What Is The Maximum Acceptable Endotoxin Level
One EU is approximately equivalent to 100 pg of E. coli lipopolysaccharidethe amount present in approximately 105 bacteria. Humans can develop symptoms when exposed to as little as 5 EU/kg body weight. These symptoms include, but are not limited to, fever, low blood pressure, increased heart rate, and low urine output. Even small doses of endotoxin in the blood stream are often fatal.
The FDA has set the following maximum permissible endotoxin levels for drugs distributed in the United States:
-
Drug – 0.2 EU/kg body weight
-
Drug – 5 EU/kg body weight
-
Sterile water – 0.25-0.5 EU/ml
What Does Prokaryotic Mean In Biology
prokaryote also spelled procaryote any organism that lacks a distinct nucleus and other organelles due to the absence of internal membranes. Bacteria are among the best-known prokaryotic organisms. The lack of internal membranes in prokaryotes distinguishes them from eukaryotes. Some prokaryotes have flagella.
What Does Ecto Mean In Biology
ecto
. Beside this, what does Endo mean in biology?
The prefix means within, inside or internal.
Likewise, what does Cyto mean in biology? Cyto-: Prefix denoting a cell. “Cyto-” is derived from the Greek “kytos” meaning “hollow, as a cell or container.” From the same root come the combining form “-cyto-” and the suffix “-cyte” which similarly denote a cell.
Also question is, what does endo and ecto mean?
Ecto-, a prefix meaning “outside” ex- or Exo-, a prefix meaning “outer”
What is EKTO?
Ecto, a prefix from Greek meaning “outside” Ectoderm, in biology, the outermost tissue layer. Ectoplasm , the outer part of the cytoplasm. Ectotherm, in biology, a cold-blooded animal. For other possible words, see All pages with titles beginning with Ecto.
Recommended Reading: Kuta Software Infinite Algebra 2 Operations With Complex Numbers
What Does Eu Mean In Science
The European Union is a group of 27 member countries that are located in the Western Hemisphere. The EU is a political and economic union made up of sovereign states that are member states of the European Union. The EU has a common currency, the Euro, and a common defense and foreign policy. The EU has also created a number of bilateral treaties and agreements with other countries.
What Does Eu Mean In Microbiology

In microbiology, the European Union is a political entity consisting of 27 member states that are currently part of the European Union. The EU is a cooperative organization that aims to promote economic, social, and environmental justice. The EU has a variety of policies and regulations in place to promote food safety and hygiene, reduce environmental impact, and protect the health of its citizens.
Recommended Reading: Beth Thomas Brother Now
What Does Hetero Mean In Genetics
There is no one definitive answer to this question, as hetero means different things to different people. However, a few general definitions of hetero could include someone who is not of the same gender as another person, or someone who is not of the same race or ethnicity as another person.
Components Of Prokaryotic Cells
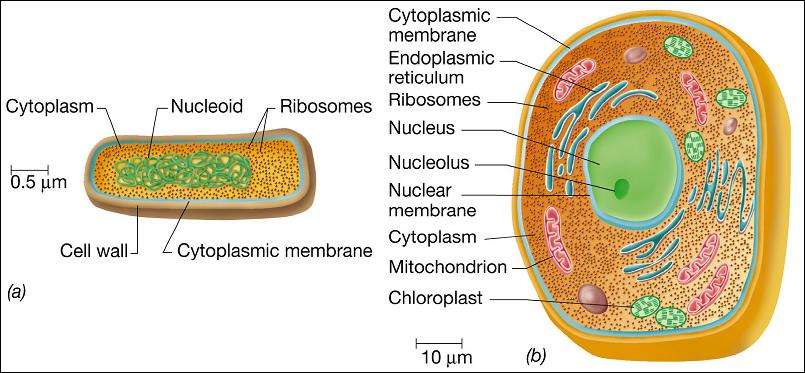
All cells share four common components: a plasma membrane, an outer covering that separates the cells interior from its surrounding environment cytoplasm, consisting of a jelly-like region within the cell in which other cellular components are found DNA, the genetic material of the cell and ribosomes, particles that synthesize proteins. However, prokaryotes differ from eukaryotic cells in several ways.
Figure 1. This figure shows the generalized structure of a prokaryotic cell.
A prokaryotic cell is a simple, single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus, or any other membrane-bound organelle. We will shortly come to see that this is significantly different in eukaryotes. Prokaryotic DNA is found in the central part of the cell: a darkened region called the nucleoid .
