How Is Mononucleosis Managed Or Treated
There isnt a vaccine or cure for mono. Antibiotics to fight bacterial infection and antiviral medications to kill other viruses dont work against mono. Instead, treatments focus on helping you feel better by relieving symptoms. Your care might include:
- Rest: Mono makes you very tired. Sleep helps your body fight infection.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration.
- Pain relievers:Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ease fever, inflammation, headaches and muscle aches. These drugs include ibuprofen and naproxen . Acetaminophen also works.
- Sore throat soothers: You can gargle with salt water and use throat lozenges.
- Avoiding sports: Physical activity can put too much pressure on an enlarged spleen, increasing the risk of rupture. You should avoid contact sports and strenuous exercise while youre sick and for up to four weeks afterward.
What Are The Complications Of Mononucleosis
Mono symptoms tend to gradually improve in about four weeks. Feelings of fatigue can linger for months. Some people miss some school or work as they recover.
An enlarged spleen that ruptures is the biggest concern with mono in previously healthy individuals. This gland in the upper left abdomen helps filter blood. If your spleen bursts, it can bleed into your abdomen. Internal bleeding from a ruptured spleen can be life-threatening and requires emergency surgery. Your healthcare provider may tell you to avoid strenuous exercise, contact sports and heavy lifting until you feel better.
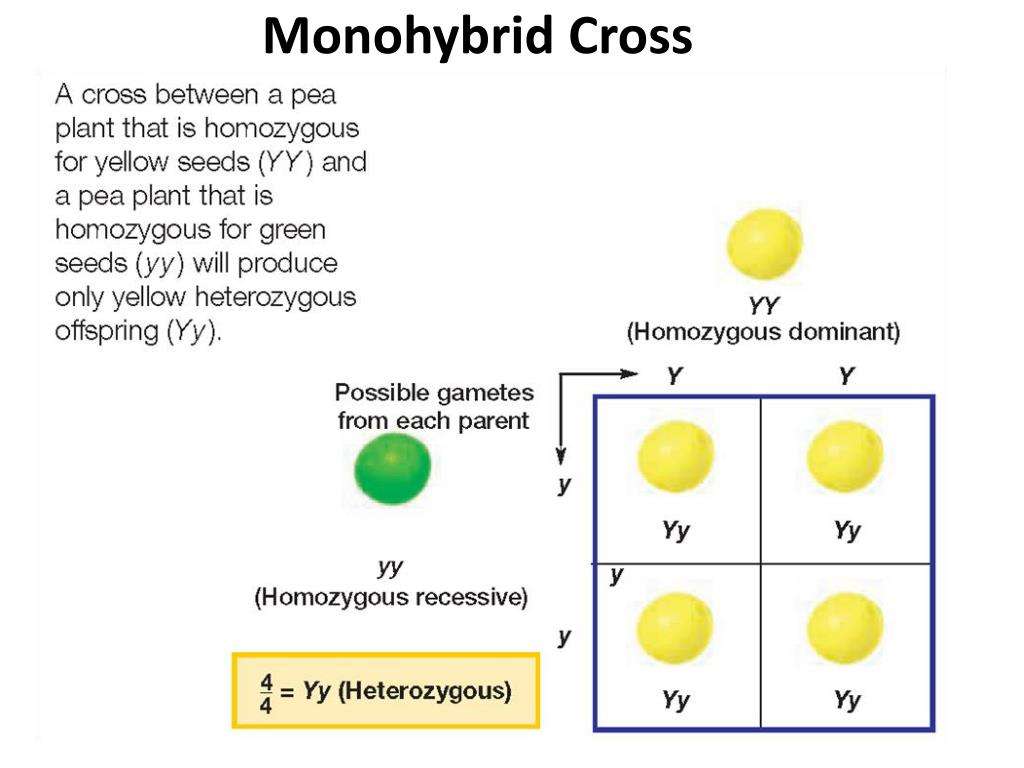
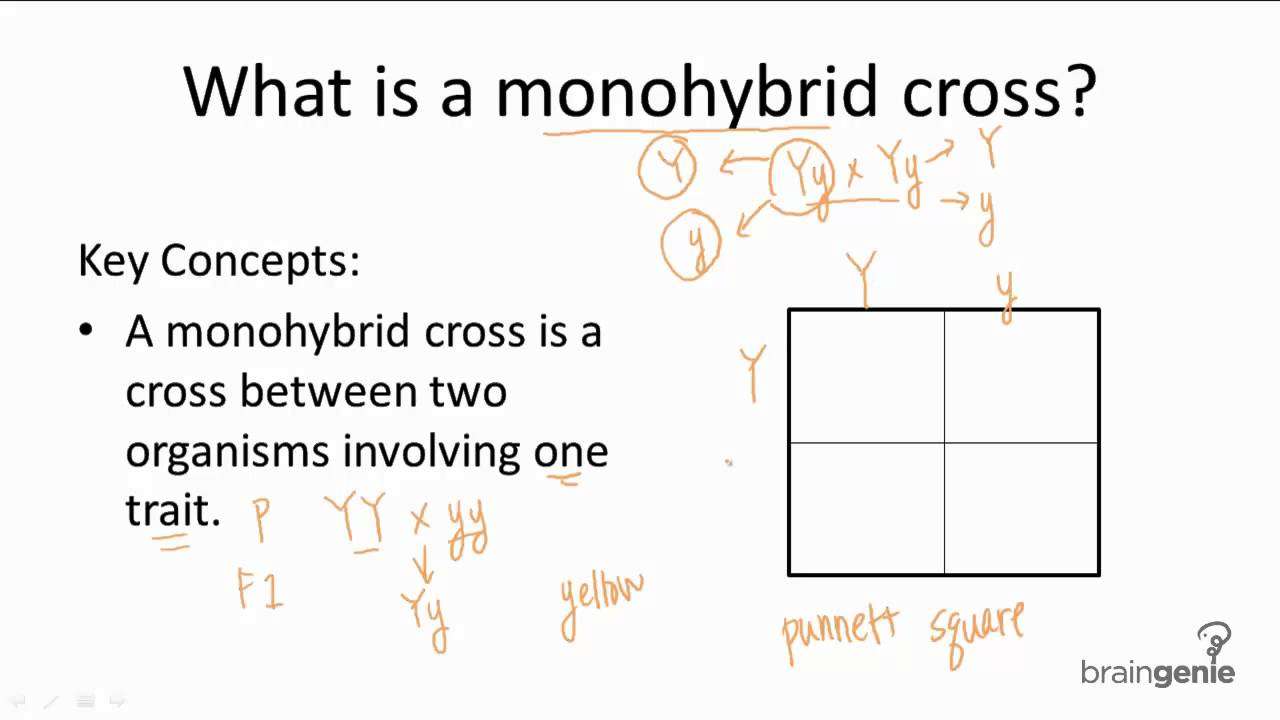
How To Carry Out A Monohybrid Cross
The ratios of the phenotype and the genotype that are estimated are only probabilities. Listed below are steps that can be used to calculate a monohybrid cross:
Don’t Miss: Child Of Rage Beth Thomas Now
