection of outlier loci. We used the software package FDIST2 to identify microsatellite loci showing unusually high FST values, taking into account their heterozygosity . We ran 500,000 coalescent simulations to characterize the joint distribution of FST and heterozygosity, using a 50-demes island model with an average differentiation equal to that observed across loci . Although the true demographic history of A. funestus populations is likely to depart from the island model assumptions, the distribution of FST estimates so obtained should be robust to the vagaries of demographic history . We used a stepwise mutation model as implemented in FDIST2. We obtained a close approximation to the expected joint distribution of the estimates following , using a 2D histogram of 100 × 100 square cells . We used the averaged shifted histogram algorithm to smooth the simulated data and provide a more continuous region. For each observation in the sample data set, we computed its associated probability in the simulated data set . Then, we derived the empirical P value for this observation as one minus the sum of all cell probabilities within the simulated data set that are more probable than the observed data.
Read Also: Is It Possible To Break The Laws Of Physics
Microsatellite Genotyping And Analysis
Sixteen physically mapped microsatellite loci were selected from published data . Microsatellite markers were distributed on all chromosome arms inside and outside common polymorphic chromosomal inversions . Polymerase chain reaction amplifications were performed for each locus individually in a 25 l reaction volume containing 5× PCR buffer including 7.5 mM MgCl2 at pH 8.5 , 200 M of each dNTP , 0.5 units of Taq Polymerase , 10 pmol of each primer, and 510 ng of template DNA. The forward primer was 5-end labeled with PET, VIC, 6FAM, or NED fluorescent dye to allow for multiplexing prior to electrophoresis. PCR amplifications were carried out in a GeneAmp 9700 thermocycler . Cycling conditions were 94 °C for 2 min followed by 36 cycles at 94 °C for 30 s, 54 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s and a final extension step at 72 °C for 10 min. PCR products were diluted 1:751:100 depending on the fluorescent dye and loaded onto a AB3130sequencer as three multiplex sets. Alleles were scored at each locus using the software GeneMapper v4.0 .
Population Description Genotyping And Sequencing
In addition to the birds genotyped on the SNP chip, we also used sequence data from 29 birds . Each bird was sequenced at an average depth of around 10× using paired-end sequencing libraries. Details of sequencing analysis, as well as information regarding the origin and sample quality of each bird are provided elsewhere .
Also Check: What Is Visual Information Processing In Psychology
How Do Inversions Evolve
Like other types of mutations, inversions evolve under selection and random drift. Many inversions, particularly small ones in intergenic regions, are likely to evolve neutrally . Selection can result in three ways. Inversions can generate structural problems with meiosis, as with some pericentric inversions. Alternatively, a breakpoint can disrupt an open reading frame or alter gene expression. The consequences can be deleterious, as in some human genetic diseases , but in other cases could cause an adaptive mutation. Finally, selection can act on an inversion when it carries one or more selected alleles.
Many pericentric inversions are underdominant , which poses an evolutionary puzzle. An underdominant inversion is selected against, so long as it’s rare. Closely related species often show fixed differences, however, which implies that an inversion must have nevertheless appeared and spread through one of the two lineages since their last common ancestor. Some researchers have invoked drift to resolve this riddle ,. One line of support for that hypothesis is the observation that annual plants show high rates of evolution for underdominant chromosomal rearrangements ,. Many annual plants have large demographic fluctuations and at least occasionally self-fertilize, both of which dramatically decrease the effective population size and so enhance the power of drift.
Ld And Haplotypes Across The Inversion
We used the unphased SNP genotypes from all birds to characterize LD across Chromosome 1A by calculating D . As expected for regions with low recombination, a large LD block which overlaps the whole inversion was identified . This LD block is not present in norm-norm birds , suggesting that recombination is only restricted in birds heterozygous for the inversion. On the other hand, when R2 is used as a measure of LD inference, an LD block is only observed in the middle of the chromosome . This R2 LD block overlaps the region that causes the two distinct genotype distributions among the 117 inv-norm birds .
Genotype distribution within/outside the center of the inversion in inversion carriers. The number of genotypes is represented on a log2 scale to improve the visualization but untransformed values are shown on the upper x axis. Based on the number of AA genotypes it is possible to identify inv-norm-birds which harbor a different genotype distribution at the center of the inversion and therefore possibly have different inversion haplotypes .
Recommended Reading: What Difficulty Has Japan Faced Due To Its Geography
Inversion Biology Is An Approach To Physics That Taking A Look At Gravity From A Different Angle
Instead of being viewed from the bottom up, inversion physics views gravity in the leading down. With inversion, forces are depicted in the outdoors seeking in instead of the inside seeking out.
Inversion physics may be the system of looking at a motion in the bottom up. It incorporates Newtons Second Law and Newtons third law, which states that the force of gravity is straight proportional for the distance to the center from the planet.
In humans, gravity behaves like a pull towards the center with the earth. A continuous force pulling us towards the center of the earth acts like a pull to our bodies. This creates a net force that pulls us toward the center of the earth.
Inversion physics buy my essay combines all of this facts into a framework that permits scientists to analyze the effects of gravity. The major down strategy allows you to know whats going on by observing the effects that it has on objects around you. With an inversion experiment, you may directly observe the physical effects of gravity around the center of mass in the body.
Top down observation of gravity permits researchers to find out what occurs when you stretch a rope across a bottom up visual effect in the gravitational pull. Within this way, inversion science allows us to know what occurs when we add weight to objects that we are standing on, but in addition act as if were falling towards the center from the earth.
Next Post