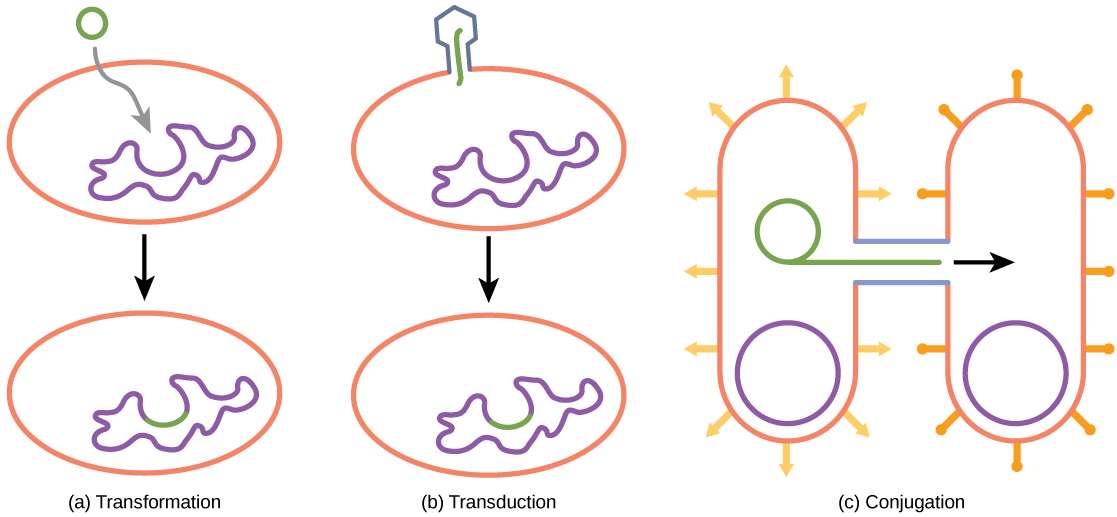
Unlike Archaea and eukaryotes, bacteria have a cell wall made of peptidoglycan, comprised of sugars and amino acids, and many have a polysaccharide capsule . The cell wall acts as an extra layer of protection, helps the cell maintain its shape, and prevents dehydration. The capsule enables the cell to attach to surfaces in its environment. Some prokaryotes have flagella, pili, or fimbriae. Flagella are used for locomotion, while most pili are used to exchange genetic material during a type of reproduction called conjugation.
Don’t Miss: Hawkes Learning Systems Statistics Answer Key
In Summary: Comparing Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms of the domains Bacteria and Archaea. All prokaryotes have plasma membranes, cytoplasm, ribosomes, a cell wall, DNA, and lack membrane-bound organelles. Many also have polysaccharide capsules. Prokaryotic cells range in diameter from 0.15.0 µm.
Like a prokaryotic cell, a eukaryotic cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes, but a eukaryotic cell is typically larger than a prokaryotic cell, has a true nucleus , and has other membrane-bound organelles that allow for compartmentalization of functions. Eukaryotic cells tend to be 10 to 100 times the size of prokaryotic cells.
Objections To Scientific Validity
Eugenic policies may lead to a loss of genetic diversity. Further, a culturally-accepted “improvement” of the gene pool may result in extinction, due to increased vulnerability to disease, reduced ability to adapt to environmental change, and other factors that may not be anticipated in advance. This has been evidenced in numerous instances, in isolated island populations. A long-term, species-wide eugenics plan might lead to such a scenario because the elimination of traits deemed undesirable would reduce genetic diversity by definition.
While the science of genetics has increasingly provided means by which certain characteristics and conditions can be identified and understood, given the complexity of human genetics, culture, and psychology, at this point there is no agreed objective means of determining which traits might be ultimately desirable or undesirable. Some conditions such as sickle-cell disease and cystic fibrosis respectively confer immunity to malaria and resistance to cholera when a single copy of the recessive allele is contained within the genotype of the individual, so eliminating these genes is undesirable in places where such diseases are common.
Also Check: What Is Harder Chemistry Or Physics
Eukaryotic Cell Vs Prokaryotic Cell
The difference between a eukaryotic cell and a prokaryotic cell is simple: eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles. Within a prokaryotic cell the DNA simply floats around the cytoplasm. While prokaryotic cells do have one type of organelle , these organelles are not covered in a plasma membrane.
By contrast, eukaryotic cells are full of membrane-bound organelles that divide the cell into many different compartments. The nucleus houses the DNA. The endoplasmic reticulum creates many chambers to carry out specific biochemical reactions. The Golgi apparatus folds and packages various proteins and cellular products. Lysosomes store digestive enzymes to break down incoming food. Plus, eukaryotic cells contain mitochondria to create ATP molecules from glucose and chloroplasts to create glucose from sunlight .
Who Runs The Eu
The European Union is a group of 27 member countries that are located in the Western Hemisphere. The EU was founded in 1957, and it is made up of a variety of different institutions, such as the European Parliament, the Commission, and the Council. The EU is responsible for a variety of policies, like trade, culture, and security.