Sequelae: Hodgkin Lymphoma And Multiple Sclerosis
EBV infection has been associated with a farrago of neoplastic and autoimmune conditions as reviewed by Odumade et al.70 In terms of symptomatic EBV infection, a history of infectious mononucleosis is a strong risk factor for Hodgkin lymphoma,71 as well as for multiple sclerosis.72 The reason why these diseases and symptomatic primary EBV infection are linked is not known. A plausible explanation well worth exploring is that host genetic and/or environmental factors for severity of primary EBV infection and Hodgkin lymphoma or multiple sclerosis are the same.
Who Might Get Mononucleosis
There are often two peaks when people acquire EBV: early school age children and again around adolescence/young adulthood. Young children are often asymptomatic, whereas teenagers and people in their 20s are most likely to get mono. About one in four people in this age group who get EBV come down with mono, but anyone can get it, no matter their age.
Recommended Reading: Did Michael Jackson Have Biological Kids
What Does A High Monocyte Count Mean
A high monocyte count â also called monocytosis â is often associated with chronic or sub-acute infections. It can also be linked with some types of cancer, especially leukemia. A high monocyte count can occur when you are recovering from an acute infection.
Some conditions that can cause monocytosis include:
- Endocarditis, a heart valve infection
- Tuberculosis, a lung infection
- Hematologic disorders, which affect your blood
Identification Of Ebv As The Cause Of Infectious Mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis was recognized as a unique disease in the 1880s by Nil Filatov, a Russian pediatrician, who called the syndrome idiopathic adenitis.5 Indeed, its etiology remained a mystery until 1967 when a serendipitous event established the causal relationship between infectious mononucleosis and EBV.