Europe is the continent that includes the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Italy, and Spain.
Don’t Miss: How To Find Half-life Of A Reaction
Realising European Potential In Synthetic Biology: Scientific Opportunities And Good Governance
Synthetic biology covers the design and construction of novel biological components, systems and processes “that are not already known to exist in nature” together with the re-design of existing biological systems. Synthetic biology is interdisciplinary, drawing on precepts and practices from a wide range of methodologies and disciplines, including the techniques of genetic engineering. Although it can be sometimes difficult to demarcate synthetic biology from other established research areas, many within the scientific community believe that, by applying the principles of engineering and chemical design to biological systems, synthetic biology will lead to new applications of considerable societal value. Among the potential products and services are new systems for energy, materials and chemicals production medical diagnostics, therapeutics and vaccines and innovative approaches to the clean up of hazardous waste. Synthetic biology is important for Europe. There is significant potential for the European Union to invest in synthetic biology research and to capitalise on the emergent innovations.
Which Endotoxin Detection Method Should I Choose
Three things to consider before choosing an endotoxin detection method: the type of sample to be tested, its interference characteristics, and the endotoxin limit that you want to detect. The Gel-clot method is the simplest and most widely used method for endotoxin detection, and its sensitivity is up to 0.03 EU/ml. The Chromogenic method defines its sensitivity to be the lowest endotoxin concentration in the standard curve and requires a spectrophotometric instrumentation to read the results.
Don’t Miss: Bridge To Algebra Punchline Answers
What Does Eu Mean In Anatomy
The European Union is a political and economic union of 27 countries that are located in the Western Balkans. The union has been in place since the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989. The union includes seven member states: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, and the United Kingdom.
Eugenics In The United States
Anti-miscegenation laws in the United States made it a crime for individuals to wed someone categorized as belonging to a different race. These laws were part of a broader policy of racial segregation in the United States to minimize contact between people of different ethnicities. Race laws and practices in the United States were explicitly used as models by the Nazi regime when it developed the Nuremberg Laws, stripping Jewish citizens of their citizenship.
You May Like: My Hrw Com Algebra 1
What Is Eu Role
The European Union is a political and economic union of 27 member countries that are located in Western Europe. The union has been in place since the early 1990s, and was created as a response to the European Economic Community , which was founded in 1957. The EU is made up of a single currency, the euro, and a series of treaties that govern its members. The EU has been in operation since 1999, and has seen a number of major reforms, including the introduction of the euro, the enlargement of the EU, and the introduction of the single market.
Does Any Substance Interfere With The Binding Of Endotoxin To Endotoxin Removal Resin
Yes. Other detergents and high levels of chaotropes can reduce the affinity of Polymixin B for LPS. Proteins such as BSA can bind tightly to endotoxin, reducing its ability to interact with and bind to the endotoxin Removal Resin. This reduction in binding capacity can sometimes be overcome by increasing the volume of immobilized polymixin B. However, some proteins bind tightly to endotoxin without inhibiting its binding to ligands. In this case, the protein will remain bound to the resin with the endotoxin, possibly causing a loss of the protein of interest.
You May Like: My.hrw.com Algebra 1
What Does Eu Mean In Biology
Explanation: Eukaryotic Cells Eu means Well and Karyon means Nucleus the name tells us that eukaryotic cells have a nucleus a WELL DEFINED NUCLEUS. The nucleus is well protected inside the nuclear membrane. They contain a true nucleus consisting of nuclear membrane & nucleoli.Explanation: Eukaryotic Cells Eu means Well and Karyon
an organelle found in eukaryotic cells
How Does Eu Work
The European Union is a political and economic union of 27 member states that are located in the Western Balkans. The union was formed in 1993 as a result of the Maastricht Treaty, which granted European citizenship to all European citizens. The union has since become an important actor in the world economy, with member states contributing more than two-thirds of the EUs GDP.
Don’t Miss: Edgenuity Algebra 1 Answer Key
Nazism And The Decline Of Eugenics
The scientific reputation of eugenics started to decline in the 1930s, a time when Ernst Rüdin used eugenics as a justification for the racial policies of Nazi Germany. Adolf Hitler had praised and incorporated eugenic ideas in Mein Kampf in 1925 and emulated eugenic legislation for the sterilization of “defectives” that had been pioneered in the United States once he took power. Some common early 20th century eugenics methods involved identifying and classifying individuals and their families, including the poor, mentally ill, blind, deaf, developmentally disabled, promiscuous women, homosexuals, and racial groups as “degenerate” or “unfit”, and therefore led to segregation, institutionalization, sterilization, and even mass murder. The Nazi policy of identifying German citizens deemed mentally or physically unfit and then systematically killing them with poison gas, referred to as the Aktion T4 campaign, is understood by historians to have paved the way for the Holocaust.