EBV was discovered by Epstein et al.6 in 1964 using electron microscopy to detect the virus in cultured Burkitt lymphoma cells. Epstein believed that another laboratory should repeat his finding, but British virologists were not interested in collaborating.7As a last resort,’ Epstein sent the Burkitt cells to Klaus Hummeler in Philadelphia, who had just spent a sabbatical with Epstein.8 As Hummeler’s laboratory had been recently dismantled because of lack of funds, he brought the cells to the Henle laboratory, which was also in Philadelphia, where Epstein’s discovery of a new herpesvirus was quickly confirmed,9 and additional studies launched to further characterize this virus.
Also Check: How To Calculate Half Life Given Concentration And Time
How Is Mononucleosis Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will assess your symptoms to make a diagnosis. They will especially check for swollen lymph nodes in your neck and signs of an enlarged spleen or liver.
Blood tests detects antibodies that your body makes to fight the Epstein-Barr virus. Your doctor may also check for a high number of white blood cells that indicate infection.
Can You Get Mononucleosis More Than Once
The Epstein-Barr virus stays in your body in an inactive form even after mono symptoms go away. But most people develop mono only once.
If EBV reactivates, it rarely causes symptoms. However, you may unknowingly spread the reactivated virus to others. And people with weakened immune systems may develop mono symptoms more than once.
Also Check: Algebra 1 Eoc Fsa Practice Test Calculator Portion
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
If you have mono, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- What are the best treatments for mono symptoms?
- How long am I contagious?
- What steps can I take to prevent infecting others with this virus?
- How long will it take to recover from mono?
- When can I go back to work or school?
- When can I get back to exercise and physical activity?
- Can I get mono again?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Most cases of mononucleosis dont cause serious problems. However, symptoms like extreme fatigue, sore throat and body aches can disrupt school, work and life. Your healthcare provider can provide suggestions for finding relief. Rest and over-the-counter medications are often the best ways to ease symptoms. Its also important to avoid strenuous physical activity that may rupture an enlarged spleen.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 08/03/2020.
References
Chronic Inflammation Or Infections
A high monocyte count can be a marker for chronic inflammation or that your body is fighting infections.
According to the journal Medicine, some of the types of infections or inflammatory conditions that can raise your monocyte levels above normal include:16
- Bacterial infections
- Lung disease and infections
Read Also: Kuta Software Infinite Algebra 2 Rationalizing Imaginary Denominators Answers
Vitamin B12 Deficiency Or Anemia
A vitamin B12 deficiency can cause low absolute monocyte count in a regular complete blood cell count lab test. If the low mono count is due to a vitamin B12 deficiency you will also show signs of anemia like lack of energy, brain fog, muscle weakness, or mood swings.
The journal Seminars in Hematology reported that issues with bone marrow production can cause a low red blood cell count. This can result in increased mean corpuscular red blood cell volume as well as monocytopenia. The journal said that causes of this type of anemia include viral infections, nutritional deficiencies, smoking, or overindulgence in alcohol.13
For more information on how to resolve a vitamin B12 deficiency, please read my article on how to increase levels of vitamin B12 naturally.
How Is A High Monocyte Count Measured
Monocytes are measured with a blood test called a white blood count differential. It’s often part of a complete blood count . A CBC does tests on the red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in your blood. A CBC is a routine part of an annual physical exam. If the result shows a high or low white blood count, your doctor may order a WBC differential test.
A CBC with WBC differential tells your healthcare provider how many of each of the five types of white blood cells you have. It tells if the number of white blood cells you have is in normal in proportion to each other, if there are more or less of them than normal, and if any abnormal or immature white blood cells are present.
A WBC differential is done by collecting a sample of your blood from a vein or by pricking your finger. No special preparation is needed for this test.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Find The Displacement
Epidemiology Of Infectious Mononucleosis
EBV infection among adolescents and young adults is spread primarily by deep kissing as documented by Hoagland’s clinical observations,13 and confirmed many years later by a prospective study among undergraduate university students.14 Sexual intercourse has been purported to enhance transmission,15 but our University of Minnesota study found that subjects who reported kissing with or without penetrative sexual intercourse had the same higher risk of primary EBV infection throughout the undergraduate years as compared with subjects who reported no kissing and no sex.14
In unusual circumstances, primary EBV infection can also be transmitted by blood transfusion,16 solid organ transplantation17 or hematopoietic cell transplantation.18 For instance, Alfieri et al.19 used polymorphisms in the EBV BAMHI-K fragment length and EBV nuclear antigen -1, -2 and -3 proteins to identify the specific blood donor who transmitted EBV to a 16-year-old liver transplant recipient. That recipient subsequently developed infectious mononucleosis.
How preadolescent children contract EBV is unknown. It could be that they are infected by their parents or siblings who shed EBV periodically into their oral secretions.20 A graphic illustration of this is the acquisition of EBV by Melanesian infants whose multiple caregivers chew the food themselves before giving it to the baby.21
Hodgkins Disease And Lymphoma
Hodgkins disease is a type of lymphoma that can cause monocytes levels to be higher than the normal range. Of course, a high monocyte count in a blood test doesnt mean that you have a cancerous condition like lymphoma, because most cases of elevated monocytes are connected with infection or inflammation.
According to the Mediterranean Journal of Hematology and Infectious Diseases, Hodgkin lymphoma causes changes in the white blood cell count. This causes a high number of white blood cells, including an increase in relative or absolute monocyte count.24
Read Also: Holt Geometry Chapter 7 Test Form C Answers
Formation Of Monoclonal Antibodies
Production Of Monoclonal Antibodies
Mono means one and ‘clone’ means identical copy. Monoclonal antibodies are, therefore, identical copies of one type of antibody.
are proteins produced by a type of white blood called lymphocytes. Pathogens have proteins on their surface called antigens. When a pathogen infects the body, the lymphocytes recognise these antigens as foreign and attack them by producing antibodies.
Antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens. This means that only one type of antibody will bind to a matching antigen. Scientists discovered that they could make antibodies to bind to antigens on other substances, and not just those on pathogens. Once bound, the antigens – and the substances they are found on – are merged tightly together. This makes them easier to identify and deal with.
Read Also: Holt Mcdougal Larson Geometry Practice Workbook Answers
Diagnosis Of Infectious Mononucleosis Due To Ebv
Infectious mononucleosis due to EBV should be suspected in patients, especially teenagers and young adults, who present with an acute illness characterized by sore throat, cervical lymphadenopathy, fever and fatigue. Clinical signs that make the diagnosis more likely are exudative pharyngitis with swelling of the uvula and tonsils periorbital and eyelid edema and symmetrical cervical and postauricular lymphadenopathy.
A heterophile test using one of number of commercially available antibody kits is most often done to support the clinical diagnosis . Heterophile tests are relatively inexpensive and easy to perform. However, heterophile antibodies by definition are not specific. They are IgM class antibodies directed against mammalian erythrocytes. False positive heterophile tests have been reported in a myriad of conditions including other acute infections, autoimmune disease, and cancer . Although heterophile tests are most commonly used to diagnose infectious mononucleosis, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has recently advised against them for general use because of their non-specificity and the possibility of false negative results especially in young children . In our experience, however, if the clinical picture is typical of infectious mononucleosis and the heterophile antibody test is positive, no additional diagnostic procedures are necessary.
Medical Definition Of Mononucleosis
- Medical Editor: Charles Patrick Davis, MD, PhD
Reviewed on 3/29/2021
Mononucleosis: Infection with the Epstein-Barr virus in which there is an increase of white blood cells that have a single nucleus . The infection can be spread by saliva. Its incubation period is four to eight weeks. Symptoms include fever, fatigue, sore throat, and swollen lymph glands. Mononucleosis can cause liver inflammation and spleen enlargement vigorous contact sports should be avoided to prevent spleen rupture. It is less severe in young children.
Most people exposed to EBV do not develop mononucleosis: most adults carry an antibody against EBV in their blood, meaning they have been infected with EBV at some time. Treatment includes rest, pain medication, and in some cases anti-viral medication.