Definition & Meaning: Eu
The Greek eu, well, comes from eus, good Examples derived directly from Greek words include eu-phony, the quality of being pleasing to the ear, the valved brass musical instrument called the euphonium derives from the same root eulogy, a speech or piece of writing that praises someone or something highly euphoria, a feeling or state of intense excitement and happiness.
Also Check: Algebra 1 Week 1 Fsa Countdown Answers
What Has The Eu Done
The European Union has been in place since the early 1990s and has come to play a significant role in the world. It has developed a number of policies, such as the single market, which have helped to make the Continent more prosperous. Additionally, the EU has been a leading force in the development of the worlds economy, and has played a leading role in the peace and security in the world.
European Policy On Protected Areas
European policy regarding protected areas is mostly the product of initiatives from two main sources: the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity and the European Union itself. Several instruments have promoted the creation of protected areas through specific provisions such as the Ramsar Convention, the World Heritage Convention, UNESCO Man and the Biosphere Programme. At the pan-European level, the Convention on the Conservation of European Wildlife and Natural Habitats has also led to the designation of protected areas .
At the EU level, several directives have been particularly important for the creation of protected areas: the Birds Directive and the Habitats Directive. As the European Union is also a signatory to the Bern Convention, the Natura 2000 network is in practice the EUs contribution to the Emerald Network.
The EU biodiversity strategy to 2020 is the main policy frame for EU action to address wider biodiversity goals. Target 1 of the strategy refers to the completion and good management of the Natura 2000 network. Centralised information about European biodiversity policies, data and assessments including further information about the Biodiversity Strategy to 2020 can be found in the Biodiversity Information System for Europe .
Hoces del río Riaza Natural Park, ES. Photo: Paco Sánchez
Read Also: Diffusion In Geography
Examples Of Eutrophication In A Sentence
eutrophication The Christian Science Monitoreutrophication The Christian Science Monitoreutrophication Twin CitieseutrophicationNewsweekeutrophicationFox News
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘eutrophication.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
Characteristics Of A Eukaryotic Cell
Eukaryotic cells contain a variety of organelles, which perform various functions within the cell . All of the organelles are stabilized and given physical support through the cytoskeleton, which is also involved in sending signals from one part of the cell to the other. In eukaryotic cells, the cytoskeleton is composed mainly of three types of filaments: microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments. The watery solution that surrounds all the organelles in the cell is called cytosol.
The figure below shows the structure of a eukaryotic cell. This is an animal cell. The nucleus and other organelles are shown. The cytosol is the blue substance surrounding all of the organelles. Together, the cytosol with all organelles besides the nucleus is known as the cytoplasm.
You May Like: Geometry Textbook Mcdougal Littell Answers
Eutrophication Has Greek Roots
Eutrophication, which comes from the Greek eutrophos, “well-nourished”, has become a major environmental problem. Nitrates and phosphates, especially from lawn fertilizers, run off the land into rivers and lakes, promoting the growth of algae and other plant life, which take oxygen from the water, causing the death of fish and mollusks. Cow manure, agricultural fertilizer, detergents, and human waste are often to blame as well. In the 1960s and ’70s, the eutrophication of Lake Erie advanced so extremely that it became known as the “dead lake”. And many areas of the oceans worldwidesome more than 20,000 square miles in extenthave become “dead zones”, where almost no life of any kind exists.
Examples Of Eukaryote In A Sentence
eukaryoteThe New York Review of Bookseukaryote Quanta Magazineeukaryotes New York TimeseukaryotesNew York TimeseukaryotesQuanta Magazineeukaryotes Smithsonianeukaryotes SmithsonianeukaryotesCNN
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘eukaryote.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
Don’t Miss: Ccl4 Lewis Structure Polar Or Nonpolar
Nuclear Envelope And Pores
The nuclear envelope consists of two membranes, an inner and an outer nuclear membrane.:649 Together, these membranes serve to separate the cell’s genetic material from the rest of the cell contents, and allow the nucleus to maintain an environment distinct from the rest of the cell. Despite their close apposition around much of the nucleus, the two membranes differ substantially in shape and contents. The inner membrane surrounds the nuclear content, providing its defining edge.:14 Embedded within the inner membrane, various proteins bind the intermediate filaments that give the nucleus its structure.:649 The outer membrane encloses the inner membrane, and is continuous with the adjacent endoplasmic reticulum membrane.:649 As part of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane, the outer nuclear membrane is studded with ribosomes that are actively translating proteins across membrane.:649 The space between the two membranes, called the “perinuclear space”, is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum lumen.:649