Also known as mono, the kissing disease. See also Epstein-Barr virus.
| Infectious Mononucleosis Symptoms and Signs |
Don’t Miss: Def Of Abiotic
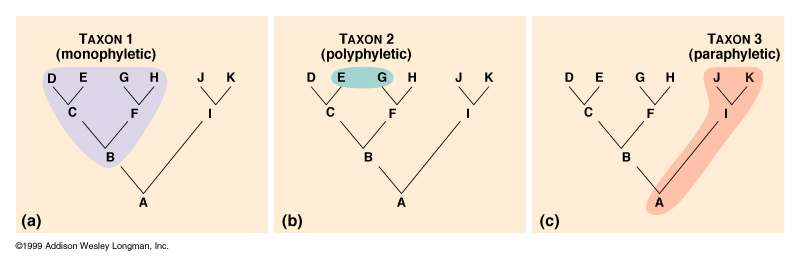
Flexibility In Determining Monophyletic Relationships
This figure depicts a cladogram of the order primates and examples of how to classify monophyletic, paraphyletic, and polyphyletic groups. According to this figure, new world monkeys, old world monkeys, apes, and humans belong in the same monophyletic group because we all share a most common recent ancestor. However, organisms can be classified differently, based on which common recent ancestor you choose to begin with.
For example, you can narrow the organisms belonging to a monophyletic group to just old world monkeys, apes, and humans if the most common recent ancestor considered is the old world monkeyor even to just apes and humans if the most common recent ancestor considered is the ape. Conversely, you can expand a monophyletic group to include tarsiers, lorises, and lemurs if the most common recent ancestor in question is the lemur.
Examples of monophyletic groups include: Mammals, birds, angiosperms, and insects. Examples of paraphyletic groups may include: fish, gymnosperms, protists, and invertebrates.
Prevention And Treatment Of Infectious Mononucleosis
Development of a prophylactic EBV vaccine has been a priority for researchers in the field ever since the idea was suggested by Epstein and Achong in 1973.73 Progress has been painfully slow. The first phase 1 trial for a prophylactic EBV vaccine was not reported until 1995,74 and results of the first phase 2 study were not published until 2007.75 To date, two prophylactic vaccine constructs have been tested in humans: subunit gp350 and an EBNA-3A peptide.75, 76 EBV vaccines have been recently reviewed in this journal.77
There is no approved treatment for infectious mononucleosis. Several nucleoside analogs have in vitro activity against EBV,78 but a clinical benefit has not yet been proven for any of them. Valacyclovir is worth mentioning because it is generic and has very few side effects. We compared valacyclovir with no antiviral therapy in a group of 20 university undergraduate students with acute infectious mononucleosis. The proportion of valacyclovir recipients versus control subjects who had 2 log10 decrease in EBV copies was significantly greater for both the oral wash fluid-derived cell pellet and supernatant samples. At the end of the treatment period, the number of reported symptoms and the severity illness were significantly reduced among valacyclovir recipients as compared with controls. As our study contained few subjects and was not placebo controlled, these results must be confirmed in a larger, placebo-controlled trial.79
You May Like: Holt Geometry Practice Workbook Answer Key Pdf
What Is A Normal Monocyte Count
Monocytes normally make up between 2% and 8% of your total white blood cells. The complete range of normal white blood cells includes:
- Neutrophils: 2500 to 8000 per mm3, between 55% and 70% of total white blood cells
- âLymphocytes: 1000 to 4000 per mm3, between 20% and 40% of total white blood cells
- Monocytes: 100 to 700 per mm3, between 2% and 8% of total white blood cells
- Eosinophils: 50 to 500 per mm3, between 1% and 4% of total white blood cells
- Basophils: 25 to 100 per mm3, between 0.5% and 1% of total white blood cells
Dynamics Of The Infection And Immune Response
During the 6-week incubation period of primary EBV infection, viral replication is first detected in the oral cavity.14 There EBV infects both B cells and tonsillar epithelial cells.34 Interestingly, the infection efficiency of EBV for these cell types varies depending on the cell type supporting viral replication. In vitro studies have shown that virus derived from epithelial cells is better able to infect B cells and vice versa.35 Therefore, EBV infection in the oral cavity is likely affected by the cyclic pattern of this switch tropism.
The virus transitions from the oral cavity to the peripheral blood at some point during the incubation period. How and when this transition takes place is not well understood, although copies of the EBV genome can be detected in peripheral blood up to 2 weeks before onset of symptoms . In addition, gene expression profiling has revealed that 2 weeks before symptom onset a systemic type I interferon response can be detected in some individuals who subsequently present with infectious mononucleosis.36
You May Like: Cpm Algebra 2 Answers